

Catamaran Parts Explained: Interactive Guide (For Beginners)
As an Amazon Associate, we earn from qualifying purchases. We may also earn commissions if you purchase products from other retailers after clicking on a link from our site.
Learning a new skill can sometimes be time-consuming, and learning to sail also means learning a new language with tons and tons of new words that, in the beginning, makes no sense at all.
Some of the words you will read about in this article stem from the early days of sailing. Some are only a decade old; in this article, I have tried to compile all the basic terminology that I believe a beginner needs if he or she wants to understand sailing and catamarans.
Feel free to use this article as a resource and come back to it when you want to look something up or just to learn more!
Table of Contents
Main sections on a catamaran
- Hulls; are what separates a cat from other sailboats, a catamaran has two hulls, a trimaran three, and a regular sailboat, aka monohull, has one. The hull is the part of the sailboat which makes it float and to where all other things are attached. The hulls are usually divided into sections, such as usable and non-usable area. An example of a usable area is the engine room.
- Cockpit ; is from where the boat is maneuvered; it is to here that all halyards, sheets, etc. go. The cockpit contains navigation and steering equipment and is from where the sails, rudder, and engine are controlled.
- Deck; is the top part(roof) of a catamaran covering the hulls and bridge deck. The deck is made hard enough to walk on. To the deck, attaches lifelines and other equipment.
- Sugarscoops ; are the aftmost part that gets their name from their scoop-shaped appearance; this is where the deck/cockpit meets that water and usually encompasses a stair or ladder for easy access depending on the size of the boat.
- Cabin; is basically any area on the inside of the boat that is protected from the weather and is made to offer the crew space to rest, eat, and hangout. Inside the cabin, you will find berths (beds), a galley (kitchen), and sometimes specialized areas for repairs or storage.
- Bridgedeck; connects the two hulls; the inside is the cabin, the top part is the deck, and the entire unit is called the bridge deck. Bridge deck clearance, the bridge deck’s height above the water, is an important factor on a catamaran since a too small clearance will create excess noise and vibrations and fatigue not only the crew but also the boat.
Main areas on a catamaran
Bow (front).
Nothing complicated here; the bow is just a nautical term for the foremost part of your boat. This is where the waves and the sea first meet the hull and depending on the type of boat, the bow(s) can be shaped differently.
Center (Middle)
The part between the bow and the stern is rarely called the center part( middle) of a boat; more common is to speak about the specific area situated within the middle part of the vessel, such as the cabin or the mast.
- Cockpit; as mentioned above, here you will (usually) find everything that you need to maneuver and navigate the boat, such as a compass, GPS, sheets, steering wheel, and throttles for the engines. Some boats may not be set up this way and require you to move around the boat to access certain controls.
Cabin (inside of the boat)
The boat’s interior is where you will find everything that is made for the crew’s enjoyment; it is a place to eat, sleep, rest up, and hide away from nasty weather.
- Berths; is a bed; sailors need to sleep too!
- Galley ; is another name for kitchen, usually set up in a very primitive way with a gas stove on a stabilized platform to ensure your food won’t get tossed around.
- Navstation; or navigation station, is a place, usually with a table, chair, and equipment for planning and logging a journey.
Stern (Back)
Stern is the name for the rearmost part of the boat; there is no clear definition as to where the stern stops and other parts begin, so it is something that the crew will have to figure out on their own through good communication.
Communicating directions on a sailboat
Not only will you have to know the different names of different areas on the boat, but it will also be essential to communicate clearly in what direction something is happening, for example, in a situation where you, the captain, want the crew to observe in a specific direction or pick up a piece of gear somewhere on the boat.
Communication on a sailboat is vital when you want to sail safely and efficiently; here, I have listed the words or phrases used to communicate a direction.
- Forward; easy as it sounds, it is the same direction as where the bows are pointing. When giving directions towards or beyond the bow, you will use the word “forward” for example; the fender is located forward of the mast.
- Aft ; is the behind the boat. When you are giving directions towards the stern, you will use the word “aft”; for example, the cockpit is located aft of the mast.
- Port ; this will be your left side. Fun fact, in the good old days, you would always dock with the port on your left side; hence port is the left side. If you ever forget which one is which, “port” has 4 letters and so has the word”left”!
- Starboard ; is your right side!
Types of sails
Sails come in very different shapes and sizes and are a science in itself; in this article, I will focus on the mainsail and three common types of staysail.
- Mainsail; is, per definition, the sail attached to the mast; its sideways movements are controlled by the boom. When the mainsail is triangular in shape, as on most modern sailboats, it is called a Bermuda rig. Most mainsail uses something called battens.
- Staysail; mainly comes in two versions, a staysail that does not overlap the mainsail is called a jib. A staysail that is larger and thus overlaps the mainsail is called a genoa.
- Spinnaker ; is a big balloon-like sail that replaces the jib when sailing downwind.
Parts of a sail
- Luff; the front part of the sail, is connected to the mast through a rail system which makes it possible to hoist or reef.
- Leech; the back part of the sail.
- Foot; the bottom part that reaches from the clew to the tack.
- Clew; back bottom corner.
- Tack; is the front bottom corner (remember “tacking”?).
- Head; is the top triangle of the sail and this is where the mainsail halyard attaches.
- Battens; are pieces of flexible material sewn into the mainsail to increase its aerodynamic shape. Battens can be full length or partial length.
Standing rigging
Everything that keeps the sails and mast upright are parts of the standing rigging; it is comprised of wires, cables, and lightweight metal structures.
- Forestay; usually a metal wire running from the top of the mast to the bow, is sometimes combined with an inner forestay that connects to the mast at a lower point. If the forestay attaches to the top of the mast, the setup is called a masthead rig; if it attaches lower, it is called a fractional rig.
- Backstay ; same as the forestay but attaches to the stern; most catamarans do not employ a backstay system but instead moves the side stays aft.
- Shroud ; much like the forestay but stabilizes the mast sideways and runs from the top to the port or starboard side. Spreaders are used to change the angle of the wire against the mast and better support the mast.
- Sidestay ; connects to the mast below the shrouds and is not pushed outwards with spreaders. On a catamaran, these attach aft of the mast to eliminate the need for a backstay; this makes it possible for a fully battened mainsail with a large roach.
- Jumpers; are used on a fractional rig with diamond shrouds to add structural integrity to the mast without adding excess weight.
- Bowsprit; is a pole amidship at the bow that allows for separation of the tacks (foremost, lower part of the sail) for increasing sail efficiency when using two headsails.
Other stabilizing parts
- Spreaders; act to lessen the angle between the shrouds and the mast; a wider angle will result in forces acting sideways (stabilizing) instead of up and down (bending). This increases stability and decreases the risk of unwanted bending of the mast.
Running rigging
The running rigging on a catamaran is any piece of equipment used to control the shape of the sails, including what is needed to raise them.
- Sheet; are the ropes (or wire, cables, etc.) that connect to the clew of a sail; on a catamaran, it connects to the staysail (genoa or jib, depending on the shape).
- Mainsheet ; is the rope that makes it possible to change the mainsail’s angle; the mainsail can only move in a port to starboard direction(right and left) and not up and down.
- Staysail sheet ; is called after whatever type of sail it is connected to, i.e., jib sheet or genoa sheet. Worth notice is that since the staysail operates on both sides of the catamaran (depending on if your tacking or gybing), it is connected with two ropes, one for the port side and one for the starboard side.
- Halyards ; are the ropes that connect to the top of a sail and make hoisting (or raising) possible. Halyards have different names depending on what sail they are raising, such as Mainsail halyard or jib halyard. Not to be confused with sheets that act upon the sail once they are already hoisted. If the staysail is using a roller furling, then “hosting” is done differently.
- Furling line; is used together with a roller furling and makes it possible to spool up the sail on the forestay instead of raising and lowering. This makes for a faster and easier way to reduce sail area.
- Reefing lines; reefing is when you lower parts of your sail to reduce the sail area and reduce the boat’s power and speed; reefing lines are put through holes in the mainsail and attach to the boom.
- Boom vang; is connected between the boom and deck; it is used to change the mainsail’s shape by pulling downward on the boom. (not very common on Catamarans)
In this category, we will look at the hulls and some of the vital parts that attach to them under the waterline.
- Hulls; differ in their shapes depending on the boat’s purpose, a racing cat would have narrower hulls to reduce drag, and a cruising cat wider hulls to encompass more storage.
- Rudder; is what changes the direction of the boat. When water passes around the rudders(two on a catamaran), it creates a “pushing force” that makes the boat turn. The rudder is connected to a steering wheel or a tiller at the cockpit through chains and linkage.
- Centerboard and daggerboards ; are sorts of keels that can be raised or lowered to attain certain sailing characteristics. When the keel is up, drag is lower, and so is the draft (how deep the boat sticks in the water). A small draft makes it possible to travel in very shallow waters. The difference between a daggerboard and a centerboard is that a centerboard swivels into place, and a daggerboard is pulled straight up.
- Mini-keel; is just what it sounds like; it is a keel but very small (a few inches deep) and has no ballast.
- Crossbeam ; is a multihull-only feature and keeps the two hulls from moving in relation to each other. If the crossbeam is damaged or nonexistent, the bridge deck is the only thing that keeps the hulls in place. This will increase wear and sooner or later lead to cracks, or even worse, separation of hull and bridge deck.
Most catamarans have two engines, one on each hull aft the stern; usually, they are internal with only the propeller in the water. The other option, which is cheaper and most often found on smaller boats, is to have one outboard engine placed amidship (middle).
- Inboard ; engines are situated in a compartment inside the boat at the stern. On an inboard engine, the propeller and the shaft are the only parts outside the hull. Sometimes the prop shaft (propeller shaft) is replaced by a sail drive.
- Outboard ; is a standalone engine usually mounted on the bridge deck amidship(if only one is used) or mounted at the sterns when used in pairs. They are linked together with pushing rods and wires so it can be manipulated from the cockpit.
- Saildrive ; is a type of gearbox that is quieter and vibrates less than a regular propeller and shaft setup.
- Propeller and shaft; are the most common and cheapest way to propel your boat. It is basically just a watertight axel that sticks out of the hull, and at the end of it, you’ll find the propeller.
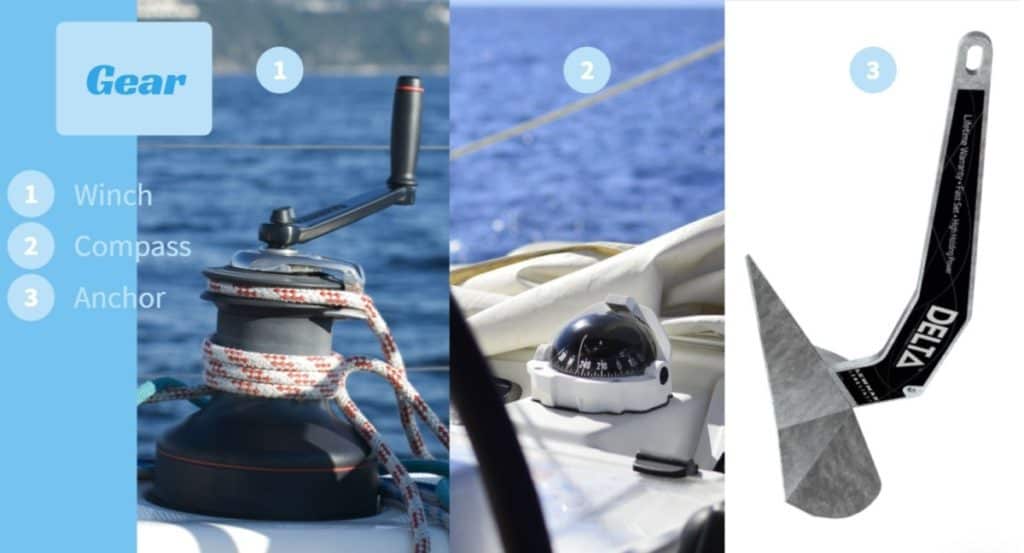

There are so many pieces of gear aboard a catamaran that an all-encompassing article would probably fill up the entire internet. Below I have listed the most common equipment that you will most likely encounter on any sailboat.
- Winches; makes handling lines and ropes much easier. Instead of pulling them with your bare hands, you loop them around your winch and use the handle to crank. Winches come in mechanical style or electrical style.
- Anchors ; is basically just a big hook made to stick to the bottom of the sea. Anchors have different shapes and weights depending not only on the seabed but also on the boat’s weight and size.
- Navigation ; compass, GPS, and maps are all vital pieces of equipment making your trip safe.
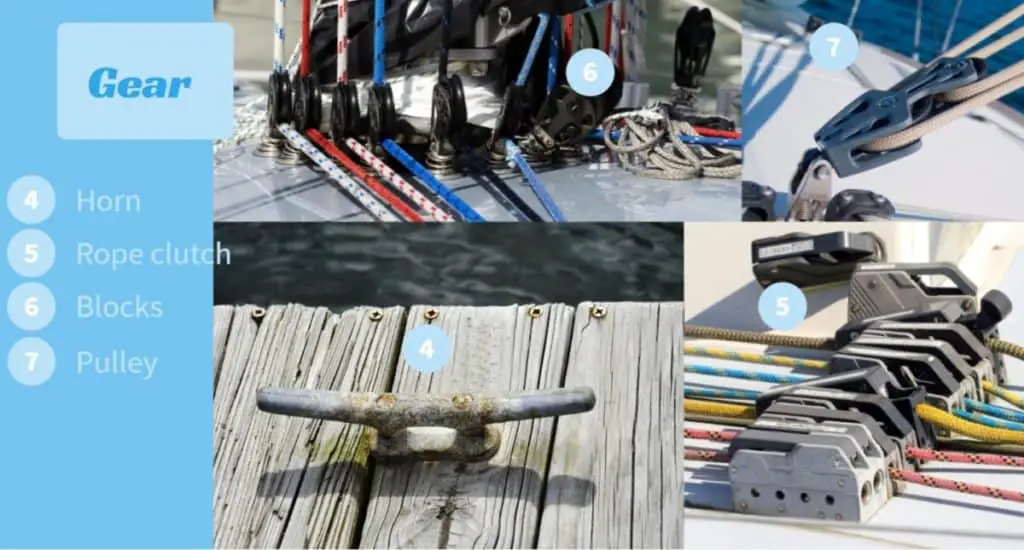
- Cleats ; is any equipment that is made to fasten a rope. Cleats come in different configurations; jam, cam, rope clutch, or the most common horn cleat.
- Block ; is a device that can be used in pairs as a pulley (to reduce the force needed to lift something) or on its own to reduce the friction of a rope when the rope can not be drawn in a straight line.

Owner of CatamaranFreedom.com. A minimalist that has lived in a caravan in Sweden, 35ft Monohull in the Bahamas, and right now in his self-built Van. He just started the next adventure, to circumnavigate the world on a Catamaran!
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name and email in this browser for the next time I comment.
Recent Posts
Must-Have Boat Gear for Catamaran Sailors!
Sailing is probably the most gear-intensive activity I've ever done; there are so many decisions to be made about what gear to buy now, for tomorrow, and what to definitely never buy. The gear on...
6 Best Trailerable Trimarans For Bluewater and Coastal Sailing
Having a boat costs a lot of money, even when you are not using it, marina fees, etc. And once it is in the water most sailors never go very far from their "home marina" and sailing will be somewhat...

Parts of Catamaran: A Comprehensive Guide to Understanding the Components
by Emma Sullivan | Aug 2, 2023 | Sailboat Racing

