- PRO Courses Guides New Tech Help Pro Expert Videos About wikiHow Pro Upgrade Sign In
- EDIT Edit this Article
- EXPLORE Tech Help Pro About Us Random Article Quizzes Request a New Article Community Dashboard This Or That Game Happiness Hub Popular Categories Arts and Entertainment Artwork Books Movies Computers and Electronics Computers Phone Skills Technology Hacks Health Men's Health Mental Health Women's Health Relationships Dating Love Relationship Issues Hobbies and Crafts Crafts Drawing Games Education & Communication Communication Skills Personal Development Studying Personal Care and Style Fashion Hair Care Personal Hygiene Youth Personal Care School Stuff Dating All Categories Arts and Entertainment Finance and Business Home and Garden Relationship Quizzes Cars & Other Vehicles Food and Entertaining Personal Care and Style Sports and Fitness Computers and Electronics Health Pets and Animals Travel Education & Communication Hobbies and Crafts Philosophy and Religion Work World Family Life Holidays and Traditions Relationships Youth
- Browse Articles
- Learn Something New
- Quizzes Hot
- Happiness Hub
- This Or That Game
- Train Your Brain
- Explore More
- Support wikiHow
- About wikiHow
- Log in / Sign up
- Cars & Other Vehicles

How to Sail a Boat
Last Updated: May 13, 2022 Approved
This article was co-authored by Nitzan Levy . Captain Nitzan Levy is a Sailor, Social Entrepreneur, and the Founder of Sailors NYC, a recreational sailors’ club based in Jersey City, New Jersey that specializes in cruising boats and a variety of community programs. Capt. Levy has over 20 years of sailing experience and has sailed in many places around the world including: the Atlantic Ocean, the Mediterranean Sea, The Caribbean, and the Indian Ocean. Capt. Levy is a U.S. Coast Guard Licensed Master of vessels up to 50 Tons with Auxiliary Sail and Assistance Towing Endorsements. Capt. Levy is also a NauticEd Level V Captain Rank Chief Instructor, an American National Standards Assessor, an SLC instructor, an ASA (American Sailing Association) Certified Instructor Bareboat Chartering, and an Israeli licensed skipper on Boats for International Voyages. There are 9 references cited in this article, which can be found at the bottom of the page. wikiHow marks an article as reader-approved once it receives enough positive feedback. This article received 25 testimonials and 92% of readers who voted found it helpful, earning it our reader-approved status. This article has been viewed 972,148 times.
For centuries, the sea has captured the spirits of sailors and adventurers all over the world. In his poem "Sea Fever", John Masefield claimed that all he needed was "a tall ship and a star to steer her by" to feel complete. Breaking into the sailing world can be challenging, but this article will help guide you through the ebb and flood of the nautical world. As a note, this article will help get you started, but it cannot be overstated that before you begin, have an experienced sailor show you the standing and running rigging on your boat and their functions before you venture out on the water on your own.
Gaining a Basic Knowledge of Sailing

- Block: This is the nautical term for a pulley.
- Boom: The horizontal support for the foot of the mainsail which extends aft of the mast. This is what you want to watch out for when changing directions in a sailboat. It can give you quite a wallop on the head if it hits you.
- Bow: This is what the front of the boat is called.
- Centerboard: This is a (usually fiberglass) plate that pivots from the bottom of the keel in some boats and is used to balance the boat when under sail.
- Cleat: Cleats are what lines (or ropes) get fastened to when they need to be kept tight.
- Halyard: Lines that raise or lower the sails. (Along with the sheets, aka running rigging.)
- Hull: The hull is the body of the boat and consists of everything below the deck.
- Jib: This is the sail at the bow of the boat. The jib helps propel the boat forward.
- Genoa: A foresail which is larger than a jib.
- Keel: The keel is what prevents a boat from sliding sideways ("making leeway") in whatever way the wind is blowing and stabilizes the boat.
- Line: Lines are ropes. They are everywhere on boats. There is only one "rope" on a sailboat, the bolt rope which runs along the foot of the mainsail.
- Mainsail: As the name implies, this is the mainsail of the boat. It is the sail attached to the back of the mast.
- Mast: The mast is a large, vertical pole that holds the sails up. Some boats have more than one mast.
- Painter: This is a line positioned at the front of small boats. It is used to tie the boat to a dock or another boat.
- Rudder: The rudder is how the boat is steered. It is movable so that when you turn the wheel or tiller, the rudder directs the boat in the direction you would like the boat to go.
- Sheets: The lines that control the sails. (aka running rigging.)
- Spinnaker: The usually brightly colored sail used when sailing downwind or across the wind.
- Stays and Shrouds: Some wires make sure the mast stays upright, even in very heavy winds. (aka standing rigging.)
- Stern: This is the term for the back of the boat.
- Tiller: The tiller is a stick attached to the rudder and is used to control the rudder.
- Transom: This is what we would call the butt of the boat. It is the back part of the boat that is perpendicular to its centerline.
- Wheel: The wheel works the rudder, steering the boat.
- Winch: Winches help tighten the sheets and halyards. When these lines are wrapped around a winch (in a clockwise direction), a sailor can turn the winch with a winch handle, providing mechanical advantage which makes it easier to bring in the lines.

- Sloop : Sloops are the most common type of sailboat (when you think of a sailboat this is probably the one you picture in your mind.) It has a single mast and is rigged up with a jib in the front and a mainsail attached to the back of the mast. They can range in size and are ideal for sailing upwind.
- Catboat : A Catboat has a mast set up near the front of the boat and is a single-sail boat. They are small (or large, for that matter) and easily operated by one or two people.
- Cutter : Cutters have one mast with two sails in the front and a mainsail on the back of the mast. These boats are meant for small crews or groups of people and can be handled relatively easily.
- Ketch : A Ketch has two masts, with the second mast called the mizzen mast. The mizzen is shorter than the mainmast and is in front of the rudder.
- Yawl : Yawls are similar to ketches with the difference being that their mizzen masts are located behind the rudder. The reason for this placement is that the mizzen on yawls is for keeping balance, rather than for moving the boat forward.
- Schooner : Schooners are large sailboats with two or more masts. The mast in the back of the boat is either taller or equal in height to the mast at the front of the ship. Schooners have been used to commercially fish, transport goods and as warships.