Short answer: The key parts of a catamaran include the hulls, bridgedeck, mast(s), rigging, sails, rudders, and daggerboards. These components work together to provide stability, propulsion, and control for this type of multi-hulled watercraft.
Exploring the Essential Parts of a Catamaran: A Comprehensive Guide
From cruising the open seas to enjoying lazy afternoons by the shore, catamarans have become a popular choice for water enthusiasts. With their unique design and exceptional stability, these vessels offer an unmatched sailing experience . But have you ever wondered what makes up a catamaran and how each part contributes to its overall functionality? In this comprehensive guide, we will take you through the essential parts of a catamaran, uncovering their purpose and shedding light on why they are instrumental in making these boats such fantastic options for adventure seekers.
1. Hulls: The hulls are the twin structures that form the main body of a catamaran. These structures play a pivotal role in providing stability and buoyancy while at sea. Catamarans boast wider hulls compared to traditional monohull sailboats, resulting in increased surface area and enhanced stability. The design allows for smoother sailing even in rough waters, as each hull slices through waves independently.
2. Keels: Unlike monohull sailboats that rely solely on a single keel positioned beneath the waterline for both lift and resistance against sideways drift (known as leeway), catamarans often feature two separate skegs or keels attached to each hull. These auxiliary structures enhance directional control and offer excellent stability while reducing drag.
3. Deck: The deck is where all the action takes place! It serves as the primary horizontal surface on which passengers can relax, sunbathe or engage in various activities while aboard the vessel. Catamaran decks usually come with ample space due to their wider design compared to monohull sailboats .
4. Trampoline: One of the standout features of a catamaran is its trampoline – a mesh-like netting stretched between the two hulls just above sea level. While it may seem like an unconventional addition, trampolines provide multiple benefits including giving passengers an exhilarating sensation as they sit or lay above the water. This ample recreational area additionally offers an unobstructed view of the sea, making it an ideal spot for stargazing or simply enjoying the soothing sound of the waves.
5. Cockpit: The catamaran’s cockpit is strategically positioned closer to the waterline, ensuring a thrilling and immersive sailing experience. It acts as the primary control center where the helm is located, allowing sailors to expertly navigate their vessel through various seascapes. Additionally, some catamarans offer spacious cockpits that provide sufficient seating capacity for socializing with fellow passengers or hosting intimate gatherings while at anchor.
6. Rigging: The rigging refers to all lines, cables, and hardware necessary for controlling and adjusting the sails . Catamarans typically employ a simple yet effective rigging system that ensures easy maneuverability and efficient sailing performance. By skillfully managing these components, sailors can harness wind power optimally and maintain smooth cruising speeds in any weather conditions.
7. Sails: Sails are central to a catamaran’s propulsion system, enabling it to move gracefully across bodies of water without relying on fuel-based engines alone. Modern catamarans often embrace a sail plan consisting of multiple sails designed to maximize efficiency and adapt seamlessly to varying wind strengths and directions. With innovative designs such as fully battened mainsails and lightweight genoas, these boats have become incredibly agile even when faced with challenging wind patterns.
8. Engines: While a catamaran’s sails provide a significant portion of its power source, auxiliary engines are still crucial for many aspects of sailing life – be it docking in tight spaces or maneuvering during low-wind situations. These engines are usually mounted within each hull beneath deck level as part of an integrated propulsion system comprising shafts, propellers, and operational controls.
9. Navigation Instruments: In today’s era of advanced technological aids, catamarans make use of a range of navigation instruments to enhance safety and efficiency. From GPS systems providing precise positional information to depth sounders measuring water depth, these sophisticated tools are essential for ensuring smooth journeys and avoiding potential hazards.
So there you have it – a detailed glimpse into the essential parts of a catamaran. Wherever your sailing adventures take you, now you can fully appreciate how each component contributes to the incredible performance and unrivaled experience offered by these magnificent vessels. So hop aboard a catamaran and embark on your next nautical journey with confidence!
How to Identify and Understand the Various Components of a Catamaran
Catamarans are fascinating vessels known for their unique design and exceptional performance on the water. Whether you are a seasoned sailor or just interested in learning more about these incredible boats, understanding their various components is essential . In this blog post, we will take a detailed, professional, witty, and clever dive into the world of catamarans and shed light on how to identify and understand their different parts .
1. Hulls: At the core of any catamaran are its hulls – the main supportive structures that keep the boat afloat. Unlike traditional single-hulled vessels, catamarans have two parallel hulls connected by a deck. These hulls play a vital role in providing stability and minimizing drag while sailing. Think of them as the sturdy legs that help the catamaran gracefully glide through the water .
2. Deck: The deck serves both as a platform for enjoying your time onboard and as an important structural element that connects various parts of the catamaran. It consists of multiple areas such as the helm station (where you control the boat), seating areas, dining spaces, trampoline nets for lounging, and storage compartments. Sunbathing or hosting friends for a sunset gathering? The deck has got you covered!
3. Rigging: If you’ve ever looked up at a sailboat’s mast with admiration, then you’ll love discovering how rigging contributes to a catamaran’s overall performance and elegance. The rigging includes all the supporting wires and ropes that hold up the mast(s) on your catamaran and control its position relative to wind direction (known as “trimming”). Understanding how to properly trim your sails can greatly enhance your sailing experience – from capturing optimal wind power to achieving picture-worthy maneuvers.
4. Sails: What could be more mesmerizing than watching billowing sails against an azure sky? Catamarans utilize various types of sails based on their purpose – mainsails, jibs, genoas, spinnakers – each designed to maximize performance under specific wind conditions. Learning about the different sails and their characteristics will help you navigate efficiently and make the most of your sailing adventures. Plus, understanding the art of sail trim is sure to impress your fellow sailors!
5. Rudders: Just as a captain relies on his or her compass for navigation, catamarans depend on rudders to steer through the water with precision. Mounted at the stern (rear) of each hull, these ingenious components allow you to control your course by diverting the flow of water passing beneath them. Rudders are essential for maintaining stability and maneuverability when tacking, jibing, or navigating challenging waters.
6. Engines: Catamarans aren’t solely reliant on wind power; they often incorporate engines as auxiliary means of propulsion. These mechanical marvels provide added security and flexibility during low-wind situations or when maneuvering in confined spaces like marinas or crowded anchorages. Understanding how to handle your catamaran’s engines confidently will ensure smooth sailing even when Mother Nature plays hard-to-get.
By expanding your knowledge about these various catamaran components – hulls, deck, rigging, sails, rudders, and engines – you’ll unlock a whole new level of appreciation for these magnificent vessels and gain confidence in navigating them.
Lastly, remember that wit and cleverness go hand-in-hand with professionalism when exploring any topic. So have fun while unraveling the mysteries of catamaran anatomy! Perhaps envision yourself as an expert sailor who can distinguish port from starboard blindfolded or sharpen your comedic skills by jokingly referring to hulls as “feline foundation” (though cats might not appreciate sharing their name with boats!).
Happy sailing!
Step-by-Step Breakdown: Unraveling the Mysteries behind Catamaran Anatomy
Catamarans have become increasingly popular in recent years, mainly due to their unmatched stability and impressive speed capabilities. But have you ever wondered what lies beneath the sleek exterior of these remarkable vessels? In this blog post, we will delve into the intricate details of catamaran anatomy, providing you with a comprehensive understanding of how these boats are constructed and why they excel on the water.
1. The Hulls: The Foundation of Stability At the core of every catamaran lies its hulls – two parallel structures that run alongside each other. Unlike traditional monohull boats that feature a single hull, catamarans distribute their buoyancy across two hulls, offering superior stability even in rough waters. These hulls are typically made from fiberglass or aluminum and are designed to cut through waves effortlessly, minimizing resistance and maximizing speed.
2. Bridging the Gap: The Trampoline One striking feature present in many catamarans is the trampoline located between the two hulls. This sturdy mesh-like material serves various purposes. Firstly, it provides an additional platform for sunbathing or relaxing while underway. Secondly, it acts as a safety net by preventing crew members or passengers from falling into the ocean should any unexpected jolts occur during navigation .
3. Connecting Hulls: The Crossbeams In order to maintain structural integrity and connect both hulls securely, catamarans utilize crossbeams that stretch between them. These crossbeams play a vital role in sharing weight distribution evenly across both sides, ensuring stability and balance at all times.
4. Above Deck: Central Cockpit and Living Space Moving upwards onto the deck area, you’ll discover a central cockpit where most controls and steering mechanisms are located. This strategic placement allows for optimum visibility and easy maneuverability while sailing. Additionally, catamarans often feature large living spaces, including saloons and cabins that provide ample room for socializing, dining, and sleeping. Their spaciousness is a significant factor contributing to their growing popularity among cruising enthusiasts.
5. The Power of Sails: Rigging and Sail Plan Catamarans rely on sails for propulsion, utilizing a complex system of rigging to hoist and control them effectively. A unique feature of catamarans is the absence of a single mast; instead, they employ multiple masts strategically positioned between the hulls. This configuration optimizes sail area while reducing heeling (when a boat tips sideways due to windy conditions), resulting in smoother sailing experiences even during stronger winds.
6. Additional Features: Daggerboards or Foils To enhance performance further, some catamarans are equipped with daggerboards or foils – retractable appendages located beneath each hull. These boards reduce lateral slippage by providing lift, improving upwind capability and enhancing overall speed. As technology advances, advanced hydrofoil systems have also been introduced in certain catamaran models, allowing these boats to glide above the water ‘s surface entirely.
By unraveling the mysteries behind catamaran anatomy step-by-step, it becomes evident why these vessels are highly sought after by both leisure sailors and competitive racers alike. From their stable hull design to innovative features such as trampolines and foils – every element plays its part in creating an exceptional sailing experience that combines comfort, speed, and versatility. Perhaps now you can fully appreciate these engineering marvels whenever you set sight on one gliding gracefully through the waves!
Frequently Asked Questions about the Different Parts of a Catamaran Answered
Have you ever looked at a catamaran and wondered what all those different parts are called? Or maybe you’re thinking about buying or renting a catamaran and want to be familiar with its components . Well, look no further! We’ve compiled a list of frequently asked questions about the different parts of a catamaran and will provide detailed, professional, witty, and clever explanations just for you.
1. What is a Catamaran? A catamaran is a type of boat that consists of two parallel hulls connected by a deck. It offers increased stability compared to traditional monohull boats due to the wider beam. This unique design allows for smoother sailing experiences and more spacious interiors.
2. Hulls – What Are They? The hulls are the main structure of a catamaran, providing buoyancy and supporting the entire vessel. Typically made from fiberglass or aluminum, they have curved shapes that help reduce resistance in the water while providing stability. Think of them as the legs of the feline-inspired boat!
3. Trampoline – Isn’t That for Jumping? While it may sound similar to the equipment used for bouncing around at your local playground, in the world of catamarans, trampoline refers to an open area between the hulls where passengers can relax or even stretch their sea legs! Made from durable materials like nylon mesh or PVC canvas, trampolines provide excellent circulation and an unobstructed view below deck.
4. Rigging – Is it Related to Sailing Techniques? Indeed! Rigging refers to all the elements involved in controlling sails on a catamaran . This includes mast(s), boom(s), standing rigging (shrouds & stays), running rigging (halyards & sheets), winches, cleats – basically everything needed to manipulate wind power efficiently and safely navigate through various conditions.
5. The Mast – How Tall Should It Be? The mast, often made of aluminum or carbon fiber composite, is the tall vertical pole that holds up the sails. Its height depends on several factors, such as boat size, intended use, and the desired sail area. Think of it as the catamaran’s lighthouse – guiding you along your aquatic adventures with grace.
6. Boom – Not Just a Sound Effect! Nope, not just an imitation of an explosion! The boom is a horizontal spar attached to the bottom of the mast, helping support and control the lower edge (foot) of the mainsail. It swings back and forth with changes in wind direction – think of it as a catamaran’s wagging tail!
7. Daggerboards – Are They Catamaran Ninja Weapons? While they may sound dangerous and ninja-worthy, daggerboards are actually retractable foils that extend from each hull into the water. Their purpose? Providing lateral resistance against sideways motion caused by wind force while improving upwind performance by reducing leeway – no martial arts skills required!
8. Rudders – Steering Like a Pro Like most boats, catamarans have rudders for steering purposes. These underwater blades at the stern help control direction by redirecting water flow around them when turned. Whether you’re tacking or gybing through waves or researching rudder-related puns like this one—we’ve got you covered.
So there you have it – frequently asked questions about the different parts of a catamaran answered in detail! Now you can impress your fellow sailors with your newfound knowledge or confidently embark on your next seafaring adventure aboard one of these sleek double-hulled vessels ! Remember to keep exploring and enjoy every nautical mile!
The Key Elements That Make up a Catamaran: Everything You Need to Know
Title: The Key Elements That Make up a Catamaran: Everything You Need to Know
Introduction: Catamarans have long fascinated sailing enthusiasts with their unique design, efficient performance, and spacious interiors. Whether you are a seasoned sailor or a curious novice, understanding the key elements that make up a catamaran is essential. In this enlightening article, we will delve into the intricate details of these remarkable vessels, uncovering the secrets behind their success on the open seas .
1. Hull Design: Stability Meets Speed At the heart of every catamaran lies its dual-hull structure. Unlike traditional monohulls, catamarans feature two separate hulls connected by a spacious deck. This design offers enhanced stability and reduced heeling, making them less prone to capsizing compared to their single-hulled counterparts. The inherent buoyancy allows for faster speeds and smoother sailing experiences—enabling both exhilarating adventures and relaxed cruising.
2. Beam: Embracing Extra Space One of the most significant advantages of a catamaran is its beam—the width between its two hulls—which can be quite impressive. The ample beam creates an exceptionally generous living area that sets catamarans apart from other sailboats . More space means greater comfort for passengers and crew alike; accommodating larger groups, luxurious amenities, and even personalized additions such as Jacuzzis or sunbathing decks.
3. Stability & Balance: A Steady Journey In addition to their unique structural design, catamarans offer exceptional stability through weight distribution and physics principles. With twin hulls spread apart at a considerable distance, it becomes significantly easier to maintain balance during sailing motions—a significant advantage for those susceptible to seasickness or seeking effortless navigation under challenging conditions.
4. Sailor-Friendly Handling: Ease-of-Use at Sea Catamarans excel in terms of maneuverability due to several factors working harmoniously together. Their shallow drafts allow for exploration in shallower waters, and docking becomes a breeze with the ability to navigate narrower marinas. Furthermore, their twin engines operate independently, offering excellent control even in tight spots or challenging wind conditions—a maneuverability dream for sailors of all skill levels.
5. Sailing Performance: Effortless Speed When it comes to performance on the water, catamarans stand tall once again. The efficiency gained from their two hulls reduces drag and enables quicker acceleration, resulting in higher average speeds than traditional monohulls. Even when faced with light winds, their ample deck space allows for customized rigging options—such as efficient sails or high-tech foiling capabilities—that can unlock extraordinary speed potential.
6. Comfortable Living Spaces: An Unprecedented Haven Catamarans redefine on-board living by providing both ample space and superior comfort. The expansive interior saloon offers panoramic views of the surroundings while being versatile enough to cater to various activities—from hosting lively social gatherings to peacefully reading a book by the window. Additionally, private cabins are often located in each hull, creating secluded sanctuaries for relaxation and tranquility amidst enchanting seascapes.
Conclusion: As we conclude our exploration into the key elements that make up a catamaran, it becomes evident why these vessels have become revered in the sailing world . The revolutionary dual-hull design ensures stability and faster speeds while offering unparalleled comfort and spaciousness aboard. Whether you seek adventure or serenity on the seas, understanding these elements will help you appreciate catamarans’ remarkable qualities truly—an embodiment of innovation and maritime excellence brought together harmoniously by human ingenuity.
Mastering the Parts of a Catamaran: A Beginner’s Guide for Sailing Enthusiasts
Are you a sailing enthusiast who is fascinated by the sleek and efficient design of catamarans? If so, then you’ve come to the right place! In this comprehensive beginner’s guide, we will delve into the key components of a catamaran and unlock the secrets to mastering its various parts. So grab your sailor’s hat and get ready to embark on an exciting journey through the intricate world of catamaran sailing!
The first component that sets a catamaran apart from other sailboats is its dual-hulled structure. Unlike traditional monohull sailboats, which have only one hull, catamarans feature two parallel hulls connected by a deck or bridge. This unique design grants them exceptional stability, speed, and even more interior space for amenities such as cabins and lounging areas.
Now let’s move onto a crucial part of any sailboat – the rigging . The rigging system on a catamaran consists of numerous elements that work harmoniously to control and manipulate the sails . Firstly, there are the masts: tall vertical structures that support the sails. Catamarans typically have two masts placed towards each end of the boat , allowing for efficient distribution of power.
Attached to these masts are various types of sails, including mainsails, jibs or genoas (fore-sails), and spinnakers (used for downwind sailing). The main sail is the largest sail on a catamaran and is hoisted up the mast using halyards – ropes specifically designed for this purpose. Jibs or genoas assist in maneuverability by generating additional power when sailing upwind.
For those seeking exhilarating downwind adventures, spinnakers add an extra element of thrill to your journey! These expansive triangular or bulbous-shaped sails catch wind from behind and propel your catamaran with remarkable swiftness. Learning how to handle these different types of sails will be crucial to seamlessly controlling the boat and maximizing performance on the water.
Next in line are the helm and steering system, responsible for guiding your catamaran ‘s path as it gracefully glides through the waves. The helm, often referred to as the steering wheel , is used to control the rudders located at each hull’s stern. One unique characteristic of catamarans is their tilting tendency caused by wind pressure acting upon the exposed surface area of their broad decks. Therefore, mastering steering techniques, including adjusting sail configurations and keel positions, will help you navigate with finesse and maintain balance.
One particularly innovative feature found in some catamarans is a daggerboard or a centerboard system. Located between the two hulls beneath the waterline, these retractable fins can be individually raised or lowered to vary their depth while sailing. By adjusting these boards according to wind conditions and point of sail , you can minimize resistance, optimize speed, and even prevent lateral drift.
We cannot overlook catamarans’ anchoring systems when discussing their components . Anchors are vital for keeping your vessel secure when moored or stopping for a leisurely swim in crystal-clear waters. Most modern catamarans employ bow rollers integrated at the front end that facilitate effortless anchor deployment and retrieval. With an array of anchor types available — from plows to flukes — it’s essential to understand each one’s characteristics in various seabed environments.
Lastly, let’s not forget about safety equipment onboard! While mastering catamaran parts allows for glorious adventures on calm seas, unforeseen challenges may arise during your sailing odysseys. It’s important always to have safety essentials like life jackets, fire extinguishers, first-aid kits, emergency flares, and navigational tools like GPS systems.
So there you have it – a comprehensive overview of key components necessary for mastering the art of sailing a catamaran! Understanding how each piece of the puzzle fits together and harmonizes uniquely will set you on a path to becoming a skilled catamaran sailor . Whether you’re gliding across tranquil bays or tackling exhilarating rough seas, this guide will equip you with the knowledge and confidence to embark on unforgettable nautical journeys!
Recent Posts

- Sailboat Gear and Equipment
- Sailboat Lifestyle
- Sailboat Maintenance
- Sailboat Racing
- Sailboat Tips and Tricks
- Sailboat Types
- Sailing Adventures
- Sailing Destinations
- Sailing Safety
- Sailing Techniques

- Ocean Play Bahia
- Ocean Play Bug
- Ocean Play Pico
- Ocean Play Vago
- Laser Bahia
- ILCA dinghy
- Optimist - Race
- Optimist - School
- Bung - Drain plug
- Complementary parts
- Fairleads - Deck bushes
- Furlers - Swivels
- Gudgeon fittings
- Hatch covers
- Lacing eye strap
- Swivel cleats and Jammers
- Tiller extensions
- Tension gauges
- Wind Indicators
- Boat repair
- Maintenance
- Accessoires
- Buoyancy aids
- Coastal gear
- Hooded towel
- Lycra - Spandex
- Sailcenter Beanie
- Sailcenter Hoody
- Hiking straps
- ILCA Dinghy
- Control lines
- Optimist School
- Country code
- Laser - ILCA
Sailcenter supplies various parts for all catamarans, Hobie Cat, Nacra Catamaran, Topaz Catamaran, RS Catamaran, Capricorn Catamaran, C2 Catamaran.

Sikaflex 291 - 70 ml
- Multifunctional adhesive sealant
- Polyurethane sealant for gluing, sealing
- White - 70 ml
Harken 57 mm Carbo automatic ratchet block
Harken upper furling swivel high load.
- Series: Harken Small Boat Furling
- Standard upper halyard swivel
- Use with Harken drum 165
Harken furling drum high load
- Standard furler
- Use with Harken swivel 164
FiberFoam tapered batten 1650mm x 18mm
- The most used cat batten in the World
- Supplied for Hobie, Nacra, Goodall, etc
Ronstan drain plug and housing
Windesign magnetic protest kit, ronstan swivelling cleat unit, self vulcanizing tape.
Best tape to secure clevis pins, rings
A strong, rubbery and (sea)waterproof layer
Automatically hardens and leaves no adhesive residue after removal
Harken 57 mm triple Carbo ratchet block with becket and cleat
- Series: Harken Ratchet Carbo Block
- 57 mm Triple Ratchet Block - Becket - Cleat
- Maximum line diameter 10 mm
FiberFoam C2 batten set
- Complete Goodall C2 catamaran batten set
Gorilla Sailing carbon tiller extension oval 250 cm
- Oval tiller extension for maximum grip
- Can be cut to the correct length
- Equipped with rotating flexi joint
Ronstan hatch cover
Harken 57 mm carbo 5 - sheave ratchet block with cleat and becket.
- 57 mm 5 sheave ratchet - cleat and becket
EuroTrax asymmetrical cradle with handwheel
Hobie 14, Hobie 16
Prindle 15, Prindle 16, Prindle 18
Supplied incl tube clamp for 50 mm tube
FiberFoam tapered batten 1850mm x 18mm
Spinlock pxr cam cleat 2 - 6 mm vertical.
- Precise control for hand tensioned lines
- Suitable for polyester and dyneema lines
- Hard anodised alloy cam and base
Ronstan hatch cover ring
Fiberfoam hobie tiger stx batten set.
- Complete Hobie Tiger batten set
Sailcenter Tell Tales
- 8 Red tell tales and 8 Green tell tales
- Dacron self adhesive tell tales sticker
- With tell tales instruction manual
Harken Torlon traveller balls
- Series: Harken 22 mm Micro Track
- Suitable for Harken 2726 traveller
Harken high load furling drum and swivel set
- Standard furling kit complete
- Harken 164 and Harken 165
Harken 40 mm Carbo pivoting lead block with aluminium cleat
- Series: Harken Carbo Air Block
- Cam cleat can be mounted up site down
- Used for either up or down cleating
EuroTrax uni symmetrical cradle with handwheel
Tornado, Dart Hawk, Hobie Tiger, Nacra F18, Tornado
Hobie Cat 17/18/20/21, Prindle 18-2/19, Nacra 5.2/5.5/5.8/6.0
- Accessoires 21
- Beam fittings 8
- Hull - Deck fittings 7
- Rudder - Rudder fittings 3
- Spar fittings 10
- Spipole fittings 3
- Trailer - Trolley 14
- Trapeze parts 7
Save products on your wishlist to buy them later or share with your friends.

The best way to find out about new boats, new products, inventory, and sales.

In stock and ready to ship
Example Product Title $19.99

The A Class Worlds are coming to the US!
Check out the site for more details: http://aworlds.com

Welcome to Fast Boat Stuff!
Your best source in North America for gear for A Class Catamarans.
We are your dealer for Exploder Catamarans and Fiberfoam masts and all the parts to keep them in top shape.
Looking forward to serving all your needs and seeing you at the next A Cat Regatta near you!
- choosing a selection results in a full page refresh

Beneteau Spare Parts: Lagoon Catamarans
Spare parts from beneteau usa for lagoon catamarans.