- Port: When you are facing the bow (the front of the boat) the side to your left is the port side.
- Starboard: Starboard is the right side of the boat when facing the bow.
- Windward: As the name might imply, windward is the direction from which the wind is blowing, upwind.
- Leeward: This is also called ‘Lee’. This is the direction to which the wind is blowing, downwind.
- Tacking: Tacking is when you turn the bow of the boat through the wind so that the wind switches from one side of the boat to the other. This is when you most need to be mindful of the boom, as the boom will swing from one side of the boat to the other when you tack (you don’t want to be in its way when it does that.)
- Gybing (Jibing): This is the opposite of tacking, which means that it is when you turn the stern (or back) of the boat through the wind so that wind shifts to the other side of the boat. This is a more dangerous maneuver in a strong breeze than tacking since the boat's sails are always fully powered by the wind, and may react violently to the change in the orientation of the boat to the wind. Care must be exercised to control the boom during this maneuver as serious injury is a possibility if the boom travels across the cockpit uncontrolled.
- Luffing: This is when the sails begin to flap and lose drive caused by steering the boat into wind or easing (loosening) sheets.

Preparing The Boat

- Check the lines ( running rigging ) that raise and control the sails ( halyards and sheets respectively). Make sure that they are separated, not wrapped around each other or fouled on anything else, and that they all have a figure-eight knot or other stopper knot on the free ( bitter ) end so they cannot pull through the mast or sheaves.
- Pull all lines out of their cleats and off their winches. There should be nothing binding any line; all should be free to move and be clear at this point.
- If you have a topping lift—a small line that holds the back of the boom up and out of the way when the sail isn't in use—let it out until the boom sags downward freely, then re-tie or re-cleat it. Watch out for the boom; it's just swinging around at this point; it will cause a painful "clunk" if it happens to hit you or your crew. The boom will return to its normal, horizontal position when you hoist the mainsail completely.
- If so equipped, be sure that the tiller is properly attached to and controls the rudder. Your sailboat is now prepared for you to hoist the sails!

- If your boat doesn't have a windex, tie a couple of nine-inch pieces of old cassette tape, VHS tape, or oiled yarn to the shrouds—the rigging cables that hold up the mast. Place them on each side, about four feet up from the sides of the boat. These will show you from which direction the wind is blowing, although some sailors find cassette tape to be just too sensitive for this purpose.

- If your boat has a motor, use the motor to keep the boat pointed into the wind while you hoist sail.
- Here's a handy tip: if the water is not deep at your dock, or if you have no side pier, walk the boat out away from the dock and anchor it into the sand, and the boat will automatically point itself into the direction of the wind!
Hoisting The Sails

- There will be a small line ( outhaul ) attaching the rear corner of the mainsail ( clew ) to the end of the boom. Pull it so the foot of the main is taut, and cleat. This helps the mainsail have a smooth shape for the air flowing over it.
- Hoist the mainsail by pulling down on its halyard until it stops. It will be flapping around ( luffing ) like crazy, but that's OK for a short period of time. (Excessive luffing will drastically reduce the life and durability of the sail).
- The leading edge of the sail ( luff ) must be tight enough to remove folds, but not so tight as to create vertical creases in the sail.
- There will be a cleat in the vicinity of the halyard where it comes down from the top of the mast. Cleat the halyard. Using the jib halyard, raise the front sail ( jib , genoa or simply the headsail ), and cleat the halyard off. Both sails will be luffing freely now. Sails are always raised mainsail first, then the jib, because it's easier to point the boat into the wind using the main.

- Turn the boat to the left ( port ) or right ( starboard ) so it's about 90 degrees off the wind. This is known as a beam reach .
- Pull on the main sheet ( trimming ) until the sail is around 45 degrees away from straight back ( aft ). This is a safe place for the main while you trim the jib.
- You will start moving and tilting ( heeling ) away from the wind. A heel of more than 20 degrees usually indicates that you're being overpowered. Releasing the mainsheet momentarily ( breaking the main ) will lessen the amount of heel, and you will return to a more comfortable sailing angle of 10 to 15 degrees.

- The jib will form a curve or pocket; trim the sail until the front edge just stops luffing. Keep your hand on the tiller (or helm ) and stay on course!

- If you or the wind hasn't changed direction, this is the most efficient place to set the sails. If anything changes, you have to adjust them in response.
- You have just entered the world of the sailor, and you will have to learn to do many things at once, or suffer the consequences.
Sailing Your Boat

- When the wind is at your back and side ( aft quarter ), it's called a broad reach . This is the most efficient point of sail as both sails are full of wind and pushing the boat at full force.
- When the wind is at your back, you are running with the wind . This is not as efficient as reaching, because air moving over the sail generates lift and more force than just the wind pushing the boat.
- When running with the wind, you can pull the jib over to the other side of the boat where it will fill. This is called wing-on-wing , and you have to maintain a steady hand on the tiller to keep this sail configuration. Some boats have a "whisker pole" which attaches to the front of the mast and the clew of the jib which makes the jib much easier to control and keep full of wind. Be sure to be vigilant of obstacles and other vessels, as having both sails in front of you blocks a significant portion of your view.
- Be careful —when the boat is running, the sails will be way off to the side, and because the wind is basically behind you the boom can change sides suddenly ( jibe or gybe ), coming across the cockpit with quite a bit of force.
- If you have a wind direction indicator at the top of your mast, do not sail downwind (run) so that the wind indicator points toward the mainsail. If it does, you are sailing with the boom on the windward side ( sailing by the lee ) and are at high risk of an accidental jibe. When this happens the boom can hit you with enough force to knock you unconscious and out of the boat ( overboard ).
- It's a good practice to rig a preventer (a line from the boom to the toe rail or any available cleat) to limit the travel of the boom across the cockpit in case of an accidental gybe.