How to Order Lagoon Catamaran Parts
American and Canadian owners of Beneteau-built Lagoon catamarans can order directly from the Beneteau USA spare parts service website. You must have a customer code (account login with password) to access the online catalog. Here is how it works:
- If you don’t have a customer code, get one using the Beneteau Spare Parts Account Request Form. Note it can take a couple of days to receive your login credentials.
- If you have an account, login at Beneteau Spare Parts Catalog.
- IMPORTANT: Our boat owners report that the catalog ordering system is not intuitive so you will want to watch the video. There is a video link on the catalog login screen, but as of August 2021, it was not working, so this video shown here may help.
- Call Beneteau Customer Service at 843.629.5320 to work with a sales rep or request a link to the online catalog (in case the link above stops working).
- Your closest Lagoon dealer or certified service location. If in South Florida, contact Lagoon Technical Services – Multitech Marine Fort Lauderdale 954.522.1114 .
- If your part is not in stock, it will be ordered from France and you will receive a weekly back-order status email.
- Once the part is shipped, you will receive a tracking number.
Voila! Lagoon catamaran parts from Beneteau made easy!
If You Cannot Find the Lagoon Part You Need in the Catalog
If by chance you cannot find the Lagoon part you need in the catalog, you will be redirected to send an email to Lagoon After-Sales France at [email protected] . The Lagoon staff will research the part identification number and pass it on to Beneteau USA. They will email you with the part number so can order the part from the Beneteau parts website.
Parts for any Lagoon models not listed on the Beneteau USA parts catalog above as well as technical questions of any kind (if your dealer cannot help) should be directed to Lagoon in Bordeaux, France by sending an email to [email protected] .
Connect with other Lagoon owners for help and advice by joining the ‘Lagoon Catamaran Owners Group’ on Yahoo Groups .
Estelle Cockcroft
Join our community.
Get the latest on catamaran news, sailing events, buying and selling tips, community happenings, webinars & seminars, and much more!
9 thoughts on “Beneteau Spare Parts: Lagoon Catamarans”
I’m looking for a hydraulic swim platform to install on a 2008 440 lagoon. I’m starting a dive spearfishing charter biz that will have handicapped wounded warriors and other handicapped people on board. I need to safely lower and raise them out of the water from the stern if possible
Scott, I think Stephen has already spoken with you and he has just suggested that perhaps you should also contact Dedicated Marine in Florida. They may be able to either help or guide to a supplier.
I signed up for spare parts but did not get my username or password from the original screen. Can you please email to me. Thank you.
If you own a Lagoon and need parts, good luck. It has been a big run-a-round.
Catamaran Guru DOES NOT SELL PARTS. They will refer you to Multitech, who is a wholesaler and will not sell to boat owners. When you ask Multitech for a list of companies that they will sell to, it turns out that everyone of them only sells boats and they do not deal in parts.
When I called Beneteau I was number 99 in line. Lagoon and Beneteau need to get it together. Those two manufacturers have made a million boats, it would be nice if they could take care of their customers after the sale.
You are absolutely correct that Catamaran Guru DOES NOT SELL Lagoon parts and we never claimed to. The link on our website was provided by Beneteau / Lagoon and also is or was on their own websites. I am afraid that I cannot be responsible for their reaction times. As for the dealers, contact the dealer you bought the boat from and hold their feet to the fire to help you source parts. Lagoon America is located in Annapolis and you could call them. There is also a very vibrant Lagoon owners group on Facebook that is very helpful. People who buy Lagoon catamarans from us, are always taken care of and your broker / dealer should do the same for you.
Could anyone tell me if there is another dealer in the USA other than Multitech Marine. They have been extremely unhelpful in the past.
e.g. I ordered an anchor frame from them several years ago, but it did not turn up, despite many emails and calls. I ordered light switches and they sent momentary switches. I ordered fuses and they sent the wrong ones.
They make no effort to rectify their errors, or to provide customer service. Its cost me a lot of money and I have received nothing of value.
I’m afraid I cannot help with that. Your dealer should be able to help.
It appears that they have closed the site for taking orders Anyone have any ideas how can I order parts?
Manny the only info we have is perhaps to contact Multitech Marine in Florida or Lagoon America in Annapolis MD.
Leave a Comment Cancel Reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Recent Posts

Annapolis Boat Show 2024
Meet with our team! Want to learn more about the Bali and Catana

Exploring the Catana OC 50 Catamaran: A Comprehensive Overview
The Catana OC 50 Catamaran, the latest addition to the Catana Ocean Class series,

Lessons Learned from Selling our Catana 50 OC
Stephen and I are in the process of selling our Catana OC 50 Catamaran.
How is Your Yacht Brokerage Adapting to the Digital Age?
You may have noticed that we have a lot more catamarans for sale in

For more than 30 years, we have been a part of the catamaran community and created Catamaran Guru™ to encourage and educate all the aspiring sailing out there. We understand the dream of traveling the world by catamaran and created a one-stop-shop to make that dream a reality for you.

- Stephen & Estelle
- Testimonials
Get Started
- Yacht Sales
- Used Yachts
- Charter Management
- Boat as Business Programs
- Seminars & Events

My Cruiser Life Magazine
Illustrated Guide to Sailboat Parts [Updated 2023]
The lingo of sailing is baffling to many newcomers. While the actual sailing is pretty easy, it’s hard to wrap your mind around the bookwork when it seems like every little thing on a boat goes by its own nautical term.
Here are a few names for parts of a sailboat that you might not have thought about before. For even more nautical word play, check out our complete guide to sailing terms .

Parts of Sailboat Hulls
The boat’s hull is its main body. Most are made of fiberglass, but there are a few aluminum sailboat models out there too. Wood is more traditional but more difficult to maintain than these modern alternatives. Sailboat hulls are displacement hulls, which means they sit low in the water and move relatively slowly. The hull’s job is to displace water, so you stay afloat!
Bow The forward “pointy end” of the boat.
Stern The rear end of the boat.
Transom If the stern of a boat has a flat section, it is called the transom. (I wrote about it in detail here: What Is the Transom on a Boat )
Canoe Stern or Double-Ender Some boats lack a transom; instead, their stern comes to a point like a bow. This is a “double ender” or a canoe stern.
Port and Starboard Sides Port is the left side, and starboard is the right side.
Freeboard This is the height of the sides of the boat above the water.
Deck The upper portion of the boat that you walk on.
Sheer Sheer is the curve of the deck when viewed from the side. Some boats have none, and some boats have a lot.
Cabin Coach Roof Most sailboats have a raised coach roof on top of the cabin area.
Bottom of a Sailboat – Keels and Things
There are tons of parts on a sailboat that you only ever see if it’s out of the water. Boats are hauled out at boatyards by giant cranes, or a special machine called a travel lift .
Keel The boat’s keel is the underwater feature that counters the effects of wind pressure on the sails. It keeps the boat from tipping over, but it also keeps the boat going in a straight line as it moves through the water. If a boat has no keel, the wind will push it downwind.
A keel is heavy–it is weighted with thousands of pounds of ballast (usually lead). So when someone refers to a “keelboat,” they mean that it is a big boat with a weighted keel built for cruising. The built-in weight of a keel keeps the boat from capsizing. Also, the water flow over the curved surface of the keel helps the boat sail into the wind.
Smaller boats with centerboards or daggerboards are on the opposite end of the spectrum from keelboats. These aren’t weighted and could tip over (capsize) in the wrong conditions.
Types of Keels
Full Keel A classic and time-tested design, full keel boats are favorites among passage-making and ocean-crossing cruisers. They’re stable and comfortable at sea and very safe. However, they have a reputation for being slow compared to more modern designs.
Modified Full Keel The modification is a cut-away forefoot. That means it looks like a full keel, but there isn’t as much keel up near the bow. This reduces the underwater “wetted surface area” and makes the design a little bit faster while preserving the other good things about full keel designs.
Fin Keel The fin keel looks like a shark’s fin pointed downward. Some are narrow and very deep, while others are longer and shallow. Fin keels are bolted to the bottom of an otherwise flat-looking hull design. The fin has a foil shape that creates a lifting force as water flows over it. In addition to its ballasted weight, this opposes the sails and leeway. Most modern sailboats have some version of a fin keel.
Bulb Keel The ballast should be placed as low as possible to lower the boat’s center of gravity. The bulb keel is a fin keel with a lead bulb added to the bottom. The bulb has an efficient shape, making it more efficient than just the fin alone.
Wing Keel Like a bulb, a wing keel works by adding more weight and hydrodynamic force to the bottom of the keel. As a result, the wings look like a little airplane mounted on the bottom of a fin keel.
Swing Keel A swing keel is a fin that pivots up and into the boat, meaning that you can have a very shallow draft when you are docking or anchoring but also a very deep draft when you are sailing in open waters. This heavy keel requires a powerful and complicated electric or hydraulic-electric system.
Lifting Keel A lifting keel is similar to a swing keel, only the keel lifts up into the hull vertically.
Bilge Keels A bilge keel boat has two fin keels mounted at 45-degree angles below the hull. The advantage is that the boat can “dry out.” This makes them very popular in harbors around England, where the massive tidal range means that the harbor is only mud for half the day.
Centerboard Centerboards look like swing keels, but the “keel” part is just a board. It isn’t weighted with lead or iron, so it doesn’t change the ballast of the boat any. They are often found on smaller sailboats like sailing dinghies, but there are also large cruising boats that have full keels or long-fin keels with centerboards, too.
Daggerboard A daggerboard is like a centerboard, only it doesn’t swing. Instead, it goes straight up and down like a dagger into its sheath. They’re not only common on very small sailing dinghies but also large cruising catamarans.
Canting Keel Canting keels are some of the latest technology items in racing, so they aren’t found on cruising boats yet. They move from side to side, allowing the crew to precisely control the forces made by the keel.
Types of Rudders – What Steers a Sailboat
As with keels, you’ll see various types of rudders on sailboats. The rudder is one of the most critical parts of a sailboat’s equipment, so the differences in rudders are mostly about how protected it is from damage.
Rudder The rudder is the thing that steers the sailboat. It’s mounted on the back of the boat, sometimes looking a bit like a second keel. When the operator turns the steering wheel or tiller, it moves the rudder one way or the other. That, in turn, turns the yacht’s bow left or right.
Transom-Hung Rudder The most basic type of rudder is hung on the transom. It’s usually controlled with a tiller instead of a wheel. You can see a transom-hung rudder above the water.
Keel-Mounted Rudder On a full keel boat, the rudder will be mounted on the back edge of the keel. This protects it completely from damage since anything the boat might hit will hit the keel first.
Skeg-Mounted Rudder The rudder might be mounted to a skeg if a boat has a fin keel. A skeg is a small fixed surface that holds the rudder and supports it. In the case of a full skeg, it also protects the rudder as a full keel would.
Spade Rudder Spade rudders have no skeg, so the entire underwater surface moves when you turn the wheel. Most modern yachts have spade rudders because they are incredibly effective. They are easily damaged, however, which is why some offshore sailors still prefer skeg-hung rudders.
Bottom of Sail Boat – Running Gear
Running gear is the generic name given to all equipment under the boat that connects to the engine and moves the boat under power. It consists of the propeller, prop shaft, and supports.
Propeller Also called the prop or screw, the prop is what converts the engine power into thrust. The water flow over its blades creates a pushing force that moves the boat. Since the sailboat doesn’t use the propeller when it is sailing, sailboats often have folding or feathering props that stop moving.
Prop Shaft The metal shaft that connects the engine to the propeller is called the prop shaft.
Cutlass Bearing Where the prop shaft exits the hull, a rubber cutlass bearing keeps it centered and rotating freely.
Saildrive A saildrive is a common arrangement on modern sailboats that uses a vertical drive leg with the propeller. The saildrive installs on the back of the engine and includes the transmission. It’s like the lower unit of an outboard motor, but you cannot raise it out of the water.
Up Top – Types of Sailboat Designs
Aft Cockpit The “classic” design of the modern sailboat, if there is such a thing, is called the aft cockpit. This layout has the cockpit in the rear-most section of the hull, behind the cabin.
Center Cockpit The center cockpit sailboat has the cockpit closer to the mast. That leaves a lot of space in the rear of the hull for a huge stateroom. This design means that the cockpit will be closer to the boat’s center, making handling easier. But it is also higher, making more windage and motion at sea.
Pilot House A pilot house sailboat has a second helm inside a protected area. These are popular in colder climates, where the pilot house provides a warm place to steer the boat from. The rear cockpit is usually smaller than a typical aft cockpit, but it’s still where the sail handling occurs. A pilot house has a raised level, so the salon typically surrounds the interior helm to utilize that space and visibility when not underway.
Deck Salon Like a pilot house, a deck salon has big windows and better visibility than a typical sailboat cabin. But it lacks a true interior helm. Many, however, have nav stations with forward visibility and autopilot controls, making it a comfortable place to sit and keep watch during a passage.
Flush Deck Most sailboats have a raised coach roof where the interior cabin is. But some designers make their decks flush with the sides of the boat, making a wide open deck that is easy to move around on.

On Deck Sailboat Components – Sailboat Front
The deck of a sailboat is all about safety at sea. Most modern cruising boats are rigged such that there are few things you might need to go “out on deck” or “go forward” for. Instead, these things are rigged back to the cockpit, so you can stay safe and dry while doing your thing.
Since the wet pitching deck of a sailboat at sea is tricky, many of the things you’ll find there are safety-related.
Handholds Places to grab should be located all over the boat, so there’s never a risk of not having something to hold onto to stabilize yourself.
Lifelines Lifelines run the perimeter of the boat and provide a last-ditch safety device. You can grab them, and they should be high enough that they’ll keep you from going overboard.
Stantions The stands that lifelines attach to.
Bow Pulpit The solid rail around the front of the boat provides a safe handhold and a starting point for the lifelines.
Stern Pushpit The same, but on the stern of the boat.
Bulwarks The raised edges of the deck on the sides so that you can’t slip overboard on accident.
No-Skid Decks In areas where people will be walking, the deck is treated with a special product to make the deck “no-skid.” That way, it isn’t slippery, even when wet.
Harness Sailing harnesses are designed to clip onto the boat and keep a sailor onboard even if the boat takes a huge wave or the sailor slips. The harness is the staple of offshore safety.
Jack Lines Jack lines are temporary lines secured on the deck where sailors can attach their harnesses.
Safety Rails Many boats also have extra rails and handholds located in spots where sailors might work on deck, like around the base of the mast.
At the bow of the sailboat, you’ll find her ground tackle.
Bowsprit The bowsprit is the spar that extends from the deck forward of the bow. They’re used on sailboats to gain more sail area since getting the sail farther forward means you can fit a bigger sail. Some have just a spar, while others have a bow platform that is part of the deck.
Ground Tackle The generic word for the anchor, chain, and all the equipment needed to use it.
Anchor The anchor is “the hook” that digs into the seabed and keeps the boat in the same place. Anchors are safety devices since they allow you to stop in shallow water. But they also provide access to areas with no marinas since you can anchor offshore and go in on your dinghy.
Windlass A winch that pulls up the anchor and chain. They can be manual, with a handle, or electric, with a button.
Anchor Rode The generic name for the anchor line. It can be a chain or rope.
Snubber A short length of rope that attaches to the chain to secure it to the boat.
Cleat A horn-shaped piece of deck hardware used to secure a line or rope.
Dorade A large vent opening on the deck of a boat which is designed to let air in but not water.
Hatch Hatches are upward-facing windows that you can open to increase ventilation in the cabin.
Locker A generic term for a cabinet or compartment on a boat.
Going Aloft – Basic Boat Parts of a Sailing Rig
The rig of a boat is the mast and all of its associated parts. If you’re wondering about the many different kinds of rigs that are out there, check out our rundown on sailing terms . There you’ll find definitions for boats with just one mast or multiple masts, like sloop rig and what a boat with two sails in front might be called. It’s a cutter, if you’re wondering.
Spar A generic name for a mast, boom, or any other long pole used to hold a sail. It can be wood or metal or vertical or horizontal.
Mast A vertical spar upon which a sail is hoisted.
Boom A horizontal pole that holds a sail and gives it shape.
Standing Rigging The wires or rope that holds the mast upright.
Stay Standing rigging that goes fore to aft. The head stay runs from the masthead to the bow, and the backstay runs from the masthead to the stern.
Shroud Standing rigging that goes to the sides of the boat. From the masthead to each side runs a cap shroud. Some masts also have intermediate and lower shrouds.
Running Rigging All lines that are used for sail handling are called running rigging.
Halyard A halyard hoists a sail to the top. Each halyard is named for the sail it hoists, i.e., main halyard, jib halyard, spinnaker halyard.
Sheet The sheet controls the sail. If you ease the sheet, the sail is loosened. If you winch the sheet in, it is tightened. Like all running rigging, each sheet is named for the sail it controls, i.e., main sheet, jib sheet, etc.
Traveler If a sail has a boom, the traveler can be used to adjust it from side to side. The sheet is attached to the traveler. Most main sail travelers are located near or in the cockpit.
Gooseneck Fitting The articulating attachment that holds a boom on a mast.
Topping Lift A line that holds the rear end of a boom up. It runs from the masthead to the boom.
Vang A control line pulls the boom down and puts pressure on the sail to keep it flatter. Large boats may have hydraulic or solid vangs.
Blocks The rest of the world would call this a pulley, but sailors call it a block.
Fairleads Deck organizers that keep the lines tidy and running in the direction they should go on deck.
Furler Wraps the sail around the stay so that it doesn’t not have to be raised and lowered each time. Instead, you pull on the sheet and the sail unrolls or “unfurls.”
On Deck – Back of Sailboat
On most boats, the cockpit is located at the back.
Cockpit The main operations center and party central on a sailboat. This is where the skipper sits at the helm, and the linesmen control the sheets.
Coaming The cockpit is protected from waves and splashes by the coaming, the tall walls that enclose it. It also makes the cockpit safe since you are unlikely to get swept overboard from here.
Lazarette The main storage locker in the cockpit.
Helm The station where the skipper steers the boat from.
Tiller If a boat doesn’t have a wheel, it will have a tiller. A tiller is just a handle connected to the rudder, and the skipper pushes or pulls it to steer. Even if a boat has a wheel, it probably has an emergency tiller in case the steering system breaks.
Winch Winches provide a mechanical advantage to make it easier to haul in lines. In the cockpit, all the sheets have winches.
Rope Clutch A clutch locks a rope in place so it can be taken off a winch, even when loaded.
Jammer A jammer does the same as a clutch, but it’s a simpler device found on smaller boats.
Weathervane Steering A weathervane is used to steer the boat like an autopilot but uses wind direction and mechanical linkages. As a result, they use no power and never complain about their workload. They mount on the stern of the boat and are controlled by simple lines to the cockpit. Windvanes are often referred to by their brand name, i.e., Monitor or Hydrovane
Davits Arms on the back of the boat that lift the dinghy or tender.
Swim Platform A flat area on the transom that allows you easy access in and out of the water. A standard feature on newer boats but not on older ones that just had long swim ladders.
Catamaran Sailboat Parts Explained
For the most part, the components of a catamaran share the same terms and labels that they would on a monohull. Cats often have a few extra features with other names, however.
Hulls A catamaran is made with two hulls connected together. Each hull has an interior, just like a monohull sailboat does. The cabins and heads are usually located in the hulls, and sometimes the galley is also down below.
Owner’s Version A catamaran layout that is made for private owners. Usually, one hull will be dedicated to the owner’s stateroom with a private door, a huge head with a walk-in shower, and a large berth.
Charter Version It has more staterooms and heads than an owner’s version does. Usually, a charter cat has at least two staterooms and heads in each hull.
Bridge Deck The deck connects the two hulls, which usually has the salon and cockpit. If the design is “galley up,” the galley will be on the bridgedeck with the salon.
Cockpit Just like on a monohull, the cockpit is the operations center. But catamarans have huge cockpits, and there is usually a large outdoor dining table and entertainment area as well.
Forward Cockpit Some designs have lounge seating forward of the salon on the bridgedeck.
Flybridge Some designs have the main helm mounted on top of the salon on an upper level. It’s almost the catamaran equivalent of a center cockpit.
Trampolines Forward of the salon, the bridge deck stops, and a trampoline connects the hulls over the water. This is a great place to hang out, but it’s an integral safety feature for a catamaran. The trampolines allow any water to immediately drain away, not weighing the boat down on the bow. This prevents a pitchpole when a boat capsizes by tipping forward into the water.
Cross Beam and Dolphin Striker Since there is no center bow to mount the head stay and foresail, catamarans use a cross beam that connects the hull. A piece of rigging keeps this in place, and it’s called the dolphin striker. No dolphins were hurt in the rigging of these boats, however.
Anchor Bridle Instead of a single snubber line on the anchor, catamarans use a wide bridle that connects each hull bow to the anchor line.
Parts of a Sail Boat FAQs
What are parts of a sailboat called.
Sailing is a challenging hobby, and one reason it’s so difficult for beginners is because every part of a sailboat has its own name. From each wire and rope to every piece of deck hardware, a beginner must learn the basics before they can even start.
What is the front part of a sailboat called?
The front part of a sailboat is called the bow. Many boats also have a spar extending forward of the hull, called the bowsprit.
What are the 5 basic parts of every sailboat?
Every sailboat has at least these five parts, but most boats have many more. Hull Keel Rudder Rigging Sails
Matt has been boating around Florida for over 25 years in everything from small powerboats to large cruising catamarans. He currently lives aboard a 38-foot Cabo Rico sailboat with his wife Lucy and adventure dog Chelsea. Together, they cruise between winters in The Bahamas and summers in the Chesapeake Bay.
Leave a comment
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.

Catamarans: A Complete Guide to Multihull Boats
Catamarans have been a part of sailing history for centuries and continue to be popular for their stability, spaciousness, and performance. Developed by various cultures around the world, the principles of catamaran design have evolved over time to become optimized for both pleasure cruising and racing. This complete guide will help you understand the essentials of catamarans, their unique characteristics, and how to choose the right one for your needs.
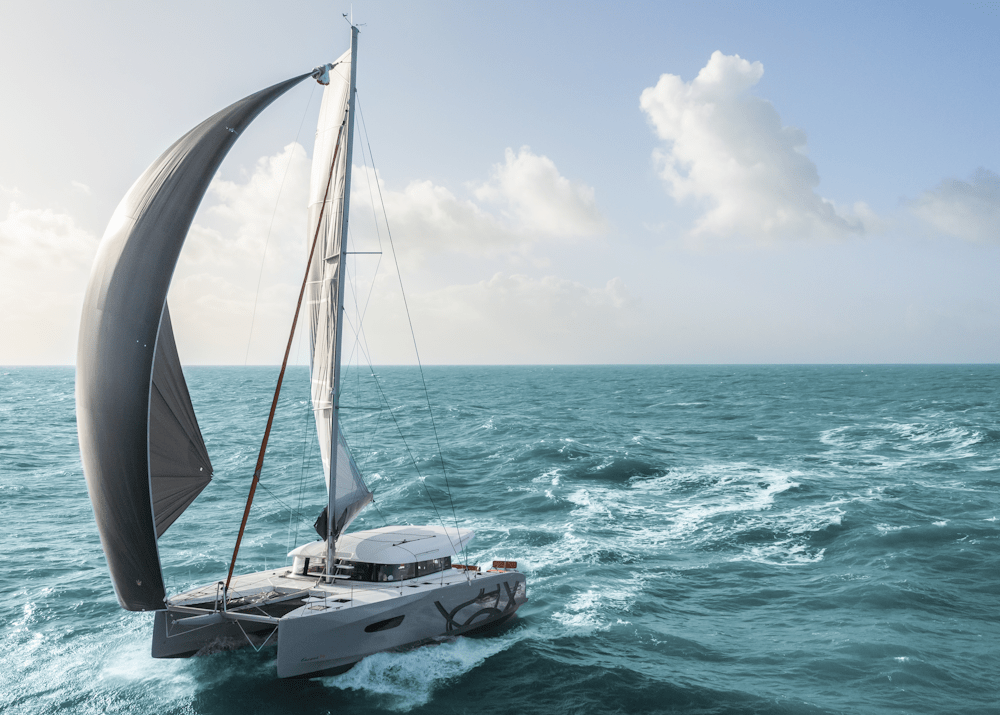

From the basic concepts of multihull design, performance, and handling, we will explore the advantages and benefits of a catamaran in terms of safety and comfort on board.
Along the way, we will discuss maintenance considerations, distinctive catamaran brands and models, and how a catamaran lifestyle can compare to more traditional sailing options .
Finally, we will provide learning resources and frequently asked questions tailored to both seasoned sailors and newcomers to the world of catamarans.
Key Takeaways
- Catamarans are known for their stability, spaciousness, and performance
- This guide covers aspects like design, handling, safety, and choosing the right catamaran
- Resources and frequently asked questions provide additional insights for potential catamaran owners
Understanding Catamarans
Design Characteristics
Catamarans are known for their unique design, which features two parallel hulls connected by a deck. This design provides several advantages over traditional monohull boats, such as stability and speed.
With their wide beam, catamarans have a reduced risk of capsizing and can access shallow waters due to their shallow drafts 1 .
One of the notable aspects of a catamaran is its twin hulls, which offer increased living space and comfort compared to a monohull. Additionally, catamarans are often favored by recreational and competitive sailors for their excellent maneuverability 2 .
The materials used for constructing catamarans range from wood to fiberglass, and even aluminum for high-performance vessels. Aluminum catamarans are known for their strength, lightweight structure, and resistance to corrosion 3 .
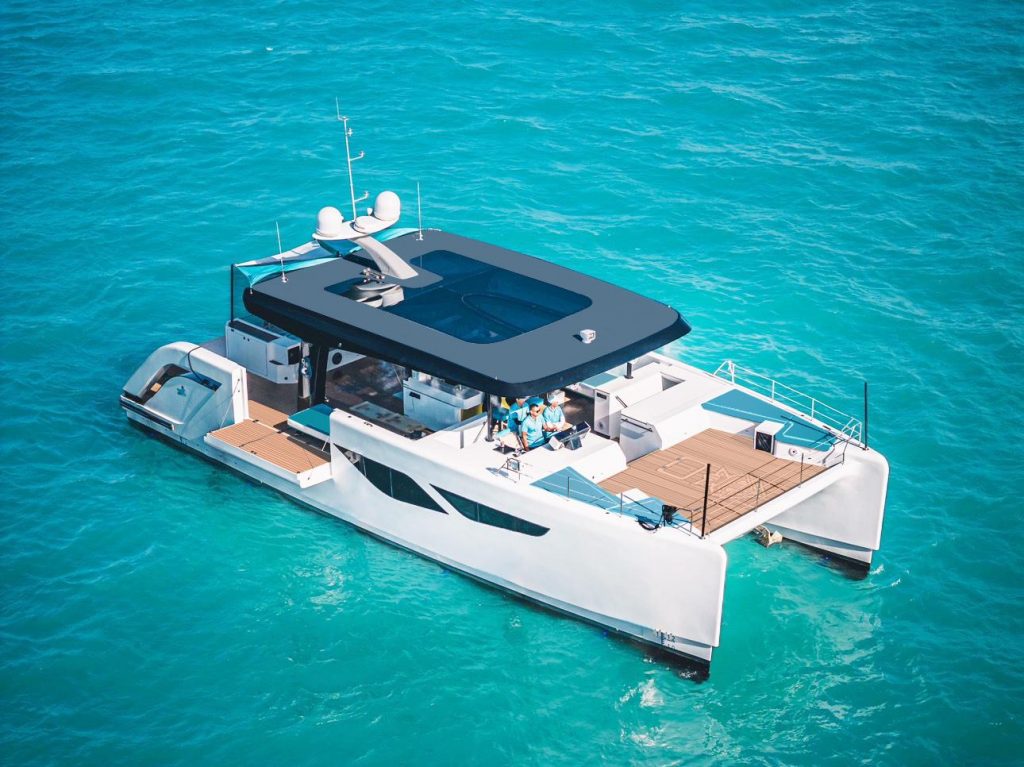

Hulls and Construction
The hulls in a catamaran are crucial to its stability and performance. These hulls help distribute the weight evenly across the water surface, minimizing drag and allowing for smoother sailing.
In general, the hulls can be categorized into two types:
- Symmetrical Hulls : The hull shape is similar on both sides, which enhances balance and stability in various sailing conditions.
- Asymmetrical Hulls : One side of the hull is designed differently than the other, which can be advantageous when sailing upwind.
The construction materials used in building catamaran hulls also play a vital role in the boat's performance and durability. Common materials include:
- Fiberglass : A popular choice due to its lightweight, strength, and ease of maintenance.
- Wood : Traditional material that offers a classic look, but requires more maintenance than fiberglass or aluminum.
- Aluminum : Lightweight and strong, aluminum is an excellent choice for high-performance catamarans 4 .

Multihulls vs Monohulls
There's often a debate between the benefits of multihull boats, such as catamarans or trimarans, and monohull boats. Here are some key differences between the two:
- Stability : Due to their wide beam and reduced heeling, catamarans offer improved stability compared to monohulls. This makes them an attractive option for those who want to avoid seasickness or feel more comfortable on the water 5 .
- Speed : Multihull boats are known for their speed, which results from their ability to minimize drag and maintain a level sail.
- Living Space : Catamarans and other multihulls generally have more living space, as both the hulls and the connecting deck can be utilized for accommodation and storage.
- Maneuverability : While monohulls are known for their agility and ability to point close to the wind, catamarans can still offer exceptional maneuverability when properly sailed 6 .
Performance and Handling
Speed and Efficiency
Power catamarans have gained popularity for offering a unique combination of speed, efficiency, and stability. Their dual-hull design allows for less water resistance, which directly translates to higher speeds and better fuel efficiency compared to traditional monohull boats.
In addition, the wide beam provided by the two hulls ensures a stable ride even at higher speeds. This makes power catamarans ideal for cruising, fishing, and watersports ( Boating Beast ).
Sailing Dynamics
When it comes to sailing catamarans , the performance is affected by factors such as keel, rudders, mast, and sails.
Their wide beam and dual-hull design provide inherent stability and reduced heeling effect, making them less likely to capsize compared to monohulls.
I should also note that catamarans have a shallow draft, which gives them the ability to access shallow waters that may be off-limits to other boats ( Navigating the Waters ).
In my experience, the lighter weight of a catamaran and its aerodynamic design can contribute to remarkable sailing performance under different wind conditions.
The larger sail area relative to hull weight allows them to harness more wind power, further enhancing their speed and agility on the water.
Maneuvering and Docking
Maneuvering and docking a power catamaran involves understanding its unique handling characteristics.
The presence of two engines in separate hulls allows for more precise control in confined spaces such as marinas.
The maneuverability of these boats is typically improved by the use of dual rudders that are located close to each powered hull for efficient steering ( BoatUS ).
When docking under power, I find it helpful to carefully assess the wind and current conditions beforehand.
This is because catamarans can be more sensitive to windage due to their larger surface area above the waterline.
By understanding how these forces may affect the boat, I can make adjustments to my approach and successfully dock the catamaran without any incidents.
Safety and Comfort on Board
Safety Features
Safety is a top priority when sailing any type of vessel, including catamarans. A well-built catamaran offers several features aimed at ensuring the safety of those onboard.
First, catamarans have inherent stability due to their wide beam and twin hull design . This makes them less prone to capsizing than monohull boats. This stability allows me to confidently navigate various water conditions .
In addition to stability, catamarans are designed with positive buoyancy, making them almost unsinkable . Of course, safety equipment such as lifejackets, flares, and first aid kits should always be onboard and well-maintained.
Furthermore, you should also stay updated on weather conditions, avoid sailing in high-risk areas, and learn your boat's safe sail limits.
Living Spaces and Comfort
When it comes to living spaces, I value comfort and practicality as essential features for my time on the water. Catamarans offer a unique advantage in this regard, as their dual hulls create spacious living areas.
Most catamarans are designed with separate cabins in each hull, allowing for privacy and comfort when sleeping. Additionally, these boats typically feature shallow drafts , which means I can access shallow waters and anchor close to shore.
The main living area, or salon, is situated on the bridge deck between the hulls. It usually includes a seating area, a dining table, and a galley (kitchen). Large windows provide ample natural light and panoramic views, making the space feel open and bright. Some catamarans even have the option for an additional living area on the upper deck where you can enjoy the sun and breeze.
One aspect of catamaran living I truly appreciate is the ample storage available. Each cabin typically has built-in storage spaces for clothes, gear, and personal items. There are also designated areas for equipment such as spare sails, tools, and water toys. This makes it easy for me to keep my belongings organized and make the most of my time on the water.
Maintaining a Catamaran
Routine Maintenance
In order to keep my catamaran in the best possible shape, I make sure to perform routine maintenance tasks. These tasks are essential to extend the life of the components and ensure smooth sailing:
- Cleaning : Regularly cleaning the deck, hulls, and sails prevents buildup of dirt, algae, and other debris that could affect performance.
- Inspection : Periodically inspecting my catamaran allows me to detect any potential issues before they become significant problems. I pay close attention to the rigging, sails, and lines on my boat.
- Lubrication : Keeping all moving parts lubricated is vital to prevent friction and wear on components such as winches and pulleys.
- Antifouling : Applying antifouling paint to the hulls of my catamaran helps prevent the growth of marine organisms that can damage the boat and reduce its speed. Make sure to do this at least once a year.
Dealing with Wear and Tear
Despite my best efforts to keep my catamaran well-maintained, wear and tear is inevitable. Here's how I deal with common issues that could arise from regular use:
- Repairs : When I notice signs of wear on sails, lines, or rigging components, I make it a priority to repair or replace them promptly. Neglecting these issues can lead to more significant problems and affect the boat's performance.
- Hull maintenance : If I find dents, scratches, or stiff rudders on my catamaran's hulls, I address them immediately. Repairing any damage not only ensures smooth sailing but also prevents further issues from developing.
- Sail care : Over time, my sails can become stretched, torn, or damaged due to exposure to sun, wind, and saltwater. Regularly inspecting them for signs of wear and making any necessary repairs or replacements helps maintain optimal performance.
- Rust and corrosion prevention : Since my catamaran is made of various metal components, I need to protect them from rust and corrosion. I routinely check for signs of corrosion and apply anti-corrosive treatments when needed.
Catamaran Brands and Models
High-Performance Models
In recent years, there has been a growing interest in high-performance catamarans. I have seen a variety of brands and models that have impressed me with their performance capabilities. One notable brand is Fountaine Pajot , which has a long history of producing a range of sailing catamarans and power catamarans. Some of their popular models include the Tanna 47 and the Bali 4.4 .
Another high-performance catamaran I've come across is the Leopard 40 . Known for their speed and exceptional handling in various conditions, the Leopard brand started with sailing catamarans and has since expanded to include power catamarans. Their models range from 40 to 53 feet long, offering both power and luxury for those looking for a thrilling experience on the water.
Cruising Catamarans
When it comes to cruising catamarans, the Lagoon brand is synonymous with luxury and comfort. With a range of sailing catamarans from 40 to 70 feet long, Lagoon offers spacious catamarans for extended bluewater cruising. Their 60- and 70-foot power catamarans are equally impressive, providing ample living space and smooth sailing experiences.
I've also found the Aquila 42 PC to be a remarkable cruising catamaran. With a focus on design and innovation, Aquila has produced catamarans perfect for exploring the open sea with friends and family. Their spacious, stable designs allow for a more enjoyable and serene journey, ensuring you arrive at your destination comfortably.
The Catamaran Lifestyle
Anchoring and Cruising
I find catamarans to be a fantastic choice for cruising and anchoring , which is a critical part of living the catamaran lifestyle . Catamarans have several advantages when it comes to anchoring and cruising, such as:
- Stability : Due to their wide beam and twin hulls, catamarans remain stable during anchoring, which reduces the risk of seasickness.
- Shallow draft : Thanks to their shallow draft , catamarans can anchor close to shore, enabling better access to protected coves and more beautiful beaches.
- Speed : Despite their large size for cruising vessels , catamarans are generally faster than monohulls. This is a result of their slim hulls and reduced water resistance.
When it comes to anchoring, catamarans can make use of their shallow draft to anchor in locations that other boats cannot. This allows for a greater range of cruising spots, which makes the overall experience much more enjoyable and unique.
Living on a Catamaran Full-time
For many catamaran enthusiasts, the dream of living full-time on a catamaran is entirely possible. While not without challenges, there are several factors that make living aboard a catamaran an enjoyable experience:
- Spacious living areas : Catamarans generally have more living area compared to monohulls, providing ample space for the whole crew.
- Privacy : The separate hulls allow for private cabins, ensuring that everyone on board has their space.
- Stability : As mentioned earlier, catamarans are stable vessels, making living on them more comfortable than monohulls.
Choosing Your Catamaran
Comparing Models and Features
When I start to look for the perfect catamaran, the first thing I focus on is comparing various models and features .
I determine the key factors that are essential for my needs, such as size, passenger comfort, and performance. By doing so, I can identify which catamaran models are most suitable for me.
For example, if I plan to sail with a large group, I would look for a catamaran that offers ample space both inside and out.
To help me with my comparisons, I usually create a table or list of the different models and their features:
| Model | Size | Comfort | Performance |
|---|---|---|---|
| A | 40ft | Spacious | High |
| B | 35ft | Average | Average |
| C | 45ft | Luxury | High |
This visual aid makes it easier for me to sort the options and prioritize my considerations, such as price, yacht type, and brand.
New vs. Second-Hand
Another critical aspect of choosing a catamaran is deciding between a new or second-hand boat.
Both options have their pros and cons, and ultimately it depends on my preferences and budget.
If I can afford a new catamaran, I get the advantage of the latest design , features, and technology. Plus, I typically receive better warranty coverage and support from the manufacturer.
However, new catamarans are more expensive and can have long wait times due to high demand.
On the other hand, purchasing a second-hand catamaran can save me a significant amount of money, and I might find a high-quality boat with low mileage or well-maintained by the previous owner.
However, this option carries more risks, as I need to be knowledgeable about potential maintenance issues and conduct a thorough inspection before purchase.
Learning Resources
Books and Manuals
When it comes to learning about catamarans, there are plenty of books and manuals available.
One of the highly recommended books is Multihull Voyaging by Thomas Firth Jones. This book provides a comprehensive understanding of multihulls, including catamarans, and is an essential guide for any beginner sailor.
Another great book to check out is Catamarans: The Complete Guide for Cruising Sailors by Gregor Tarjan.
With a foreword by Charles K. Chiodi, publisher of Multihulls Magazine, this book covers all aspects of cruising catamarans. It includes detailed information on design, construction, and maintenance, as well as tips and tricks for sailing a catamaran.
Here are a few more books that I find valuable:
- The Catamaran Book by Tim Bartlett, an excellent resource for both beginners and experienced sailors
- Catamaran Sailing: From Start to Finish by Phil Berman and Lenny Rudow, a comprehensive guide to both catamaran racing and cruising
Online Content and Photography
In addition to books, you can find plenty of online content and photography about catamarans.
Websites like Sailaway Blog and Boating Guide offer tips, techniques, and how-to articles for sailing catamarans.
Many of these sites also include stunning photography, showcasing these beautiful vessels in action.
For those who prefer Kindle or e-books, many of these resources are available in digital format.
This makes it easier for you to access them anytime, anywhere, allowing you to keep learning and improving your catamaran sailing skills.
To further enhance your knowledge, you can also join online forums and communities dedicated to catamarans.
These platforms provide invaluable advice and first-hand experiences shared by fellow sailors, as well as recommendations for additional learning resources.

Frequently Asked Questions
What factors should be considered when choosing a catamaran for full-time living?
When choosing a catamaran for full-time living, consider its space and layout , as it will become your home.
Look for a design with a comfortable living area , ample storage, and sufficient berths for the number of people living aboard.
Also, consider fuel efficiency , ease of maintenance, and the catamaran's cruising range .
Lastly, the overall cost of ownership , including insurance and mooring fees, should be considered.
How do catamarans perform in rough sea conditions?
In general, catamarans are known for their stability, which is primarily due to their wide beams. This makes them less prone to capsizing when compared to monohulls.
However, their performance in rough sea conditions will depend on the specific model and design of the catamaran. Some may perform better in certain conditions than others, so researching and selecting the right design is essential.
What are the key differences between sailing a catamaran and a monohull?
One of the main differences between catamarans and monohulls is stability.
Catamarans have a wider beam , which makes them more stable and minimizes the risk of capsizing.
They also have shallower drafts, which allow them to access more shallow waters compared to monohulls.
Additionally, catamarans often have larger living spaces, making them more comfortable and suitable for cruising and full-time living.
What are the advantages of catamarans for long-distance cruising?
Catamarans offer several advantages for long-distance cruising.
Their wide, stable design provides a comfortable ride and reduces the risk of seasickness.
They can also attain higher speeds due to their reduced drag and generally sail faster than monohulls on certain points of sail.
The shallow draft allows them to explore more coastal areas and anchor closer to shore. Lastly, their spacious interiors make them ideal for extended cruises and living aboard.
How does one assess the value of a used catamaran on the market?
Assessing the value of a used catamaran requires thorough research and inspection.
Start by comparing the age, model, and condition of the catamaran to similar listings on the market.
Take note of any upgrades or additions made to the boat, as these can affect the price.
It's essential to inspect the boat in person or hire a professional surveyor to ensure there are no hidden issues that could affect its value.
What essential features should be looked for in a catamaran intended for ocean voyages?
For ocean voyages, look for a catamaran with a strong, well-built hull designed to handle rough conditions.
Safety features such as liferafts, adequate flotation, and sturdy deck hardware are crucial.
A reliable engine and well-maintained rigging and sails are also essential.
In terms of living space, opt for a catamaran with a comfortable, spacious interior and ample storage.
Last but not least, good navigation and communication systems are necessary for long-distance ocean voyages.
Related Articles