- On most sailboats this will be about 45 degrees from the wind direction.
- When you've gone as far as you can on this tack, turn the boat through the wind (or changing direction by tacking ), releasing the jib sheet out of its cleat or off the winch drum as the front of the boat ( bow ) turns through the wind.
- The main and boom will come across the boat. The mainsail will self-set on the other side, but you will have to quickly pull in the jib sheet on the now downwind side to its cleat or winch, while steering the boat so the mainsail fills and begins to draw again.
- If you do this correctly, the boat won't slow down much and you will be sailing to windward in the other direction. If you're too slow tightening the jibsheet again and the boat bears off the wind too much, don't panic. The boat will be pushed sideways a little until it gains speed.
- Another scenario would be to fail to put the bow of your boat through the wind quickly enough and the boat comes to a complete stop. This is known as being in irons , which is embarrassing, but every sailor has experienced it, whether or not they'll admit it is another story. Being in irons is easily remedied: when the boat is blown backwards you will be able to steer, and as the bow is pushed off the wind you will achieve an appropriate angle to the wind to sail.
- Point the tiller in the direction you wish to go and tighten the jib sheet to windward, ( backwinding the sail ). The wind will push the bow through the wind. Once you've completed your tack, release the sheet from the winch on the windward side and pull in the sheet to leeward and you'll be on your way again.
- Because speed is so easily lost when tacking, you'll want to perform this maneuver as smoothly and quickly as possible. Keep tacking back and forth until you get to your destination.

- Reefing almost always needs to be done before you think you need to!
- It's also a good idea to practice capsize procedures on a calm day too. Knowing how to right your boat is a necessary skill.

Storing the Sails

Community Q&A
- Try learning to determine the wind direction using your ears. Let the wind blow onto your back, then slowly turn your head left to right and back until you feel it "equalize" over your ears. Once you find that point, you now know the wind direction, and using this method, you can understand the wind more without having to use your eyes. [7] X Research source Thanks Helpful 2 Not Helpful 0
- Know how to read clouds and the weather they may bring. [8] X Research source Thanks Helpful 2 Not Helpful 2
- If something bad happens—too much wind, man overboard, etc.—remember that you can bring the whole thing to a halt simply by pulling all three sheets out of their cleats or off their winches. The boat will (mostly) stop. Thanks Helpful 3 Not Helpful 0

- Going overboard is a serious matter, especially if you are alone. Cold water, currents, and other boats all can account for serious dangers, and if the sails are up, the boat will take off much faster than you might expect. Additionally, many boats float so high on the water ( freeboard ) that it is difficult to climb in or haul people in without assistance. When sailing at night, always wear a shoulder-mounted flashlight and strobe emergency signaling device, which makes it much easier for a SAR (Search And Rescue) crew to spot you in the water. Thanks Helpful 36 Not Helpful 4
- In sailing, your very life may depend on doing things before they need to be done, when they first cross your mind. If you wait until it needs to be done, it may be too late or very difficult. Follow your instincts. Thanks Helpful 30 Not Helpful 5
- Remember the old maxim "It's better to be on the dock, wishing you were on the lake, than to be on the lake, wishing you were on the dock". Don't let enthusiasm overcome your good judgement on a day you should not go out. The apparent wind while tied alongside at the dock may be very different out on the water. Many novices (and experienced sailors, for that matter) get into trouble venturing out when there is too much wind to sail safely. Thanks Helpful 4 Not Helpful 0
- It is highly recommended that you at least have working knowledge of the nomenclature of the boat and have done some reading of in-depth material before attempting this sport yourself. Some highly recommended reads are: The Complete Idiot's Guide to Sailing , Sailing for Dummies , and Sailing the Annapolis Way by Captain Ernie Barta. Thanks Helpful 2 Not Helpful 1
- Know how how to use VHF radio to make a Mayday call from a Marine Vessel . In an emergency, it is usually the quickest way to summon help. Cell phones may be used, but VHF will be able to contact a nearby vessel much more quickly should you need assistance or be able to render same. [9] X Research source Thanks Helpful 2 Not Helpful 0
Things You'll Need
- A life vest (Personal Flotation Device) is mandatory on all boats for all passengers. (A pealess whistle attached to the PFD is an excellent idea!) You should wear one at all times. If you have children with you, they should wear one even when you are at the dock.
- Every vessel, regardless of length is required to have a certain amount of safety gear aboard. This ranges from an anchor with sufficient rode, flares, and other equipment as may be mandated by the Government. These regulations are for your safety and should be adhered to.
You Might Also Like

- ↑ http://www.lovesailing.net/sailing-theory/sailing-basics/parts-of-a-boat/parts-of-a-boat.php
- ↑ https://www.boats.com/resources/sailing-101-sailboat-types-rigs-and-definitions/
- ↑ http://www.discoverboating.com/resources/article.aspx?id=243
- ↑ https://www.uscgboating.org/images/486.PDF
- ↑ https://www.cruisingworld.com/learn-to-sail-101#page-2
- ↑ https://www.discoverboating.com/resources/how-does-a-boat-sail-upwind
- ↑ https://www.dummies.com/sports/sailing/finding-the-winds-direction/
- ↑ https://weather.com/news/news/read-clouds-meteorologist-20130826
- ↑ https://www.boatus.org/marine-communications/basics/
About This Article

To sail a boat, start by performing a detailed visual check of the cables and ropes that support the mast. Next, determine the wind direction by referring to the wind direction indicator at the top of the mast, then point the boat into the wind. Secure the bottom front of the mainsail and jib to the shackles on the boom and bow of the boat, then trim the jib sheets and mainsail before letting out the main sheet! For tips on monitoring wind indicators, read on! Did this summary help you? Yes No
- Send fan mail to authors
Reader Success Stories
Sep 13, 2017
Did this article help you?
Tobias Tanti
Dec 25, 2020
Nov 19, 2017
Mar 30, 2016
Nov 22, 2016

Featured Articles

Trending Articles

Watch Articles

- Terms of Use
- Privacy Policy
- Do Not Sell or Share My Info
- Not Selling Info
Get all the best how-tos!
Sign up for wikiHow's weekly email newsletter
- Setting sail: A beginner's guide to sailing a yacht
Sailing a yacht, with its billowing sails and the gentle sound of water against the hull, is an enchanting experience that beckons adventurers and dreamers alike. Whether you've always been drawn to the allure of the open waters or you simply seek a new and exhilarating hobby, setting sail on a yacht is an extraordinary journey that awaits you.
The allure of sailing
There's something truly captivating about sailing on a boat, where the wind becomes your guide and the vast expanse of the ocean becomes your playground. The sense of freedom and connection with nature is unparalleled as you navigate the waters, leaving behind the noise and haste of everyday life.
Preparing to sail
Before embarking on your sailing adventure, it's essential to make necessary preparations. Learn about weather conditions, tides, and navigational charts to ensure a safe and enjoyable voyage. Familiarize yourself with the yacht's equipment, safety protocols, and communication systems.
Understanding the basics of sailing
For beginners, learning the fundamentals of sailboat handling and terminology is crucial. Discover the various parts of a sailboat, such as the mast, rigging, sails, and rudder, and understand how they work together to catch the wind and propel you forward.
Read our top notch articles on topics such as sailing, sailing tips and destinations in our Magazine.
Steer with confidence: How to sail a yacht
Mastering the art of steering a yacht is both empowering and rewarding. Learn the techniques to control the sails, adjust the angle, and harness the wind's power to navigate your vessel smoothly and efficiently.
Hoist the sails: Sailing techniques for beginners
As a novice sailor, it's essential to explore different sailing techniques. Learn how to tack and jibe, sail upwind and downwind, and handle different wind conditions. Practice basic maneuvers until they become second nature, building your confidence on the water.
Navigating the waters: Where to sail
The world's oceans and waterways offer a vast array of sailing destinations. Discover scenic coastlines, picturesque islands, and hidden coves as you plan your sailing routes. Research the best sailing locations that suit your skill level and preferences.
Yacht at sea.
Safety first: Sailing precautions and best practices
Safety should always be a top priority when sailing a yacht. Familiarize yourself with life-saving equipment, emergency procedures, and safety checks before each voyage. Understand how to respond to unexpected challenges and ensure the well-being of yourself and your crew.
Weathering the storm: Dealing with challenging conditions
Mother Nature can be unpredictable, and weather conditions can change rapidly at sea. Learn how to interpret weather forecasts and respond to adverse conditions. Having the knowledge and preparedness to navigate through challenging weather ensures a safe and successful sailing trip.
Sailing gear and equipment: The essentials for your voyage
Investing in quality sailing gear and equipment enhances your comfort and safety on board. From life jackets and harnesses to navigational tools and communication devices, having the right gear ensures a smooth and enjoyable journey.
A smooth sail: Troubleshooting and problem solving
In the world of sailing, unexpected challenges may arise. Knowing how to troubleshoot common issues, such as tangled rigging or minor equipment malfunctions, empowers you to handle situations effectively and continue your voyage with confidence.
So you want to get into sailing?
If you're drawn to the world of sailing but don't know where to begin, seek out sailing schools, clubs, and organizations that offer introductory courses and sailing experiences. Engaging with the sailing community provides invaluable guidance and support as you embark on your sailing journey.
Making sailing accessible: Sailing schools and training
Sailing schools offer structured courses led by experienced instructors, providing you with hands-on learning and a comprehensive understanding of sailing techniques. Consider enrolling in a sailing course to acquire the skills and knowledge needed to sail with confidence.
Sailing community: Building connections and finding support
Joining a sailing community opens up a world of camaraderie and shared experiences. Connect with fellow sailors, participate in sailing events and regattas, and exchange tips and stories with like-minded individuals who share your passion for the sea.
The joy of sailing: An sdventure like no other
As you set sail and immerse yourself in the world of yachting, you'll discover the true joy of sailing. The sense of accomplishment, the thrill of mastering the winds, and the breathtaking vistas of the open sea create memories that will last a lifetime.
So what are you waiting for? Take a look at our range of charter boats and head to some of our favourite sailing destinations .
Faqs about sailing.
What are the common sailing terms I should know?
Brush up on basic sailing terms like port, starboard, bow, stern, tacking, jibing, and points of sail.
Can I sail a yacht alone or do I need a crew?
While experienced sailors may sail solo, it's advisable for beginners to have a small crew for safety and assistance.
Is sailing a yacht physically demanding?
Sailing can require some physical effort, but modern yachts and equipment make it accessible to people of various fitness levels.

How to Sail: The Ultimate Sailing Guide for Beginners
Learning to sail can seem like a daunting process. Besides just learning how to sail a boat, the terminology of boating is completely different, and most of what needs to be learned can only be acquired by doing, meaning practice is required. But before you head out on the water, you can increase your knowledge by reading up on sailing , which will further help to keep you safe while on your boat. Discover our ultimate sailing guide for beginners !
(Guide via Jen Reviews )
Sailing Defined
Sailing is the art of taking a boat, turning off the motor, and harnessing the power of the wind to make the boat go where you want it to go. It might seem difficult, but it is really very simple, provided you take the time to understand how the boat utilizes the power of the wind. More than likely your boat will also have a motor (for times when there is no wind), but we will mainly focus on the actual process of sailing, and how that can be achieved.
Before you leave the dock
Before you head out on your own boat (or before you go to purchase a boat), search online and find the nearest sailing school or yacht club. You can find the local sailing school where you can take one on one sailing lessons, or even take an instructor out on your boat to show you the ropes, and how to safely sail. There are also free classes you can take online, which can better prepare you for learning the basics of sailing.

Make sure and check the weather before heading out. If there is a storm headed your way, or in the direction you want to go, it might be prudent to wait a few days until calmer weather is in the forecast. It also can be quite boring to head out on the water if there is no wind, as you will be forced to motor the entire time.

Dress for the weather, but be sure and bring lots of layers. Even if it’s hot out, while out on the water there is nothing to shield the wind, so it might seem colder than on land. Always have a jacket , hat, sunscreen, long pants and or shorts, shoes, and bring lots of water and snacks. Better to be over prepared than under prepared.