Mooring Buoy Installation: A Comprehensive Guide for Boaters
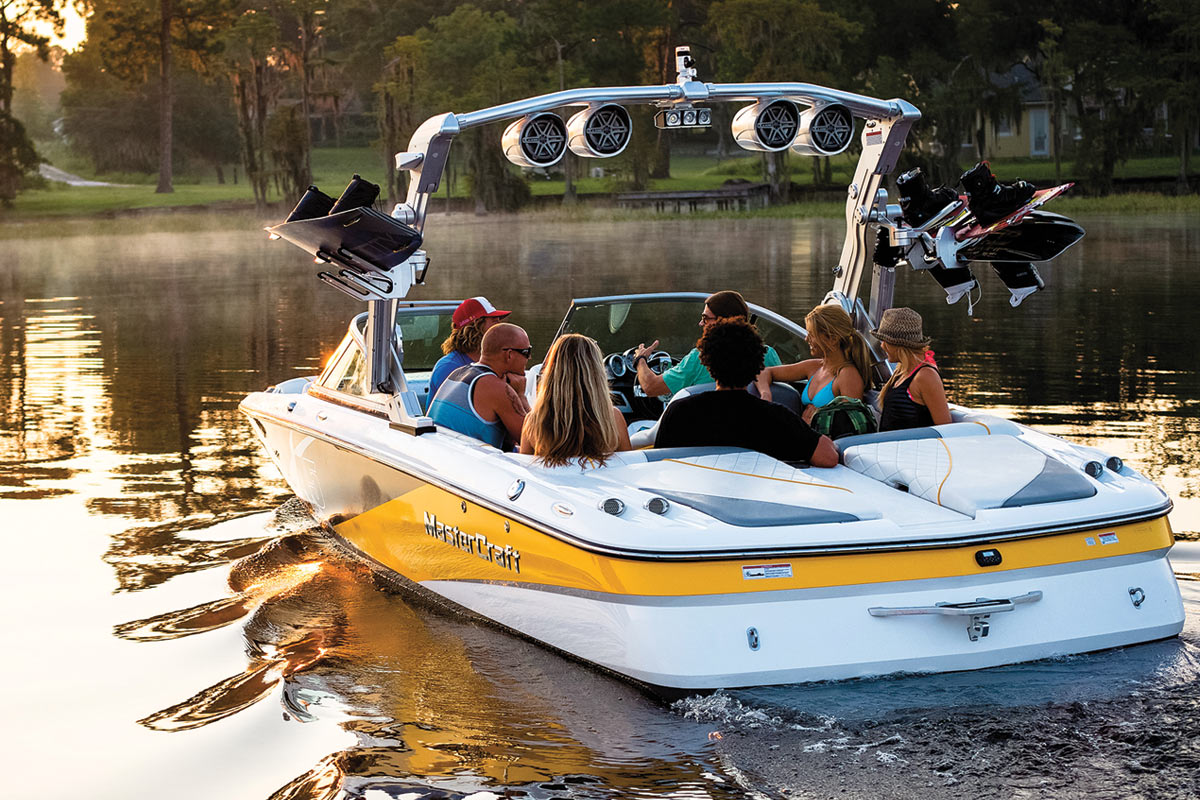

Jl Audio's Newest Offering for Boating Sound Systems: Revolutionizing Marine Audio
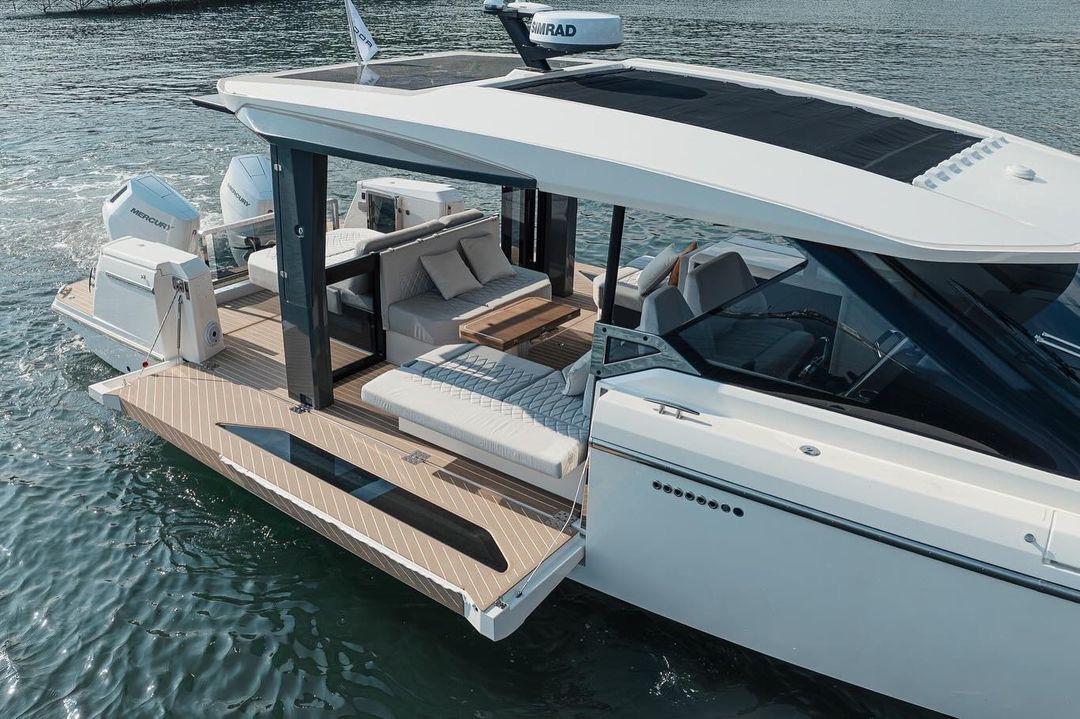

Saxdor 400 GTC- Price Breakdown: Unveiling True Value and Features

Long Tail Turbo Boats Thailand: Exploring High-Speed River Navigation

Hydrafoil for Boats: Comprehensive Guide to This Maritime Innovation

Mercury Avator:Revolutionizing Marine Propulsion
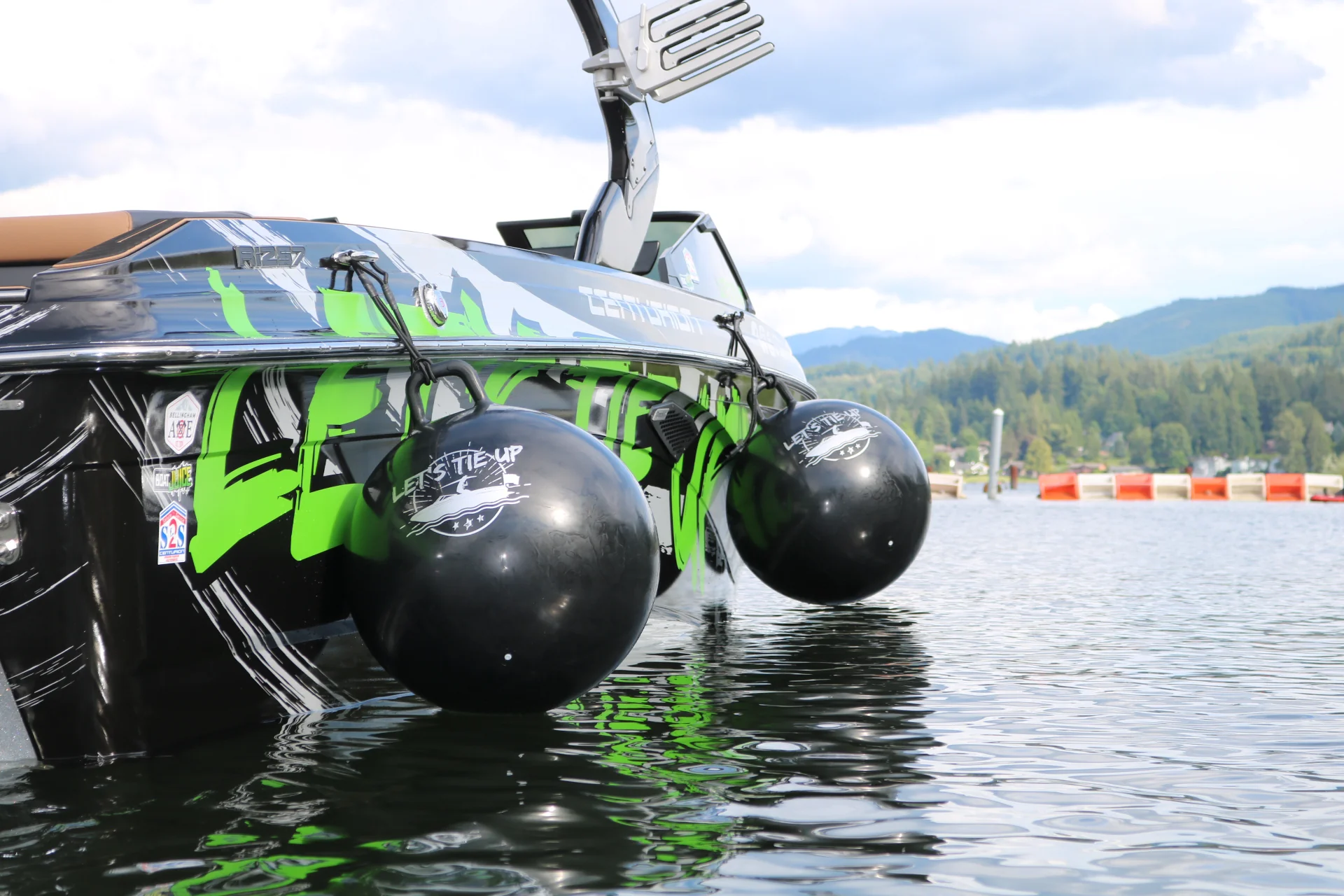

Boat Fenders -2024: Essential Guide for Proper Protection and Maintenance

Hanover Yachts, All Models, Spec, Pricing: The 2024 Ultimate Buying Guide

Your shopping cart is empty!

Sunfish Direct, Topside Non-Skid Padding, Blue, SUN-21032
Upgrade your Sunfish with 5mm SeaDek, a superior choice over marine carpet and traditional molded-in..

Sunfish Direct, Cockpit Floor Non-Skid Padding, Teak, SUN-21056
ISCA, North Race White Sail, SUN-10014
The Sunfish Racing Sail (White) is built with the racer in mind. These sails use a slightly lighter ..

Dynamic Dollies, Sunfish, 13003
Sunfish Dynamic Dolly, Type 3 Dolly style allows bow of boats with a curled gunwale to hang..

- The Sunfish is the most popular boat ever produced!
- Great for both casual sailing and racing. Explore lakes, bays, even oceans.
- Compact, lightweight, easy to transport. Ideal for one or two sailors.
- We offer customization options you won't find anywhere else!
- We have a large selection of boats, sails and parts in stock and ready to ship.

Configure your boat!

AeroSouth, FS Wood Rigged Rudder, Sunfish, FS-RDD-BLD-FOR-RIG
Improve the speed and handling of your Sunfish Sailboat with the fully rigged FS Rudder Blade. Made ..

AeroSouth, Sabre Daggerboard, Sunfish, SBR-DGG-FOR-SNF
Improve the speed and handling of your Sunfish Sailboat with a Sabre Daggerboard. Made of laminated ..

AeroSouth, Sunfish Dinghy Bob, DNG-BOB
Dinghy Bob prevents your small sailboat from turning-turtle and getting its mast or spar stuck in th..

AeroSouth, Sunfish Mainsheet Hanger Clip (Set of 3, Blue), SNF-MNS-HNG-CLP-B
Set of three Sunfish mainsheet hanger clips. Made of durable PETG plastic. Fitted for the 1.5" diam..
Did You Know That We Offer Contract to Closing Services? Click Here to Find Out More.
Need Marine Financing? Apply Here With Our Partner, First Approval Source
- Catamaran Interviews
- Catamaran Reviews
- Buying Advice
- Selling Advice
- Woods Design Advice
- Admiral 38
- Admiral 40
- Admiral 50
- African Cats
- Fastcat 445
- Americat 3014
- Antares 44
- Aquila 44
- Aquila 48 Power Catamaran
- Aventura 37
- Balance 526
- Bali 4.0
- Bali 4.1
- Bali 4.2
- Bali 4.3
- Bali 4.4
- Bali 4.5
- Bali 4.6
- Bali 4.8
- Bali 40 Catspace
- Bali 5.4
- Bali Catsmart
- Beneteau Blue II
- Broadblue 346
- Broadblue 38 Prestige
- Broadblue 385
- Broadblue 435
- Broadblue 46
- Rapier 400
- Rapier 550
- Catalac 10M
- Catalac 11M
- Catalac 12M
- Catalac 8M
- Catalac 900
- Catalac 9M
- Catana 381
- Catana 39
- Catana 401
- Catana 40S
- Catana 411
- Catana 42
- Catana 42 S
- Catana 431
- Catana 44
- Catana 471
- Catana 50
- Catana 521
- Catana 531
- Catana 55
- Catana 581
- Catana 65
- Catathai 44
- Chris White
- Chris White 48 Voyager
- Chris White 55
- Condor 40
- Contour 34
- Corsair F28 R
- De Villiers
- Dean 365
- Dean 400
- Dean 440
- Dean 500
- Dix DH550
- Dolphin 380
- Dolphin 460
- Edel 35
- Endeavour 30
- Endeavour 35 Victory
- Endeavour 36
- Endeavour 44
- Endeavour 44 TrawlerCat
- Endeavour 50 Pilothouse Trawler
- Excess 11
- F-41
- Fastback 43
- Fisher 28
- Fisher 32
- Fortuna 36 Island Spirit
- Fortuna 401 Island Spirit
- Fountaine Pajot
- FP 32 Maldives
- FP 35 Tobago
- FP 36 Mahe
- FP 37 Antigua
- FP 38 Athena
- FP 39 Fidji
- FP 40 Isla
- FP 40 Lavezzi
- FP 40 Lucia
- FP 40 MY
- FP 40 Summerland MY
- FP 41 Lipari
- FP 42 Astrea
- FP 42 Venezia
- FP 43 Belize
- FP 44 Helia
- FP 44 Orana
- FP 45 Elba
- FP 46 Bahia
- FP 46 Casamance
- FP 48 Salina
- FP 50 Saba
- FP 56 Marquises
- FP 57 Sanya
- FP 58 Ipanema
- FP 60 Eleuthera
- FP Saona 47
- Fusion 40
- Gemini 105
- Gemini 3000
- Gemini 3200
- Gemini 3400
- Gemini Freestyle 37
- Gemini Freestyle 399 Power
- Gemini Legacy 35
- Grainger 420 Mystery Cove
- Gunboat 55
- Hirondelle 7M
- HopYacht 30
- Island Packet
- Island Packet Cat 35
- Kennex 420
- Knysna 440
- Knysna 480
- Knysna 500
- Knysna 550
- Lagoon 35
- Lagoon 37 TPI
- Lagoon 380
- Lagoon 39
- Lagoon 40
- Lagoon 400
- Lagoon 410
- Lagoon 42
- Lagoon 42 TPI
- Lagoon 420
- Lagoon 421
- Lagoon 43 PC
- Lagoon 44 Power Cat
- Lagoon 440
- Lagoon 450
- Lagoon 46
- Lagoon 470
- Lagoon 50
- Lagoon 500
- Lagoon 52F
- Lagoon 55
- Lagoon 560
- Lagoon 570
- Lagoon 620
- Lagoon Seventy 8
- Leeuwin 42
- Leopard 38
- Leopard 39
- Leopard 39 PowerCat
- Leopard 40
- Leopard 42
- Leopard 43
- Leopard 44
- Leopard 45
- Leopard 45 Classic
- Leopard 46
- Leopard 46 Lion PowerCat
- Leopard 47
- Leopard 47 PowerCat
- Leopard 48
- Leopard 50
- Leopard 51 PowerCat
- Leopard 53 PowerCat
- Leopard 58
- Lidgard 73 Executive
- Looping 50
- Maine Cat 30
- Maine Cat 38
- Maine Cat 41
- Manta 40
- Manta 42
- Matrix 450 Vision
- Matrix 760 Silhouette
- Maverick 400
- Maverick 420
- Maverick 440
- Moxie 61
- Nautitech 40
- Nautitech 40 Open
- Nautitech 44 Open
- Nautitech 442
- Nautitech 46 Open
- Nautitech 47
- Nautitech 47 Power
- Nautitech 65
- Neel 45
- Oceanlake Marine AB
- Seacart 30
- Outremer 40
- Outremer 45
- Outremer 50 Standard
- Outremer 55
- Outremer 5X
- PDQ 32
- PDQ 36
- PDQ 42 Antares
- Privilege 37
- Privilege 39
- Privilege 42
- Privilege 43
- Privilege 435
- Privilege 45
- Privilege 465
- Privilege 48 Transcat
- Privilege 482
- Privilege 495
- Privilege 510
- Privilege 65
- Privilege Serie 5
- Prout 31 Quest
- Prout 33 Quest
- Prout 34 Event
- Prout 35 Snowgoose
- Prout 37 Snowgoose
- Prout 37 Snowgoose Elite
- Prout 38
- Prout 38 Manta
- Prout 39 Escale
- Prout 45
- Prout 46
- Robertson and Caine
- Royal Cape 45
- Royal Cape 500 Majestic
- Royal Cape 530 Majestic
- Sailcraft 30 Iroquois
- Sailcraft 32 Comanche
- Sailcraft 35 Cherokee
- Sailcraft 41 Apache
- Sailcraft 44 Apache
- Scape 39
- Wildcat 350
- Seawind 1000
- Seawind 1160
- Seawind 1200
- Seawind 1260
- Seawind 1600
- Simpson 48
- Solaris 36 Sunrise
- Solaris 36 Sunstar
- Solaris 42
- St Francis 44
- St Francis 48
- St Francis 50
- Stealth 11.8
- Sunreef 60
- Sunreef 62
- Sunreef 70
- Sunreef 74C
- Sunreef 82 DD
- Sunreef 88 DD
- Switch 51
- Switch 55
- TRT 1200
- Heavenly Twins 26
- Ocean Twins 38
- Vaan R5
- Vision 444
- Voyage 380 Maxim
- Voyage 400 Norseman
- Voyage 430 Norseman
- Voyage 440
- Voyage 450 Cabriolet
- Voyage 47 Mayotte
- Voyage 480
- Voyage 500
- Voyage 580
- Voyage 590
- Kronos 45
- Wharram 38 Tiki
- AMI 320 Renaissance
- Woods 22 Wizard
- Woods 35 Banshee
- Woods 35 Flica
- Woods 36 Scylla
- Woods 36 Vardo
- Woods 38 Transit
- Woods 40 Meander
- Xquisite X5
- Xquisite X5+
Catamaran Construction – Hulls, Laminates, and Composites
- Post author By BJ Porter
- Post date October 15, 2020
- 4 Comments on Catamaran Construction – Hulls, Laminates, and Composites

It’s a given that catamarans are more sensitive to weight and loading than monohulls. Catamaran builders strive to build the lightest boats they can without sacrificing strength and stiffness, and have adapted new building techniques and materials to meet this target. Cutting weight allows more passengers and gear without sacrificing performance.
And the marketing materials reflect it–they load every review and website with polysyllabic technical jargon describing the design and production choices each builder made to deliver the best boat they can.

But when you’re reading a brochure and you come across phrases like “ hand laid bidirectional GRP ” or “ vacuumed bagged e-glass with vinylester resin over a Divinycell core ” do you know what that really means?
All modern production catamarans are made with “FRP” construction (for Fiber Reinforced Polymer). Composites aren’t new–it’s just using materials together to strengthen the whole assembly. Straw was added to bricks centuries ago, and steel reinforced concrete is a staple of construction over the last century. For boats, it’s the use of stranded fibers and cured resins which make FRP different.
The term “FRP” doesn’t get into the technical detail of which fibers and which plastics, and how they’re put together to build your hull. There’s a wide variety of fiber types which can be stranded, woven, chopped or sprayed in a varied of patterns then combined with several types of resins to make hulls with different characteristics.
Some FRP techniques produce lighter, stronger shapes, while others are quicker to build and less expensive to produce. The choice of technique is a function of many factors, from the number of hulls and parts to be built, the type of parts, the budget for the project, and many design specific requirements for weight and strength.
1. FRP Basics
The principle behind all FRP construction is the same – you lay our fibers in the shape you need, then saturate them with resin, removing all the air and voids you can. Resin is left to cure, then the piece is ready to finish and use.

The reality is more complex, since building a boat isn’t like making a flat board or a simple door. You’ve got a complex shape with a designed set of curves to build. “Tooling” is the set of shapes to make the boat parts; molds to cover with fiberglass to get the right shapes.
That’s what makes FRP so effective – you can make almost anything out of it. But to do so requires a lot of choices about what you need for the project at hand.
There isn’t a “best” all around material or technique choice for all jobs, and sometimes a lower cost technique or easier to work with material may be the better solution to the problem.
A. Fiber types
Fiber choices in the last few decades have expanded past the glass fibers used in the first mass produced boats in the 1960s. FRP construction wasn’t new even then, they built the first composite boats using modern fiberglass in the 1940s.
The major fibers used in marine construction fall into three categories – glass, aramids, and carbon. The primary differences are in the strength to weight ratios of the fibers, durability, elasticity, and cost. Some construction may use blends of fiber types to combine performance characteristics.
Glass – the most common material still, because of its low cost and versatility. The most common variety used in GRP (Glass Reinforced Polymer) is “E-glass” which refers to its strand size and mineral content. Other grades have different and sometimes better mechanical properties, but may be more expensive and less appropriate for boat building use. Fiber sizes run 10 to 25 microns for E-glass, though other grades may be smaller.