Make a Checklist
Make a checklist for necessary equipment you will want to bring with you on the boat (or even things that are US Coast Guard required). This could include items such as:
- Life Jackets
- Drinking water and snacks
- Sunglasses, hat, jackets, extra clothing
- Engine fuel and spare parts
- Chart ( handheld GPS as well)
- Bucket (can be used to bail water, clean off the boat, or as a restroom if need be)
- USCG required equipment for the boat
- Sound signals (whistle or fog horn)
- Fire extinguisher
- Visual distress signals (flares or flashlight at night )
- Navigation lights (required at night, or if visibility is reduced)
- Anchor and chain/line
- Extra line (mooring or various other uses)
- Fenders (Plastic hard ‘balloons’ that keep your boat from bumping on the dock)
- VHF radio and cellphone
- First-Aid Kit and booklet
- Tool Kit and Knife
- Lifesling or throwable buoy
- Radar reflector
- Ditch kit (full of life saving necessities in case you have to abandon ship)
- Life raft of some sort (depending on where you are sailing, and the size of your vessel)
These are all useful and necessary items to have stocked on your boat: some are required by the Coast Guard , and some are just common sense. It might also be helpful to bring a sailing buddy when you head out, to assist with docking, hoisting the sails, or just giving a second opinion in case something should occur.
Know your boat
Before heading out on the water, make sure and inspect as much of your boat as you can: understand where the lines (ropes) are going, how the sails are hoisted (lifted) and lowered, and where the safe places to walk or sit will be once you are out on the water. This article will discuss the basic terminology (with important words defined in bold), and try to explain as much as you need to know about the basic parts of your sailboat.
Let’s start with the simple terminology first .
When you get on your boat, and are facing towards the front of the boat, that would be forward, with everything behind you being aft. The very front of the boat is the bow, with the aft part of your boat called the stern. The left of the boat is the port side (think left and port both having four letters), with the right side being the starboard side. That seems simple, right? So let’s keep going.
The mast is the vertical pole that supports the sail. If you only have one big sail, there will only be one mast. Some boats have more than one mast, but sailboats always have at least one. The horizontal pole that comes off the bottom part of the mast is called the boom (which is also the sound it makes when it hits you in your head… be careful of this one!).
The tiller is a horizontal lever arm that turns the rudder (steers the boat), and is either by itself or is attached to the wheel, which is what you use to steer the boat. Standing in the boat you will be on the deck, but if you go inside the boat you will be below-deck. The sides of the boat are called the hull, and the draft is the distance from the surface of the water to the deepest part of the boat underwater (important to know if you don’t want to run aground).
The lines that hold up the mast on the starboard and port sides up to the top of the mast are called the shrouds, while the wire that runs from the mast to the stern is called the backstay, and the wire that runs from the mast to the bow is the forestay (also called the headstay). The beam is the width at the widest point of your boat, and the total length overall is the horizontal length from the tip of the stern to the tip of the bow (necessary to know depending on where you want to dock or store your boat).
It may seem like quite a few terms to know, but while being on a sailboat everything is called something different. But we are only concerned with the most important terms at the moment.
When you start putting up a sail, you will be pulling on a halyard . If you are putting up the mainsail (largest sail that is attached to the mast), you will be pulling on the main halyard. To let the sail move towards the starboard or port side of the boat, you will let out the main sheet (line that is attached to the bottom aft section of each sail, which moves it side to side). You may need to use a winch, which is a round drum that increases your power capabilities to pull on a line (rope).
10 Sailing Tips Essentials to Make You a Better Sailor!
Taking your sailboat on holiday: a comprehensive guide to boat shipping, how to avoid a gybe broach – video tutorial, 5 tips for anchoring your sailboat, live your passion, subscribe to our mailing list.
A Beginner's Guide to Sailing a Sailboat
Key Information for Beginners and Sailors
There are many ways to learn to sail:
- You can just jump in a boat with a friend and try to learn from experience
- You can sign up for a formal course at a sailing school
- You can buy or borrow a small sailboat and do it all on your own
No matter which way works best for you, it helps to understand the boat and what's involved in sailing first before you're out on the water, where suddenly you might get into trouble.
The Basic Steps of Sailing
Sailing involves both specific knowledge and skills. The following are the basic steps of learning to sail- as much as you can learn while not actually on a boat. You don't have to follow this order; skip ahead if you already know some of the basics. If you're mostly new to sailing, you might want to proceed through these steps like chapters in a manual.
- Understand Basic Sailing Terms. To get into sailing, you have to understand the words that are used to talk about the sailboat and the skills used to sail. Start here with a review of basic sailing terms. Don't worry about memorizing everything as many of these terms and concepts will become clearer as you read on about how to do it.
- Learn the Parts of the Boat. Before you go on the boat, it's helpful to know the words used in different parts of the boat. Even if you have an instructor, he or she won't say "Grab that rope over there and pull it," but instead will say "Haul in the jib sheet!" Review the basic boat terms you'll need to know.
- Start an Online Course. Now you're ready to learn more about what all those parts of the boat are used for. Here you can start an online learn-to-sail course by learning more about the parts of the boat along with a lot of photos, so you'll see what to do.
- Rig the Boat. Read to go sailing now? Hold it a minute- you have to rig the boat first by putting on sails and making other preparations. Here again are a lot of photos of what to do on a typical small sailboat used by beginners.
- Review Basic Sailing Techniques. OK, now you have the boat ready- so what do you do now to make it go? Manage the sails to go in the direction you want by learning basic sailing techniques.
- Discover How to Maneuver. Sailing in a set direction is reasonably easy, but eventually, you'll have to change direction. That often involves tacking and gybing. Take a moment to learn what's involved in these critical maneuvers.
- Recover From a Capsize. Now you've got the basics down. But did anyone ever tell you that small sailboats often tip over if the wind is gusting? Be prepared and carefully see how to recover from a capsize .
- Dock or Anchor the Boat. Now you're out there sailing and you've got the boat under control. Learn how to go faster, dock or anchor the boat and use some of the equipment you've ignored so far. Take a look at some of these additional sailing skills.
- Practice Tying Knots. For thousands of years, sailors have used times where it is cold or raining by doing things like tying knots. Knots are important on a sailboat and you will need to learn at least some basic sailing knots to sail at all.
- Sail Safely. At this point, plus practice on the water, you're good to go. However, it's good to remember that water is a dangerous place. Learn the basics about sailing safety. Staying safe makes it easier to keep having fun out there.
How to Rig Your Small Sailboat and Prepare to Sail
Learn the Parts of a Sailboat and How to Communicate Them
West Wight Potter 19 Sailboat Review
Heavy Weather Sailing
The Best Sailing Books and Magazines
How to Jump on a Wakeboard
Learn How to Sail a Small Sailboat
How to Plan a Caribbean Vacation
A Beginner's Guide to Rock Climbing
Owner's Review of the MacGregor 26 Sailboat Models
RVing 101 Guide: Water Heaters
Tips for Teaching Kids to Waterski
Useful Words and Phrases in Danish
Celestyal Cruises - Greece and Turkey Ports of Call
The Various Types of Sailboats and Rigs
12 Best Things to Do in Annapolis, Maryland
- BOAT OF THE YEAR
- Newsletters
- Sailboat Reviews
- Boating Safety
- Sails and Rigging
- Maintenance
- Sailing Totem
- Sailor & Galley
- Living Aboard
- Destinations
- Gear & Electronics
- Charter Resources
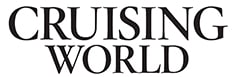
Learning How to Sail 101
- By John Rousmaniere
- Updated: May 4, 2020
Points of Sail
“The idea of sailing a boat upon the sea can seduce even the happiest farmer or mountain climber. There is something about boat and water that sends romance churning in our hearts, and simply the sight of a boat can inspire a reverie.”
I wrote those words in the first edition of my sailing manual, The Annapolis Book of Seamanship , in 1983. They’re still there today in the updated fourth edition, published in 2014. And yet, as deeply as I feel about boats, I’m certain that when you’re afloat, romantic and magical thinking is no substitute for basic skills and fundamental knowledge.
To quote some other words I wrote back then: “Limitless in her poetry, a sailboat is still restricted by the realities of wind and sea.” Here I’ll describe some important basic skills when learning to sail for dealing with a few of those realities, including some tips and tricks of the seaman’s trade that I have learned and that should make you a more able, safe and confident skipper or crew.
How to Start Sailing
The very first step when you go sailing is to properly prepare yourself for the sometimes demanding and harsh elements you will encounter on the water. Take a wide-brim hat, a waterproof jacket, nonskid sneakers and, of course, a life jacket that fits you securely. Wipe on a gob or two of high-SPF sun lotion, and take the tube with you so you can continue to apply it lavishly. Those who suffer from motion sickness should consider taking a medication, preferably one that you’ve tested for side effects. Before heading out, write up a float plan including your itinerary and important contacts and share it with your friends and family, or your sailing club.
The most unsettling moment of a new sailor’s first day learning to sail often comes when you climb on board and feel the boat move under you. There’s plenty of reserve buoyancy, but if the boat’s small and skittish, you should step into the center of the cockpit. A bigger boat can be boarded via the side deck, but even it may sway and settle a little. Forget about looking graceful. Take advantage of any handhold you can grab.
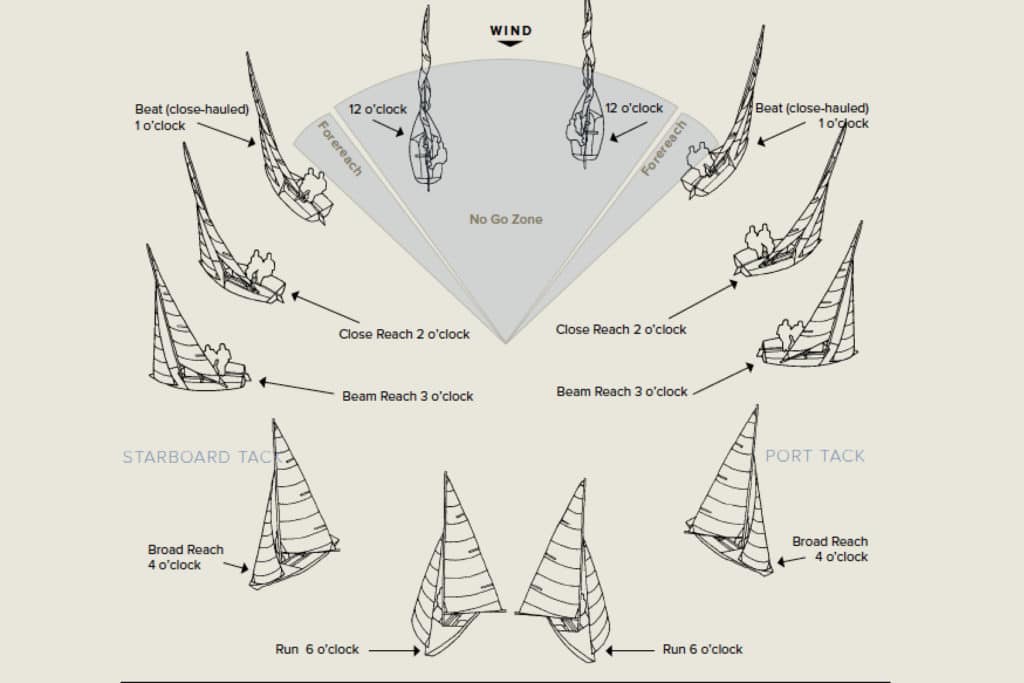
Once everyone is on board, the skipper must assert command. To quote a wise captain and safety instructor, Karen Prioleau: “When leadership is obscure, tight situations get even tighter.” Assignments are made, gear is stowed, the bilge is pumped, an inspection is conducted to see that all is in order, sails are prepared to hoist, and plans are made to get underway. If the boat has a motor, it can be used to get away from the mooring or dock into open water before setting sail. But for now, let’s concentrate on getting underway on an engineless boat. Start by setting the mainsail, the big sail. The line to the boom (called the mainsheet) must be well eased so the sail, once set, spills wind (luffs) and doesn’t fill prematurely. The boom will flop around, so keep your head low and consider controlling it with a line called a preventer.
Trimming and Tacking a Sailboat
When the skipper says to cast off, up goes the jib, the smaller sail on the bow, also with a loose sheet. Casting off under sail is a little complicated because the boat isn’t moving, which means the rudder has little to no effect. That’s why the boat must be steered with the sails until there’s enough speed (or “steerageway”) for rudder steering. When learning to sail, start with the boat hanging off the mooring or pier; the sails will luff because the wind is blowing from directly ahead. If you’re looking at the bow, you’ll feel the wind on both ears. That angle is sometimes called the “wind’s eye.” Trim the jib—using the winch to bring the sail in, not let it out—to the side opposite the one where you want to sail. If you want to head off to the port side, you “back the jib,” or trim it to the “wrong” side. As the backed jib pulls the bow off, cast off the mooring. Once the wind is on that side, trim the jib to the correct side while also trimming the mainsail as the boat accelerates. In this way, the sails help steer the boat.