Brands like Leopard, Lagoon, and most higher production volume builders use E-glass.
Aramids – this includes brand names like Kevlar, Technora and Twaron. They have higher tensile strength than E-glass, and resistant abrasion and punctures. Kevlar is a common choice for bullet proof body armor, and can built a tough, lightweight hull. The materials can be difficult to work with, as it is very tough to cut the cloth. It is often blended with carbon fiber or other materials – Catana is known for using Twaron blends in hull construction.

Carbon – the ultimate in lightweight, strong construction material. Carbon fiber is the most expensive fiber, and is available in a variety of weights, grades and strengths. Fibers are smaller than glass – down to 5 Micron.
The lightest, most expensive hulls are made from carbon, but a catamaran builder may use carbon in places other than the hull to add strength and stiffness. Carbon boards, rudders, and reinforcing structures can enhance performance without driving the price of the boat beyond reach. Carbon is the fiber of choice for many custom builds, racing cats, and Gunboat.
B. Mats, Strands, Roving, Direction, and Weights
Fibers are woven into matting and cloth for construction. Depending on the application, different weights of cloth and cloth patterns and weaves may be more appropriate for the job.
Cloth weight refers to the weight per square yard (or meter) of the cloth. A square yard of nine ounce cloth weighs nine ounces. The heavier the cloth, the stronger it is in a laminate.
Fibers carry loads along their length, so cloth weaves have directionality to their strength. Most builders use several layers of cloth with different orientations to give good universal strength to hulls. Specific FRP applications with strict load-path requirements may have more unidirectional fiber layering – for example, a chainplate manufactured from carbon fiber may use unidirectional fiber.
Cloth – fiberglass cloth is commonly used on outer layers of composites. Cloth may have unidirectional or bidirectional strength. Bidirectional cloths have maximum load strengths in two perpendicular directions. Variations on weaves like a modified twill allow a more flexible cloth for better shaping around complex molds.
Mat – is omnidirectional strands of fiber compressed into a cloth. This is often held together with a resin soluble glue, which makes mat great at conforming to mold shapes without folding and bunching as it collapses when wetted. Because the strands do not align, fiber strength is the same in all directions.

Woven Roving – a heavier cloth made from larger bundles of strands. Woven roving allows for quicker buildup of material and strand weight.
Most FRP layups include multiple layers of different cloth and mat. Finished layers may be finer cloth over courser cloth, over woven roving and mat.
Three primary resins are in common use in marine construction – polyester , vinylester , and epoxy . All resins have materials safety concerns and require care in their use and handling.
Polyester is the least expensive and requires breathing protection because of the VOC emission (Volatile Organic Compounds…nasty, smelly fumes). It doesn’t have good bonding/gluing capability, and should only be used with glass fibers for structural building. Some polyester resins are referred to as “isophthalic” resins.
Vinylester is chemically similar to a hybrid of polyester and epoxy, and performs best with fiberglass. It shouldn’t be used in high strength applications with carbon or aramid fibers. It has some adhesive qualities which polyester lacks, it shrinks less during curing, and has better impact resistance.
The added strength of vinylester coupled with increased water resistance makes it an attractive option for many catamaran builders. It costs less than epoxy, but still has better performance than polyester.
Epoxy is the most expensive, but is three times the strength of the others. It offers the best adhesion and the only resin for building structural elements with carbon and aramid. It resists water intrusion better than the other resins, resists blisters, emits no VOCs, and shrinks less. The major drawback is it is more brittle if it takes an impact.
While epoxy is “the best” in terms of strength and ease of building, there are many applications where other resins are appropriate. Budget is a big driver – a boat made from E-Glass doesn’t need epoxy resin, and considerable cost savings to meet a construction price target may drive the choice.
They can build quality boats from all material combinations, but price and performance will drive materials choices to keep some boats more affordable.
2. Cored Construction
What’s the best way to make fiberglass strong? To a point, you can make it thicker. As it gets thicker, it gets heavier. A hollow shape can take more compressive load than a solid one of the same weight, and the same principle applies to fiberglass construction.
Consider an I-Beam used in building construction. It has the same strength (or more) as a solid rectangular beam of similar mass. The compressive load on the beam is supported by the outside edges of the material, the metal in the middle doesn’t contribute much to the strength. So we can remove metal to get the “I” shape while still keeping those sides rigid, making a lighter girder with less material.
The same principle applies to cored construction with fiberglass. Making a sandwich of two layers of fiberglass with a light core between them allows for the greater strength with weight savings.
There are drawbacks – the biggest risk is damage which breaks the skin, which can let water into the core. Earlier cored construction used materials prone to saturation and rot if they got wet. Some builders opt to do cored construction above the waterline and solid below to minimize some of these risks.
But the advantages in weight savings and increased stiffness offset the drawbacks, and there may be a few other side effects like sound and temperature insulation. Like resins and fibers, core materials offer distinct advantages, disadvantages and price points.
Most builders have adopted a hybrid approach, building solid hulls below the waterline, and cored hulls and decks above. This gives a balance of weight and safety.
A. Balsa Core
Balsa is light and inexpensive. The first cored construction used balsa, but it has the disadvantage of being wood. As a natural material, if it gets wet it can rot and break down. Builders use “end grain” balsa – shorter cross cut sections – to prevent wicking of water if there is an intrusion.

B. Foam Core
Closed cell foam cores give good strength to weight savings while minimizing water intrusion. If you get water in the core, it won’t spread very far. Divinycell is a popular PVC foam core, though there are several choices with different densities and compressive strengths.

Some foam cores are not suitable for heat treatment, but infused or vacuum bagged boats like the Outremer and PDQ do well with it.
C. Honeycomb
Honeycomb cores are often the most expensive, but also give some of the best strength to weight ratios. Honeycombed cells made from resin cured aramid papers are some of the best, but also among the most costly. They offer good stiffness, but can be hard to shape. Aluminum and other resin-infused papers are other core materials builders can choose from.
3. Construction and Resin
When building a hull, there are optimal ratios of fiber to resin saturation for target strength and weight. Too little resin and you may not have enough strength (or worse, voids and gaps), and too much, and you’re just adding weight without adding strength. Resins are also a significant material cost in building the boat, so over application not only increases weight but adds cost.

There are many ways to assemble the cores, fibers and resins to build a finished laminate hull – we’re addressing the most common in boat building. Each approach has strengths and limitations, and an impact on the bottom-line cost to build the boat. Any voids or air pockets in the laminate can be disastrous; these techniques have been developed to increase saturation and reduce the risk of voids.
A. Hand Layup / Open Molding
As the name implies, this is the application of resin by hand to cloth as it’s laid into a mold. Wetting is done with a brush, and the laminate is rolled out to remove any air pockets and voids. This is the simplest way to lay up fiberglass, but also the least precise and consistent and will use the most resin.
Skilled craftsmen have built some of the finest vessels in the world this way. Though it’s more popular with monohulls, which are less sensitive to weight, many catamarans built with hand layups on open molds are still out cruising and performing well.
B. Spraying
Using chopped-strand fiber mixed with resin, a “chopper gun” can spray the mixture into a mold to lay down the composite. A consistent thickness can be difficult, but this is a low cost construction technique which makes a very resin-rich laminate. Using sprayed fibers gives lower strength in all directions compared to meticulously laid down mat and bi-directional cloth. But it is a quick technique popular with mass produced, smaller boats.
It is an excellent technique for parts with complex geometry where weight is not an issue, but you will not see it often in catamaran construction. It’s heavy with resin without any resultant increase in strength.
C. Vacuum Bagging (Wet layup)
When an open molded component has been laid up and wetted with resin, vacuum bagging takes the process a step further. After the wetting is complete, air tight plastic bagging is secured around the wetted area, and the air is pumped out of the bag. The vacuum pulls excess resin out and collapses air pockets.

The goal is to get thorough wetting and produce as strong a laminate as possible without excess resin. Knysa and Leopard are two builders that use vacuum bagging on their hulls to reduce weight.
D. Resin Infusion
For resin infusion the cloth, matting and core is laid in place dry, then sealed in an air-tight bag. A vacuum pump attaches to one side of the bag, and on the other a feed for resin. The vacuum sucks the air out of the dry cloth stack, then pulls the resin through the stack, infusing and wetting it.
Resin infusion, when done right, gives the lightest, strongest laminates with no voids and the minimum resin weight for maximum strength. SCRIMP is a variant of the resin infusion process used by some builders, including TPI which build many early Lagoon cats.
E. Pre-preg
Using pre-preg (for “Pre Impregnated”) cloth for your laminating gets rid of the resin bucket. They manufacture cloth with a partially catalyzed resin pressed into it, then it’s chilled or frozen to stop the curing process. There is no need for seperately mixed resins, and there’s no worry your resin might “go off” and harden before you’re done wetting the cloth. Instead, the cloth is assembled, vacuumed, then heated to kick off the curing process.
There are both advantages and disadvantages to using pre-preg for your laminate work. The big disadvantage is the cost; it is most expensive material to use. You also need to chill and store the cloth until you need it, though some can be at room temperature for a couple of weeks without kicking off. And you need an oven which requires some clever tricks if you’re building a forty or fifty foot boat.
But the strength to weight ratio will always be perfect. High tech honeycomb cores are best suited to pre-preg lamination, and without racing against resin cure times, you can ensure perfect cloth placement and precise layout in the build process.
The primary use for pre-preg in boating is high performance race boats. With catamarans, pre-preg may be used high load parts, like Gunboat does for foils and rudders.
4. Industry Examples
Across the catamaran building industry you’ll find almost all the above techniques and materials used, though some are less common. You aren’t likely to find chopped strand sprayed layups in ocean going cats, and hand layups can lead to heavier hulls than weight sensitive catamaran designers prefer. Most manufacturers have moved to vacuum bagging or resin infusion, with a few of the highest end boats using pre-preg for key components.
Built by Robertson & Caine in South Africa, the hull material is vacuum bagged, end-grain balsa-cored E-glass with polyester.
Hand laid, bagged vinylester over an Airex foam core in the hulls.
Earlier Prout catamarans like the Snowgoose 34 featured hand laid solid FRP hulls and decks. Over time they switched to foam or balsa cores for decks and above the waterline.
Older PDQ boats were made from vacuum bagged vinylester – solid below the waterline and cored with CoreCell foam above the waterline and in decks. Newer PDQ models switched to epoxy resin.
All glass is vacuum bagged. Below the waterline is solid E-glass and vinylester. The rest is unidirectional, bidirectional, and triaxial cloths over a Nida-Core polypropylene honeycomb core with isophthalic and vinylester resins.
The Gemini cats are built with a solid hand layup of woven roving and fiberglass mat and polyester resin. Decks are cored with end grain balsa. The Gemini 3200 introduced vinylester resin into the layup to prevent blistering.
Older Lagoons were SCRIMP infused vinylester with and end grain balsa core above the waterline and in the decks.
Newer Lagoon catamarans use polyester and vinylester resins, also infused with balsa cores above the waterline and solid below.
With a carbon fiber inner skin, Catana also uses Twaron aramid fibers in the sandwiched hull over a foam core.
Fontaine Pajot
Primary hull construction is resin-infused vinylester with a balsa cored hull and deck.
Beneath the waterline, Outremer uses a single layer, solid vinylester laminate for safety. The hulls and deck are vinylester with a Divinycell foam core. They stiffen certain components with carbon for rigidity and durability.
Gunboat hulls are epoxy infused carbon fiber with a Nomex honeycomb core. They build dagger boards and other high load components with pre-preg carbon.
- Tags Buying Advice

By BJ Porter
Owner of Hallberg Rassy 53; world explorer.
4 replies on “Catamaran Construction – Hulls, Laminates, and Composites”
Excelent. Thank you for this I learned allot. Johan
Very straight forward information. Thankyou for doing this.
Damn…What an Amazingly Informative Article. *Cheers*
Outremer publish on their website that they use polyester. Not vinyl ester as you have stated.
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
- European Union
- South Africa

The Leopard Identity
Leopard Catamarans pushes the boundaries of catamaran design.
Evolving from 50 years of customer feedback, Leopard Catamarans has pooled their expertise with builders Robertson and Caine to design today's Leopard range: spacious, robust, performance-driven blue water cruising catamarans. As the worldwide distributor, we’re proud to say that over 2,500 Leopard cats have now been delivered all over the globe.

Pricing & Options
Latest news.

Sailing a New Leopard Home: Leopard 50 Atlantic Crossing


- Forum Listing
- Marketplace
- Advanced Search
- All Topics Sailing
- Skills & Seamanship
- Learning to Sail
- SailNet is a forum community dedicated to Sailing enthusiasts. Come join the discussion about sailing, modifications, classifieds, troubleshooting, repairs, reviews, maintenance, and more!
English terms for parts of a catamaran
- Add to quote
In the frame of my program "Sailing4Youth, Cross Cultural Team Building By Sailing" there will be a workshop made to introduce among other things, the most important parts of a boat/catamaran. I searched the internet but always ended up with information about buying a boat or trailer a boat etc. Should someone have a link or even a simple document with what I am needing, I would be very grateful.
A simple google search will bring up all sorts of sample diagrams. Maybe I’m missing a subtle point.
The English names for catamaran parts are a mix of typical English names for boat parts, with a few Polynesian words such as Aka and Ama thrown in for the parts that resemble traditional catamarans. But there are too many parts to simply start naming parts. Jeff
Google 'catamaran parts'.
Its funny but when I Google 'catamaran parts' almost nothing useful comes up. Jeff
I believe there are plenty of books with glossaries of nautical terms. I have found them online too. I highly recommend Royce's Sailing Illustrated as a basic primer. It covers just about everything one needs to know to safely handle a small craft in a fun, yet comprehensive format. From anchoring to boat nomenclature and even splicing, it's got most of what you'll need for getting started, yet is still a good reference book for the most experienced of us. No preachy tome here. If I were teaching a class, it would be the textbook.
Space, comfort, and levelness? I think this must just be a poorly phrased question, and the real interest is in what are the differentiating parts, or the important structural components, or something similar. First, the OP appears to own a catamaran, so not knowing the names of the basic parts seems unlikely. Second, there really isn't much difference in important parts names from those of monohulls. Sails, rigging, rudders, engines, etc are all the same. Nobody uses terms like aka and ama for catamarans in real life (one of those isn't even applicable to catamarans). Perhaps daggerboards might be more unique if discussing larger boats only. Crossbeam and trampoline are about the only two truly unique parts to a catamaran. Mark
I think that the question posed by the original poster relates to the fact that they are in Croatia, and that the poster appears to be associated with a multicultural teaching group. My assumption is that the original post is looking for the correct English terminology for the unique parts of a Catamaran. I stand corrected on the Polynesian terminology relative to Catamarans. The only multihulls that I have owned and designed have been trimarans and so have mistaken assumed that the terms carried over to catamarans in part because the owner of the larger cruising catamaran that I used to sail on with any frequency used those terms for his boat's parts. Jeff
Jeff_H said: ... I stand corrected on the Polynesian terminology relative to Catamarans. The only multihulls that I have owned and designed have been trimarans and so have mistaken assumed that the terms carried over to catamarans in part because the owner of the larger cruising catamaran that I used to sail on with any frequency used those terms for his boat's parts. Jeff Click to expand...
Then there’s the difference between English and American terms for the same thing e.g. kicking strap/vang.
outbound said: Then there's the difference between English and American terms for the same thing e.g. kicking strap/vang. Click to expand...
Mark- Some years ago I was sailing with an Argentine and we had some confusion about terms on the boat. So I cleverly thought, well, I'll just learn the Spanish words for things, and tell it to him in Spanish next time. Port and starboard being bababoard and estaboard, IIRC. And the next week, when I hit him with "Bababoard, bababoard!" he looked at me, totally baffled and said "What?" "No, I learned to sail here in the US, I have no idea what the Spanish words for that are." The OP is in Japan and the boat is in Croatia...he might just be fluent in English. But I don't think Berlitz, or most colleges, teach nautical terms.
P435 said: .......the most important parts of a boat/catamaran........ Click to expand...
This is my first post here so hello everyone. P435 Let me help you a bit. Most of the boat parts are the same as monos except for the forward bits. The forward beam that holds the headsail is referred to as a compression beam. Usually these are aluminum but sometimes they are molded fiberglass. On small cats they are usually wire. The angled metal parts on top of this beam which can be solid metal or wire are called a seagull striker if they angle up and a dolphin striker if the angle down. I think the brits call it a pelican striker when it's angled up. Do you have a Privilege 435? On those boats is a molded center beam projecting forward that's called a nacelle. If it is smaller then it is sometimes called a longeron but most people call it a center beam. There is some descriptions here. Just click on the numbers. I can't post a link yet because I'm new but see if you can Google this. slideshare.net/JackDale/asa-114-catamaran
Thanks for all your thoughts! Searching the web was not that easy only very specific words led to the right URLs. In the meantime I found some information with hints from sailing friends. Here they are: https://www.google.com.au/imgres?im...LzbAhVLY1AKHW_hBiUQMwg4KAAwAA&iact=mrc&uact=8 https://www.google.com.au/imgres?im...j_8rTGtLzbAhVLY1AKHW_hBiUQMwhcKBowGg..i&w=921 https://www.google.com.au/imgres?im...j_8rTGtLzbAhVLY1AKHW_hBiUQMwhcKBowGg..i&w=921 https://www.google.com.au/imgres?im...j_8rTGtLzbAhVLY1AKHW_hBiUQMwhcKBowGg..i&w=921
Well, this is probably getting pedantic, but the above isn't really applicable to today's catamarans, and seems only to be a polynesian thing at that. I mean, it says the ama is the port hull of a catamaran, while the starboard hull is called an akea. Have you ever met anyone referring to their port and starboard rudders by different names (and not even using the term "rudder")? Do today's catamarans even have bow endpieces, let alone calling them a specific name? I'll bet nobody ever in history has referred to their solar panels as "papa uilas". I bet the ancient Polynesians didn't even use that term for their solar panels... Besides, catamarans are an Indian invention, not Polynesian. They became popular in Polynesia later, so the above isn't even correct, and perhaps we should go even further back in our nomenclature? For me, I'll stick with port and starboard hulls, bows, sterns, and rudders, as well as other common names. Besides, the OP asked for the English terms. And BTW, I did do basic research before answering, and I don't see anything I wrote as incorrect. Mark
- ?
- 175.5K members
Top Contributors this Month
rc sailboat compass

- BOAT OF THE YEAR
- Newsletters
- Sailboat Reviews
- Boating Safety
- Sails and Rigging
- Maintenance
- Sailing Totem
- Sailor & Galley
- Living Aboard
- Destinations
- Gear & Electronics
- Charter Resources
X-Yacht’s X40: Best Performance Cruiser
- By Herb McCormick
- Updated: December 8, 2020
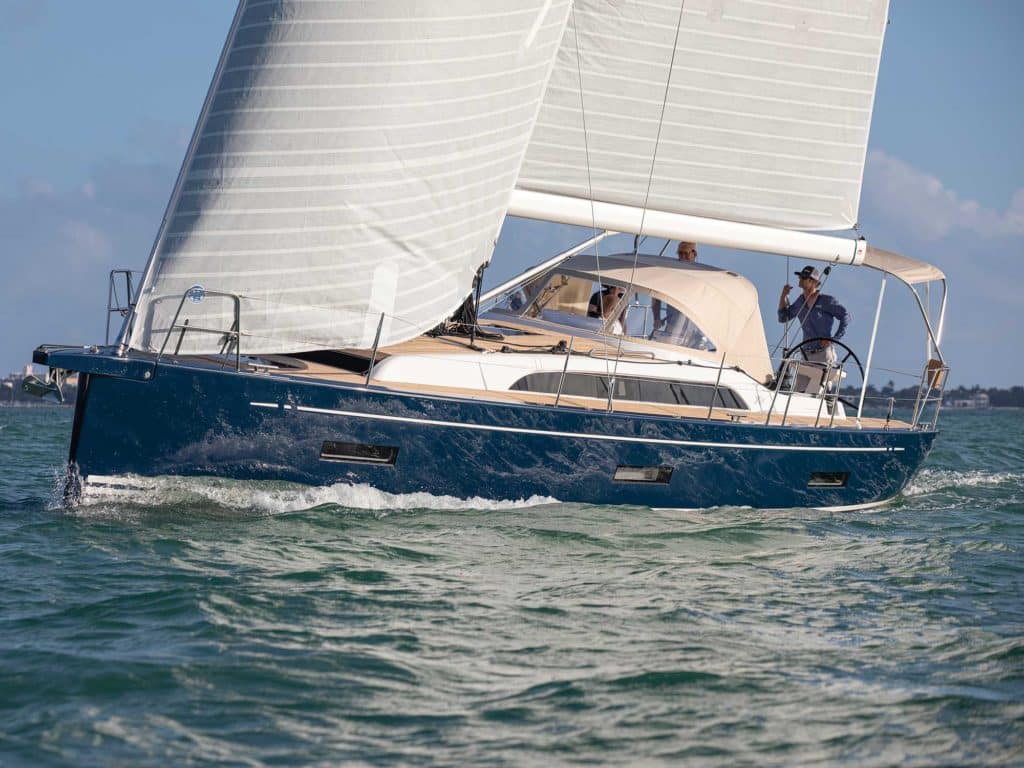