An entertaining and educational exercise is to sail a boat toward a buoy or other target on a reach, with the wind coming from the side (or beam) of the boat, and do a series of slow weaves as the sheets are eased and trimmed. When the skipper at the helm and the sail trimmers are in sync, everything goes well (see Figure 1). If you get nervous, slow down by easing the sails until they are just half-filled with wind.
Practice changing tacks. If you start off with the wind coming over the starboard side, you’re on the starboard tack. If the wind is on the port side, you’re on the port tack (see Figure 2). One of the two ways to change tacks is called “coming about,” or “tacking.” The helmsman starts the process by saying, “Ready about,” and after the crew answers that they’re ready, “Hard alee.” With a strong, fluid shove of the tiller or turn of the steering wheel, the bow passes through the eye of the wind and comes off onto the new tack (see Figure 3).
The other way to change tacks is to jibe, pulling the tiller or wheel in the other direction, easing the sheets out, and swinging the stern through the wind’s eye until the boom swings across (see Figure 4). The steerer’s commands are “stand by to jibe” and, after the crew acknowledges, “jibe-ho.” The boom will come across suddenly and rapidly, so all crewmembers must be careful to duck their head as they trim the mainsail and jib to the new sides.
Since we are talking about steering, this may be the place to encourage you to steer from the windward side of the tiller or wheel. The windward side (closer to the wind direction) is higher than the leeward side (farther from the wind) when the boat is heeling, so you will have greater visibility to see “puffs” of wind (the dark shadows moving across the water) as they approach.
Using Telltales
One phenomenon of sailing is that as the boat speeds up or slows down, the wind seems to change direction and force. That’s because there are two types of wind. One, called “true wind,” is the breeze you feel when standing still. The true wind’s velocity and direction are the same for all nearly stationary objects. But if one of those objects moves (like a boat does), its motion affects the true wind to create “apparent wind,” which is felt by people on the moving object.
Sails are trimmed to the apparent wind. You can gauge the apparent-wind direction and force by feeling it on your skin, reading it on an electronic instrument, or seeing it on a telltale, which is a short length of yarn tied to one of the boat’s side stays (shrouds) that support the mast. While all those devices indicate the wind direction, none of them tells you if your sails are trimmed correctly for that direction.
Sails are airfoils, with a deep curve that redirects the apparent wind to produce a force that pulls the boat forward (somewhat like a wing lifting an airplane off a runway). Side force is absorbed and redirected to forward force by the airfoil-shaped fins under the boat, the centerboard and keel. As airfoils, sails should be trimmed to suit the wind, and the boat should sail the most effective angle to that wind.
A simple, effective indicator of that sailing angle is a set of short lengths of special telltales—yarn or ribbons—that are sewn or glued to sails. Some telltales are placed on the jib, near its leading edge (the luff), on both sides of the sail. Ideally, there should be three pairs of jib telltales at equal intervals up and down the sail’s luff. But one pair about halfway up the sail should do the job. Other telltales are secured, one at a time, on the trailing edge of the mainsail (the leech), or at least at or near the second batten from the top. The jib telltales on both sides of the sail should stream aft most of the time, with the windward ones lifting slightly from time to time. The mainsail leech telltale should stream aft about half the time. If your telltales behave differently, try steering closer to or farther off the wind, and experiment with sail trim. An inch or two of sail trim or ease can get them flowing again and make the boat sail faster.
Sailing Rules of the Road
Once you’re sailing, you may be near other boats and worried about who is under an obligation to alter course to avoid a collision. The basic rule is that more maneuverable boats must give way (change course) to avoid boats that are less maneuverable and that, therefore, may continue on their course, giving them right of way. (These are sometimes called “stand-on vessels.”) Usually powerboats must give way to sailboats, but all smaller boats, sail and power, must give way to big ships in a narrow channel and other vessels requiring room to maneuver.
There are a few other basic rules. When one boat is overtaking another, no matter what type, the overtaking boat must give way. When boats under power meet each other bow to bow, they each should turn to starboard so they pass port side to port side. And when sailboats are sailing near each other, without engines turned on, the one on the port tack (with the wind coming over the port side) is obliged to give way to the one on starboard tack. But even if the rules give you the right of way, proceed just as sensibly and defensively as you would when you face the realities of wind and sea at other times in open waters.
Once you’ve mastered these basics, get out on the water as often as possible to hone your skills in all conditions. One of the great things about sailing is that no matter how many miles you cover, there’s something new and different to experience every time you set sail. Congratulations on taking the first step toward what, for so many of us sailors, has become an enjoyable, lifelong pursuit.
Renowned sailing writer John Rousmaniere has logged over 40,000 nautical miles of bluewater sailing, including nine Newport-Bermuda races. This article is based on material from the fourth edition of his comprehensive sailing manual, The Annapolis Book of Seamanship (Simon & Schuster, 2014).
- More: How To , learn to sail , sailing 101 , seamanship
- More How To