With this year’s aforementioned diminished nominee list, it was impossible to break down the fleet across the board to fit each boat into a neat, tidy category. One of the two notable exceptions was the Performance Cruiser class, with three strong entries: the Arcona 435, the Beneteau Oceanis 40.1 and the X-Yachts X4<sup>0</sup>. We’ll get to the Arcona and the Beneteau in the pages to come, but for 2021, the clear winner in this class of sweet-sailing racer/cruisers was the X4<sup>0</sup>. It clearly met the criteria for being the top performer in its stated design brief: a boat that will compete strongly—and well—on the racecourse, yet be comfortable and fun for coastal cruising.
With the X-Yachts, we’ve seen this figurative movie before. The Danish brand has taken home BOTY hardware four times in the past five years.
2021 Boat of the Year Winners at a Glance
- Excess 11: Boat of the Year
- X-Yacht’s X4 0 : Best Performance Cruiser
- Island Packet 439: Best Full-Size Cruiser
- HH 50: Best Luxury Cruiser
- Hylas 60: Best Luxury Cruiser
- Beneteau Oceanis Yacht 54: Honorable Mention
- Corsair 880: Best Sport Boat
- 5 New Sailboats That Were Nominees
Murphy, our resident boatbuilding whisperer—he’s worked closely with the American Boat and Yacht Council writing textbooks and creating curricula—was emphatic when it came to the quality of the X4<sup>0</sup>′s construction: “X-Yachts has built 5,000 boats since they went into business in 1979. So they have a good, long track record. They’re probably best known in performance circles, so when we board an X-Yacht, we expect the boat is going to sail pretty well, which this one certainly did. As far the build quality, this is one of the top two yachts in this year’s fleet (the other is the HH 50 cat, which we’ll get to). It’s an epoxy hull, which is the best resin you can use to build boats, in terms of both strength and resilience. It also has a galvanized-steel grid. In years past, there have been questions about the long-term integrity of that grid, but they’re unfounded. My feeling is that the massive steel structure is not encapsulated; it goes on top of the fiberglass structure, and it’s not an issue. I think this boat is straight-up wholesome. It’s a really, really lovely sailboat.”
Pillsbury found the efficient deck layout to his liking: “This boat was one of few we saw this year that actually had enough winches on it to sail it like a proper boat. We climbed on several others where a clutch was used to service several lines from a single winch. Sometimes it was hard to remember which clutch to open and which clutch to close, which took away a lot of the joy of sailing. Here you can just load up a winch and know that your line is going to be there, that you have quick access to it. I really liked that. It was also one of only a couple of boats that had a full-on traveler, which to my mind, when you carry a lot of sail, as this boat does, if you can’t really control and trim that mainsail, it’s a problem. And here’s another trend we saw for 2021: a below-deck furler for the headsail, which makes for a nice, clean deck layout.”
As far as the build quality, this x-yacht is one of the top two for this year.
Our X4<sup>0</sup> sea trials were also heavily influenced by the father/son owners who will be using the boat very differently, but who also made it quite clear that it will address and serve both of their sailing ambitions very well. Son Ryan is an avid inshore and offshore racer who has a Sydney-Hobart Race under his belt, who plans to campaign it hard; he’ll put the racing element into play. Doublehanded racing, especially in these socially distanced times, is becoming ever more popular, and the X4<sup>0</sup> should be ideal for those venues.
Ryan is a sailmaker, so there will of course be a full quiver of racing sails aboard. But the boat is also set up for his dad, Mike, and his wife to sail efficiently, with a self-tacking jib for cruising forays. (It also has a bow thruster and the electric furler for the jib, which added some weight forward and isn’t the ideal setup for racing; we’d guess Ryan and Mike had some interesting conversations about those features.)
But at the end of the day, the family wound up with a yacht that will be ideal for everyone in the household: a racer/cruiser that is every bit both. So, fair winds, Ryan and Mike. You’ve got the one boat perfect for the two of you.
- More: 2021 Boat of the Year , Boat of the Year , BOTY 2021 , performance cruiser , racer / cruiser , x yachts
- More Sailboats

New Sailboat Brand: Mishi Yachts

For Sale: 2005 Tayana 48

For Sale: 2015 Catalina 355

For Sale: 1998 Hinckley 51

Hurricane Beryl Relief Efforts: How You Can Help

Gary Jobson To Talk U.S. Prospects in Upcoming World Sailing Competitions

Make Downwind Sailing Fun Again. Turn Off That Motor and Unfurl Your Kite!
- Digital Edition
- Customer Service
- Privacy Policy
- Email Newsletters
- Cruising World
- Sailing World
- Salt Water Sportsman
- Sport Fishing
- Wakeboarding
Yachting Monthly
- Digital edition

X40 test: A reminder of how good a sub-40ft yacht can feel
- Graham Snook
- December 17, 2019
Light winds don’t usually make for fast or enjoyable boat tests, but most boats tested aren’t like X-Yachts’ new X40. Graham Snook heads to Denmark to put her through her paces

Vacuum-infused epoxy makes the hull lighter and stiffer than an equivalent polyester hull. Credit: Graham Snook
The new yacht in X-Yacht’s XRange is not a 40-footer. Let’s get that out of the way now – the X40 is 37ft 8in.
She’s great fun, and has the nimble feel and speed that most 40-footers can only dream of, but don’t think she has the accommodation of a 40ft yacht; the 40 in her name is her length overall, including her bowsprit.
Her interior is stylish, practical and well put together, she’s easily handled by a couple and can take you cruising in speed and style.
With that clarified, I can start telling you all how good she is and, oh my, she is good. It’s rare I’ll find myself having a great sail in less than 10 knots of breeze.

A soft chine in the aft sections helps makes the hull more powerful. Credit: Graham Snook
To be fair it’s also rare to sail a 40ft, sorry, 38ft, yacht with Technora sails and a carbon fibre mast and boom and a 2.40m draught.
But sailing south from Aarøsund in Denmark in 9 knots of breeze, we were having a blast and she was romping along going to windward at over 7 knots.
X-Yachts has long been a brand of proper sailing boats, thoroughbreds born to be sailed, not just comfortable yachts with masts and sails.
Its boats are well-mannered and sail fast; with its heritage in racing, even X-Yachts’ cruising range has a good turn of speed.
X-Yachts currently build three ranges of yachts; Xc for cruising, Xp for performance, and the latest XRange.
The boats in each may be similar lengths, but each are different from the keel up. The new X40 is not just the comfortable interior of the Xc38 crammed into the sleek hull of the Xp38.
The hull design characteristics on all three ranges are different: the Xc hulls have more volume to support the extra clobber required by the extended cruising sailor; the Xp are narrower with much slimmer bow sections; and the X40’s hull has more rocker than the Xp while its broader forward sections give more space for the owner’s cabin and wider aft sections with a soft, subtle chine, giving more volume aft.

The self tacking jib is standard. The genoa and fittings are optional. Credit: Graham Snook
While X’s Xp yachts have gained a more cruiser-friendly interior over time, they retain weight-saving features, less joinery (although, don’t for a minute think they are stripped out racers) and a carbon-reinforced subframe.
The XRange, in contrast, carries over some of the Xp’s sporty handling while keeping features reassuring to cruising sailors: lots of useful deck stowage, good headroom and a galvanised steel sub-frame beneath the sole which spreads the loads from the keel and mast.
With the average size of yachts gradually increasing to over 40ft, it is easy to become accustomed to their way of sailing.
There’s nothing wrong with the feel but, like the freedom of an empty winding road after being stuck behind a tractor, sailing the X40 is a reminder of how good a sub-40ft yacht can feel.
She strikes a lovely balance of nimbleness and control without being twitchy. Leave the wheel and she will veer off course, but the helm is so enjoyable you won’t want to leave it.
The test boat was fitted with a B&G hydraulic autopilot ram. In the past, when manufacturers have blamed the autopilot for heaviness to the helm,
I’ve asked for it to be removed – and the autopilot wasn’t always the cause.
On this occasion, without the ram fitted the wheel had the unrestricted preciseness I have come to expect from Jeffa cable steering, and it felt instantly lighter.
THE TEST VERDICT
There is no doubt that X40 is one of my favourite production boats; everything about her just seems right.
Of course, for a boat of this quality you pay handsomely for it and this boat did have more than £100,000 of extras added.

The Nordic oak used for the interior woodwork exudes quality and warmth. Credit: Graham Snook
No doubt these improved her performance, and it would have been nice to see how good she was without the carbon rig and with her standard 2.1m draught keel.
As she was, though, not many boats of her length can rival her, given the comfort and build quality that’s down below and, of course, the speed you’ll be sailing.
READ THE FULL TEST IN THE OCTOBER 2019 ISSUE. GET IT HERE
This two-cabin layout worked well and provided plenty of stowage.
A three-cabin layout will be available, but you’ll lose the chart table and much of the spacious heads compartment; given it’s the only heads on board, it is a compromise you’d want to weigh up carefully.
The three-cabin layout works better on the larger X43 where less compromise is needed.
Boats to rival her are few and far between, though she sits between the more expensive Faurby 396 and the Arcona 380.
While all three of these boats sail well it would be unfair to just look at the bottom line as each yacht has her own merits.
Which would I choose? That is a very tough decision and one I am loath to commit to with so few words to pontificate with.
WOULD SHE SUIT YOU AND YOUR CREW?
At 38ft, the X40 squeezes in under the 12m mark, meaning that sails, loads, berthing and costs are all kept within bounds.
The size of the yacht and her sails feel less intimidating than those on a yacht above 40ft.
If you’ve enjoyed racing in the past and still feel the need for speed, but now want a little more comfort – and you have the funds available – this boat is a good choice.

The cockpit is long with supportive coamings. Genoa winches are optional. Credit: Graham Snook
She’s a high-spec cruiser that is hugely rewarding and fun to helm, with a very comfortable, stylish interior.
It’s very rare for me to give gushing praise of a yacht.
Boats as good as this don’t come along that often, but when they do, I feel like I have the best job in the world.
X-40 Standard
Sailboat specifications.
- Last update: 3rd April 2020
X-40's main features
X-40's main dimensions, x-40's rig and sails, x-40's performances, x-40's auxiliary engine, x-40's accommodations and layout, x-40's saloon, x-40's fore cabin, x-40's aft cabin.

Similar sailboats that may interest you:

X40 Express
“we followed fundamental principles—impeccable use of scale and proportion, attention to detail in both styling and performance, and careful execution of the build.”.
The X40 Express is a modern, robust, and luxurious interpretation of the classic express design. One glance at the raked, wrap-around windscreen and flush deck forward make it clear that Reliant Yachts partners Dave MacFarlane and Jim Ewing have produced something different in this custom 40-foot, 40-knot speedster.
The X40’s profile makes a statement with its plumb bow and straight, clean lines, accentuated by the cambered teak deck. Framing that deck is an extraordinary, uninterrupted, low-profile cap rail painted the same metallic silver as the hull. Yet the X40 makes another statement entirely when the carbon-fiber hardtop is removed, turning a coupe into a convertible.
Reliant refined every detail to maximize space for the living quarters, which for this client meant working within the dimensions of the superyacht tender garage in which the X40 would live. The pay-off is a warm inviting stateroom, head, shower and galley. One of the key decisions made along the way was to choose Konrad 660b Stern Drives, which are powered by a pair of Cummins QSB 6.7 480s. The stern drives lift up before the boat slides through the garage door of its mothership.
Initial sea trials near Istanbul in light winds and calm seas proved that the X40 could run at 40 knots, topping out at 40.7 knots at 3300 rpm. The boat handled well and cruised comfortably between 27 and 33 knots.
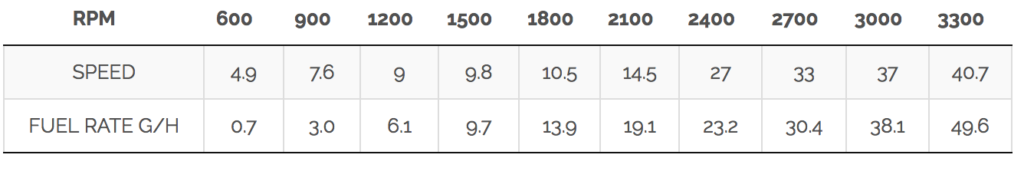
A deep cockpit provides safe, secure, comfortable seating in high-backed, leather-upholstered bench seats for eight or more. Forward-facing seats for helmsman and co-pilot provide clear sight lines and have flip-up bolsters to make leaning against the seats as comfortable as sitting in them.
At the helm, a pair of bright Raymarine Glass Bridge monitors (15.4 inches each) are set against a high-tech, flat-black, carbon-fiber dashboard. In turn, the carbon contrasts with the varnished wood both in the steering wheel and a sturdy handhold at the turn to the companionway. A full suite of Raymarine electronics include radar, autopilot, GPS, AIS, VHF, depth and speed instruments.
Hatches, cabinetry and hardware throughout the boat are flush-mounted so there’s little to trip on or bang into. Underlying Reliant’s emphasis on a clean, almost spare aesthetic, there’s much more to the X40 than first meets the eye.
In the master stateroom, 12 drawers and cabinets provide ample storage space for weekend cruises. In the helm area, a Yacht Controller joystick sits just aft of the throttles, and the controls for a Seakeeper 3 can be found close by, together promising exceptional maneuverability and stability. There’s an Onan generator, SidePower bow thruster, Webasto air-conditioning, and a state-of-the-art entertainment system.
In reviewing the overall project, designer Jim Ewing says, “We followed fundamental principles—impeccable use of scale and proportion, attention to detail in both styling and performance, and careful execution of the build.”
Reliant’s achievement is a thoroughly modern express, adapted to suit its owner’s specific requirements.
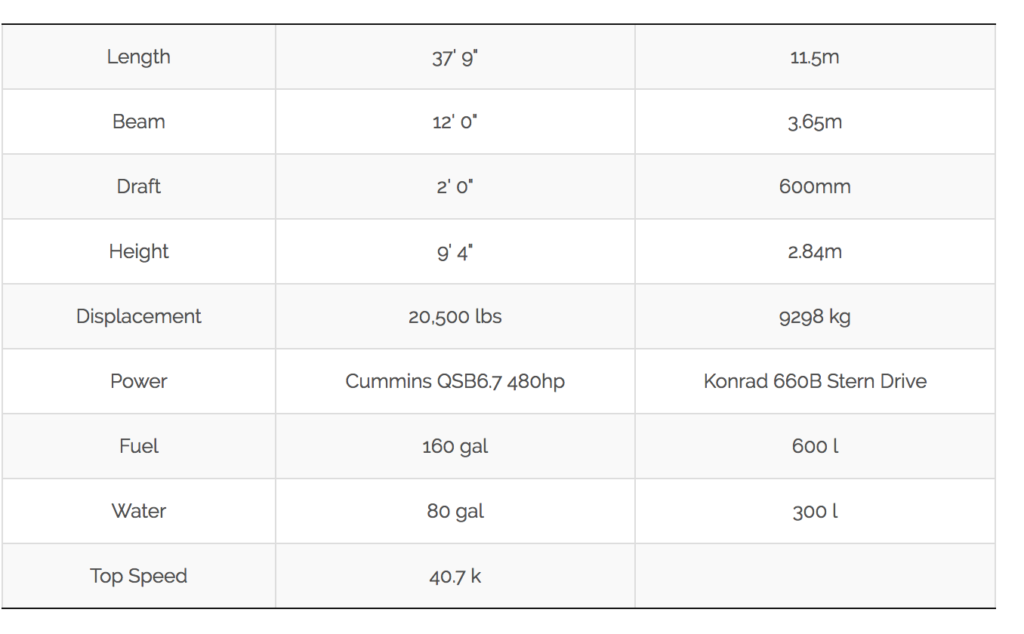
Black Crowes cancel Minnesota Yacht Club appearance set for Friday
M INNEAPOLIS — The Black Crowes have canceled their appearance set for Friday at the inaugural Minnesota Yacht Club festival at Harriet Island in St. Paul. The reason is "illness in the band," according to the fest's post on X on Thursday evening.
The veteran Atlanta rockers known for the 1990s hits "Hard to Handle" and "She Talks to Angels" did not post anything on its social media about the cancellation.
The Black Crowes had been scheduled to perform from 8 to 9 p.m. The Head and the Heart will now shift into that slot, and the set times have been adjusted.
The new schedule for Friday is:
Gully Boys 1 to 2 p.m.
Harbor and Home 2 to 2:40 p.m.
Morgan Wade 2:40 to 3:40 p.m.
Michigander 3:40 to 4:40 p.m.
Joan Jett & the Blackhearts 4:40 to 5:40 p.m.
Durry 5:40 to 6:40 p.m.
Gwen Stefani 6:45 to 8 p.m.
The Head and the Heart 8 to 9 p.m.
Alanis Morissette 9 to 10:30 p.m.
©2024 StarTribune. Visit startribune.com. Distributed by Tribune Content Agency, LLC.

Yacht Summary
- Manufacturer: X-Yachts
- Model: X-40
- Build Number: 63
- Build Year: 2006
- Lying: Netherlands
- Price: Sold
- Contact: Nanno Schuttrups

Fabulous dark blue X-40 from 2006 mostly sailed in sweet water. First and only owner has maintained his X-40 with an inspiring level of detail (partly thanks to having indoor storage available for winter). Equipped like no other 3-cabin classic version, such as carbon Selden mast. This X-40 is ready for the next owner.

Standard Specification
| Designer | Niels Jeppesen | |
|---|---|---|
| Hull Length | 12.19 m | 40'0" |
| Waterline Length | 10.17 m | 33'4" |
| Beam (max) | 3.80 m | 12'6" |
| Draft | 2.10 m | 6'11" |
| Ballast - Std | 3,200 kg | 7,055 lbs |
| Displacement - Light | 7,450 kg | 16,424 lbs |
| Engine Power | 30 kW | 41 hp |
Standard X-40 brochure
Exterior Details
- Akzonobel's AWL grip blue brushed (flag blue 5011) in very good condition
- Epoxy treatment from yard, in 2018 new epoxy treatment and International Trilux antifouling
- Antifouling white International Trilux yearly maintained during indoor winter storage
- Teak in cockpit
- Teak on side decks
- Custom designed teak cockpit table
- Cockpit shower
- Upgraded nice aluminium white painted wheel with leather
Sail Handling
- All upgraded Black Harken 40st, 46st halyard winches
- Spinaker deck package with blocks and 4 sheets
- Spinaker barberhauler and cleats
- Carbon spinaker pole
- New cruising set UK-sails carbon set tape drive membrame with 1 tafetta grey layer 2017 (Sailed 500 Nm)
- New cruising UK-Mainsail in carbon membrame tapedrive, one side grey tafetta layer
- 106% furling jib in carbon membrame tapedrive, one side grey tafetta layer
- Second set of sails (UK Sails Titanium racing 2008 only used for racing untill 2012):
- Mainsail UK Sails titanium, one side tafetta layer
- 106% furling jib UK Sails titanium, one side tafetta layer
- Additional jibs:
- 106% jib UK sails Tape drive 2009
- 80% UK sails flex furling jib for 20 knts+ use , 2008, used 2 times
- Furthermore:
- 2 * spinnaker
- Cover for mainsail 2016 (extra 2006 original mainsail cover North Sails)
- Cover for furling jib 2016
- Cover "custom made" for white painted aluminium steering wheel
Mast & Rigging
- White Carbon Selden 3-spreader mast (2010)
- White Carbon mast and carbon boom (2010)
- Upgraded Reckmann furling system for genua
- Upgraded Ronstan rail with ball bearing cars for mainsail
- Dutchman system for easy flaking of mainsail
- Lopolight 3-colour LED light in top of mast
- New halyards for main and jib 2014, new sheets 2017
- New mainsail sheet 2019
Hatches / Portlights / Ventilation / Sprayhood
- Custom blue sprayhood with EXTRA extension for total cockpit 2015
Guard rail / Anchor / Stainless Steel Fittings
- Additional midsheep mooring cleats
- Fortress anchor with chain and stainless steel removable custom feeder
Accommodation
- Hand selected teak veneer used throughout the boat in perfect condition
- 3- cabin/ 1 heads lay-out, with X-yachts custom made extended bed in forward cabin
- Eberspächer heating system maintained bij dealer in 2014
- Toilet replaced in 2018
- Sony Radio/CD player
- Refrigerator with ASU technology
- Interior LED lights installed in 2018
- Upgraded new mattrass in forward cabin (2018)
- Yanmar 40 Hp
- Upgraded alternator from yard
- New saildrive seal and bearings in 2014
- New engine mounts in 2014
- New Yanmar engine display 2019 (old one destroyed by UV light)
- Shore power connection with battery charger
- Mastervolt 250W inverter
- Additional 230V socket in galley
- Mastervolt BTI battery monitor
Electronics
- 2017 Axiom 7" plotter in cockpit, mounted on custom removable console
- Mounted in console over sliding hatch: ST60 Speed, ST60 Depth, ST60 Wind, ST70 Multi display
- Mounted in cockpit on starboard side: Raymarine autopilot ST6001+ & Raymarine VHF speaker
- Mounted at nav station: Ray240 VHF, E80 plotter, handheld remote for autopilot (smartcontroller)
- Not installed but operational on board: Raymarine Pathfinder Radar dome

Join our Mailing List
Join our monthly email mailing list to get all the latest information and news from X-Yachts directly in your inbox.
Pocket Luxury Yacht. The X4⁰ is the smallest model in the Pure X range; blending quality, performance and styling with cruising capability. Hot out of the X-Yachts Design Office came the X4⁰, a forty-foot performance cruising yacht that is just as capable for some serious mileage, as it is blasting around the cans at the weekends. The new ...
A racing sailor son and cruiser father find the perfect dual-purpose family sailboat in the X-Yachts X4 0, named Best Performance Cruiser. By Herb McCormick. Updated: December 8, 2020. Best Performance Cruiser Winner 2021 X-Yachts X40 Billy Black. With this year's aforementioned diminished nominee list, it was impossible to break down the ...
Find X-yachts X 40 boats for sale in your area & across the world on YachtWorld. Offering the best selection of x-yachts to choose from.
The new yacht in X-Yacht's XRange is not a 40-footer. Let's get that out of the way now - the X40 is 37ft 8in. She's great fun, and has the nimble feel and speed that most 40-footers can only dream of, but don't think she has the accommodation of a 40ft yacht; the 40 in her name is her length overall, including her bowsprit.
X-40 Yacht Summary. Manufacturer: X-Yachts; Model: X-40; Build Number: 56; Build Year: 2006; Lying: LORIENT, France; Price: €170,000 (VAT Paid) Dealer: X-Yachts France; Contact: Jean-Luc Chalant; Phone: +33 (0) 494 45 37 33; Email: [email protected] ; X-40 Classic Carbon rig 2017. 3 cabins with Classic layout, teak wood inside , comfort pack ...
2023 X-Yachts X-40. Hot out of the X-Yachts Design Office came the X4⁰, a forty-foot performance cruising yacht that is just as capable for some serious mileage, as it is blasting around the cans at the weekends. The new baby Luxury X-Yacht joins the hugely successful and critically acclaimed Pure X range.
The X-Yachts X4⁰ is produced by the brand X-Yachts since 2019. X-Yachts X4⁰ is a 12.09 meters sport cruiser with 2 guest cabins and a draft of 2.1 meters. The yacht has a fiberglass / grp hull with a CE certification class (A) and can navigate in the open ocean. The base price of a new X-Yachts X4⁰ is €320.2 thousand. Length.
Sailboat specifications. The X-40 is a 40' (12.19m) racer-cruiser sailboat designed by Niels Jeppesen (Denmark). She was built between 2004 and 2010 by X-Yachts (Denmark) with 140 hulls completed. The X-40 is as well listed, on Boat-Specs.com, in Shoal draft and Sport version ( see all the versions compared ).
Contact: Stuart Abernethy. Phone: +44 (0)23 8045 3377. Email: [email protected] . new to market in 2024. X-40, build number #92, built in 2006 and commissioned in 2007. White hull with blue hull stripes and 2.1m L-shaped keel. Standard aluminium mast with furling genoa. Teak on cockpit, with non-slip sidedecks and coachroof.
Find x-yachts 40 for sale on YachtWorld Europe's largest marketplace for boats & yachts. We connect over 10 million boat buyers and sellers each year! ... 2006 X-Yachts X-40. US$197,221* US $1,679/mo. Faaborg, Denmark. 40ft - 2006. Batagent. 2001 X-Yachts IMX-40. US$184,507* MARMARİS, Turkey. 40ft - 2001. Offered By: Sunbird International ...
2023 X-Yachts X-40. Request price. Forbes Horton Yachts | Annapolis, Maryland. Request Info < 1 > * Price displayed is based on today's currency conversion rate of the listed sales price. Boats Group does not guarantee the accuracy of conversion rates and rates may differ than those provided by financial institutions at the time of transaction.
Contact. +33 (0)4 42 11 00 55. 1. Sort By. Filter Search. View a wide selection of X-Yachts X-40 for sale in your area, explore detailed information & find your next boat on boats.com. #everythingboats.
Pocket Luxury Yacht. The all new X4⁰ is the smallest model in the Pure X range; blending quality, performance and styling with cruising capability. Hot out of the X-Yachts Design Office came the X4⁰, a forty-foot performance cruising yacht that is just as capable for some serious mileage as it is blasting around the cans at the weekend. The ...
Beautiful X-Yachts X-40 with white hull from first owner. Including teak deck and teak in cockpit, bowthruster, Raymarine instruments and a complete North Sails sail package. The owner has sailed in the Mediterranean the past few years, but this X-40 has just been transported back to Netherlands for a full check and cosmetic re-fit by X-Yachts ...
Description. 2007 X-Yachts X-40. Modern version with two cabins and one heads with electric toilet. The interior of the boat is in very nice condition. The upholstery, floors and woodwork are in very nice condition. The boat has two airco systems, one for the saloon and front cabin and one for the aft cabins.
X-40. Save to Favorites . Beta Marine. BOTH. US IMPERIAL. METRIC. Sailboat Specifications Definitions Hull Type: Fin w/bulb & spade rudder: Rigging Type: ... The LWL will increase as the yacht sinks into the water with the added weight of stores and equipment. BEAM: This is the greatest width of the hull and is often expressed as Beam (Max ...
Build Number: 26. Build Year: 2020. Lying: Flensburg, Select a Country. Price: €390,000 (excluding EU VAT) Dealer: X-Yachts Germany. Contact: Christoph Barth. Phone: +49 (0) 461 4 30 20 99 0. Email: [email protected] . X40 3-cabins, 1 head with white Corian galley worktop, fold-down chart table station, foldable saloon table with centre box ...
MINNEAPOLIS — The Black Crowes have canceled their appearance set for Friday at the inaugural Minnesota Yacht Club festival at Harriet Island in St. Paul. The reason is "illness in the band ...
Build Year: 2008. Lying: Croatia. Price: €160,000 (VAT Paid) Dealer: X-Yachts Slovenia. Contact: Miha Spendal. Phone: +386 41 730 970. Email: [email protected] . First owner of this beautiful 2 cabin modern version X-40 is selling his yacht. Please call +386 41 730 970 for more.
2001 X-Yachts IMX-40. US$129,000*. Price Drop: US$10,000 (Sep 26) Newport, Rhode Island. 40ft - 2001. Offered By: McMichael Yacht Brokers LTD. Contact.
X-40 Yacht Summary. Manufacturer: X-Yachts; Model: X-40; Build Number: 64; Build Year: 2006; Lying: Stralsund, Germany; Price: Sold; Dealer: X-Yachts Germany; Contact: Christoph Barth; Phone: +49 (0) 461 4 30 20 99 0; Email: [email protected] ; Sold. Beautiful X-40, in the typical X look (white with blue stripes), from 2007 for sale! She has ...
Model: X-40. Build Number: 63. Build Year: 2006. Lying: Netherlands. Price: Sold. Contact: Nanno Schuttrups. Sold. Fabulous dark blue X-40 from 2006 mostly sailed in sweet water. First and only owner has maintained his X-40 with an inspiring level of detail (partly thanks to having indoor storage available for winter).
Free Shipping Over $99 - 366 Day Returns - Expert Advice

- Call Us +1-503-285-5536
- Sign in & Register
- Recently Viewed
General Parts
General Parts, Fittings, and Accessories for Small Sailboats. We offer a full range of sailboat hardware, blocks, cleats, shackles, dollies and trailers, accessories, and more. These parts are not necessarily specific to any one model of sailboat, but rather are general fittings that often work on a variety of boats for a variety of applications.

- Qty in Cart

Ronstan Horn Cleat 6-1/2 Inch
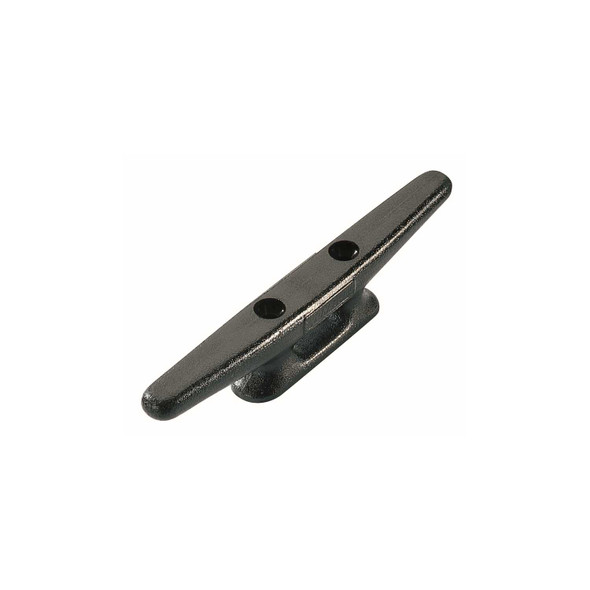

Ronstan Horn Cleat 5 Inch

Ronstan Horn Cleat 4 Inch

Ronstan Horn Cleat 3 Inch

Fabric Guard Waterproofing Spray

Dynamic Dollies Dock Cradle

Dynamic Combo Rail System Rack Over and Spar Deck Double Tongue Dolly
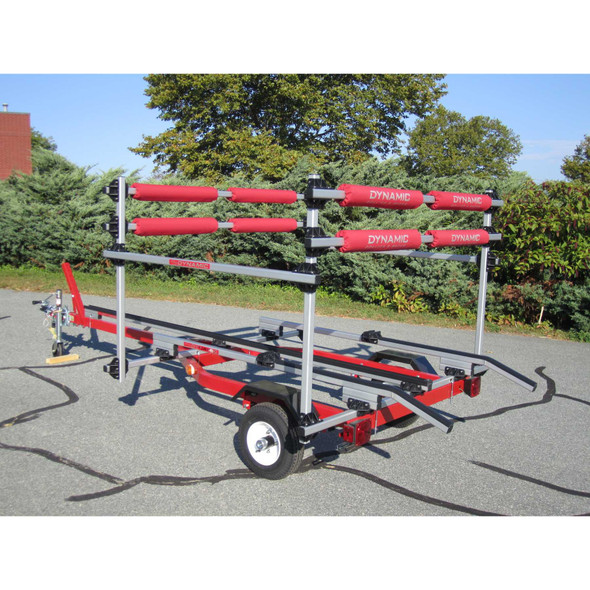

Dynamic Combo Rail System Rack Over and Spar Deck Single Tongue Dolly
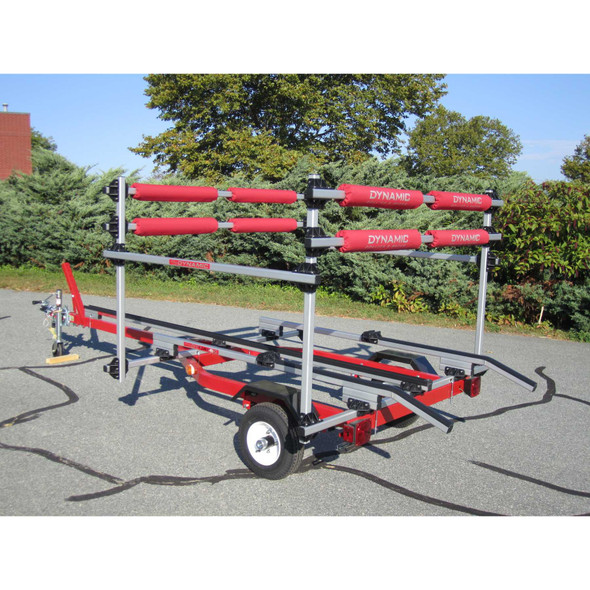

Dynamic Combo Rail System Rack Over Double Tongue Dolly

Dynamic Combo Rail System Rack Over Single Tongue Dolly

Dynamic Combo Rail System Double Tongue Dolly

Dynamic Combo Rail System Single Tongue Dolly

Gill Marine Tool

Gill Harness Rescue Tool

ILCA Cunningham / Outhaul Upgrade Kit Harken

ILCA Laser Vang Upgrade Harken
- Total: items /
- Add all to cart
Adding your products to cart
Subscribe to our newsletter.
Sign up for our newsletter to receive exclusive discounts, new product announcements, and upcoming sales.
Post comment
or continue as guest
IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Parts of a sail. Luff; the front part of the sail, is connected to the mast through a rail system which makes it possible to hoist or reef. Leech; the back part of the sail. Foot; the bottom part that reaches from the clew to the tack. Clew; back bottom corner.
Raked Mast on Dean 440. saildrive (n.) - a type of drive common on most newer catamarans which helps maximize space and minimize drag as well as being cheaper to build. The engines are in lockers in the swim platforms instead of under the aft berths. There are maintenance issues such as increased difficulty in changing oil and underwater seals which commonly deteriorate and let raw water ...
If you're looking for Hobie Sailboat Parts, you'll find virtually any item you need to repair or maintain your hobie catamaran sailboat here.Browse through our huge selection of Hobie Cat approved parts for the Hobie 14, Hobie 16, Hobie 17, Hobie 18, Hobie Bravo, Hobie Wave, Hobie Getaway, Hobie Adventure Island, Hobie Tandem Island, and more.
Short answer: The key parts of a catamaran include the hulls, bridgedeck, mast(s), rigging, sails, rudders, and daggerboards. These components work together to provide stability, propulsion, and control for this type of multi-hulled watercraft. Exploring the Essential Parts of a Catamaran: A Comprehensive GuideFrom cruising the open seas to enjoying lazy afternoons by the shore,
Regular Spares. • Water pump service kit - domestic. • Water pump service kit - other, shower, head etc., • Spare key, boat and any locks. • Water filters, house and water maker. Full Spares inventory. • Domestic water pump. • One spare water pump for other systems. • Critical electronic components, many modern electrical ...
Hobie 16. The Hobie 16 is an iconic catamaran, sailed and loved by many around the world. Shop our full selection of Hobie 16 Parts, sails, trampolines, upgrades, replacement fittings below. We have rudder parts, cams, tiller connectors, righting kits, new sails and trampolines, shrouds, trapeze handles, covers, blocks, and more.
Sailcenter is the largest specialised water sports store for dinghies and catamarans. We are the official Benelux importer of LaserPerformance dinghies, Dart catamarans, Ovington 29er, 49er, 49erFX and Musto Skiffs, SailQube, McLaughlin and Winner Optimists. We have a huge stock of spare parts for all kinds of dinghies and catamarans.
Hobie 18. The Hobie 18 is an iconic catamaran, sailed and loved by many around the world. Shop our full selection of Hobie 18 Parts, sails, trampolines, upgrades, replacement fittings below. West Coast Sailing is your source for all things Hobie Cat with easy, flat rate shipping and experts on hand to answer your questions.
Welcome to Fast Boat Stuff! Your best source in North America for gear for A Class Catamarans. We are your dealer for Exploder Catamarans and Fiberfoam masts and all the parts to keep them in top shape.
Call Beneteau Customer Service at 843.629.5320 to work with a sales rep or request a link to the online catalog (in case the link above stops working). Your closest Lagoon dealer or certified service location. If in South Florida, contact Lagoon Technical Services - Multitech Marine Fort Lauderdale 954.522.1114. Order your spare parts.
Going Aloft - Basic Boat Parts of a Sailing Rig. The rig of a boat is the mast and all of its associated parts. ... Catamaran Sailboat Parts Explained. For the most part, the components of a catamaran share the same terms and labels that they would on a monohull. Cats often have a few extra features with other names, however.
Speed and Efficiency. Power catamarans have gained popularity for offering a unique combination of speed, efficiency, and stability. Their dual-hull design allows for less water resistance, which directly translates to higher speeds and better fuel efficiency compared to traditional monohull boats.. In addition, the wide beam provided by the two hulls ensures a stable ride even at higher speeds.
One source for all of your sunfish parts and sales. In stock parts and fast shipping! (586) 372-9809; My Account. Register; Login; Wish List (0) Shopping Cart; ... We have a large selection of boats, sails and parts in stock and ready to ship. Configure your boat! Featured. AeroSouth, FS Wood Rigged Rudder, Sunfish, FS-RDD-BLD-FOR-RIG ...
The primary use for pre-preg in boating is high performance race boats. With catamarans, pre-preg may be used high load parts, like Gunboat does for foils and rudders. 4. Industry Examples. Across the catamaran building industry you'll find almost all the above techniques and materials used, though some are less common.
Hobie Cat Wave catamaran parts and accessories from the experts at West Coast Sailing. Hundreds of parts in stock with fast, flat rate shipping on your order. Free Shipping Over $99 - 366 Day Returns - Expert Advice ... One Design Boat Resources. Parts Locators. Rigging Guides. All Guides & Advice. Support. Shipping Info. Returns & Exchanges.
The Leopard Identity. Leopard Catamarans pushes the boundaries of catamaran design. Evolving from 50 years of customer feedback, Leopard Catamarans has pooled their expertise with builders Robertson and Caine to design today's Leopard range: spacious, robust, performance-driven blue water cruising catamarans. As the worldwide distributor, we ...
Upper Shroud Backing Shell, C-42 '98->. #T2156. $62.82. Catalina Direct, publishers of the Catalina 22 and Catalina 25 Owner's Handbooks and the largest supplier of parts and Lewmar winches for Catalina Yachts in the country.
12454 posts · Joined 2000. #3 · Jun 6, 2018. The English names for catamaran parts are a mix of typical English names for boat parts, with a few Polynesian words such as Aka and Ama thrown in for the parts that resemble traditional catamarans. But there are too many parts to simply start naming parts.
A variety of cruises are offered aboard the Genesee Belle Paddlewheel riverboat throughout the summer. Reservations are required for all meal cruises. Lunch cruise tickets must be purchased in advance. Reservations for the lunch cruise are accepted until the preceding Wednesday (based on availability). Specialty cruise tickets may be purchased in advance or on the boat based on availability....
Lagoon catamaran is a brand of twin-hulled boats that are designed and produced in Bordeaux, France.. The company began in 1984 as a specialist multihull division of Jeanneau, a volume monohull constructor. Jeanneau sold the division to Construction Navale Bordeaux (CNB), which was purchased by Beneteau in 1995, another French boat manufacturer
General Parts. General Parts, Fittings, and Accessories for Small Sailboats. We offer a full range of sailboat hardware, blocks, cleats, shackles, dollies and trailers, accessories, and more. These parts are not necessarily specific to any one model of sailboat, but rather are general fittings that often work on a variety of boats for a variety ...
A residential and industrial region in the south-east of Mocsow. It was founded on the spot of two villages: Chagino (what is now the Moscow Oil Refinery) and Ryazantsevo (demolished in 1979). in 1960 the town was incorporated into the City of Moscow as a district. Population - 45,000 people (2002). The district is one of the most polluted residential areas in Moscow, due to the Moscow Oil ...
Heliport information about UUDO - Orlovo, MOS, RU. Information on this site may not be accurate or current and is not valid for flight planning or navigation.