DIY Tips for Repairing Nonskid

Shaft Bearing Maintenance Tips

When the Wind Goes Light

How We Built Our Own Bulwarks

Pro-Grade Sailing Eyewear

Le Boat and Groupe Beneteau Ink Deal

Hurricane Beryl Relief Efforts: How You Can Help

Gary Jobson To Talk U.S. Prospects in Upcoming World Sailing Competitions
- Digital Edition
- Customer Service
- Privacy Policy
- Email Newsletters
- Cruising World
- Sailing World
- Salt Water Sportsman
- Sport Fishing
- Wakeboarding

Type Of Sails: A Complete Guide

Table of Contents
Last Updated on September 29, 2023 by Boatsetter Team
If you are approaching sailing and sailboats from a very beginner’s perspective , then the concept of different kinds of sails can be a strange one. We often believe we see one kind of sailboat with one kind of sail, and our simple minds lead us to believe you are only meant to move them around, and you will get to where you need to go.
However, you would not have landed on this article if you did not suspect that there was more to sails and sailboats. So here, you can have a kind of in-depth, kind of summarized review of the different kinds of sails and the most popular sail and mast configurations out there.
It is also important to understand why there are so many different kinds of sails. When you are out on the water, different weather conditions can occur. Your sail acts as a motor of some sort, moving your sailboat forwards, but your sail is also highly dependent on the wind conditions around it. This is why having different kinds of sails can help you navigate your weather conditions and turn them to your own advantage while sailing.
Different sails also come with different danger levels in case of strong wind, so knowing what kinds you might need to watch out for is also extremely important. So, without further ado, let us get into it.
You may have heard of this one before or seen it portrayed in movies and TV shows. As the name suggests, the mainsail is the most popular kind of sail on any sailboat, and they are found behind the mast. They are also attached to the boom. Because they take up so much space on your sailboat, they are also one of the most important sails to take care of and keep an eye on.
Since the mainsail is such a large sail, it does not require too strong a wind to propel it forward , as its large surface area will easily catch a breeze. At the same time, the fact that it can be moved around by moving the boom makes it, so it is easy to steer. This makes it so that the mainsail is the most important sail on your sailboat.

Headsail/Jib

The headsail, or the jib, is likely the second most popular kind of sail found on sailboats. This is because it often accompanies the mainsail, the most popular kind. On all sailboats , the headsail is put at the front of the mast over the sailboat’s bow . It is always a smaller sail than the mainsail.
The fact that the headsail is smaller can be especially useful if you are caught in strong winds. In this situation, you likely do not want to use your mainsail (or trim it as much as possible) to move slower and not be thrown around by the winds. Smaller sails catch less wind, meaning they do not propel your boat as strongly as larger sails.
Having a good headsail can be an incredible safety measure, especially if the seas you are trying to sail are known to be wild and unpredictable.
You may have seen a genoa sail before if you have been around boats or have ever lived in a coastal town. This kind of sail is a large sail that you can attach to the front of the forestay (similarly to the headsail). This is a larger sail than the headsail and can even cover the mainsail either partially or completely. For this reason, the genoa also used to be called an “overlapping jib.”
You should use a genoa if you are sailing through either light or medium winds and if your sailboat is at a dead run point of sail (this means that the wind is coming directly from the rear. If you attempt to use a genoa sail in stronger winds , you might start going too fast and put yourself and your boat at risk since it is such a large sail. So, it is important to be careful .

The spinnaker is the most whimsical kind of sail since it is a large and colorful kind. They are also often symmetrical, which means they are more appropriate for reaching different points of sail, such as the running point of sail. They are lighter sails, and they do not cover the mast as the genoa sail does. You do not attach a spinnaker to the forestay and instead let it stretch out past the boat’s bow.
The large surface area of the spinnaker means that you have to be even more careful than with others on the kind of conditions you choose to use this sail in. If the winds are too strong, you could be putting yourself and your passengers at serious risk using this sail, so you should choose to use it only at times when the wind is low or in seas that are known for their low winds and tranquility.
As the name suggests, the gennaker sail mixes the genoa sail and the spinnaker sail. These kinds of sails are more recent inventions. They are as large as the spinnaker sail, but they are not symmetrical. Unlike the genoa or the headsail, they are also not meant to be attached to the forestay, like the spinnaker sail.
The usefulness of this sail is that if the winds change from a pure dead run to a reaching point of sail, then sailors do not have to resort to using a spinnaker from a genoa, instead of being able to take advantage of different winds while still using the same sail as they were before. This kind of sail is still only meant for lighter and milder winds , but there is more flexibility with the gennaker than the genoa and the spinnaker sails.
Popular Sail and Mast Configurations
There are many different ways to place the sails we have learned about in the above section. We have compiled a list of some of the most popular ones so you can understand how these sails can be used to make a sailboat move through the oceans.

A sloop is by far the most popular configuration. It features a single mast, double sail (the mainsail and the headsail), and mast configuration. The headsail is located from the forestay on the mast to the top of it. The type of headsail used can also vary from a genoa, a spinnaker, or a gennaker sail.
Fractional Rig Sloop
A fractional rig sloop also features a single mast with a double sail setup similar to a sloop. However, what makes the fractional rig sloop different is that the forestay does not reach the top of the mast. This means the headsail is constricted to a smaller amount of surface than on a regular sloop, making it so that your sailboat captures less wind and moves slower .

Cutters are interesting because they’re like a sloop but with a second forestay. This can be useful because it allows them to carry two headsails (a mainsail and one of the jibs). Cutters are good for cruising because they offer a range of wind options, giving you more time to get from place to place.
This is a less common mast configuration than previous others on this list. This is because a ketch features two masts. There is a larger mast fit for the mainsail and the headsail and a smaller mast between the mainmast and the stern (the rear) of the boat. This kind of mast configuration is more commonly found among Northern European freighters or fishing boats. This mast configuration is also called the mizzen mast.

A schooner mast configuration features two or more masts. This is similar to the previous configuration, the ketch. It also features multiple sails. While a ketch’s aft mast (also known as the rear mast) is higher than the forward mast, a schooner’s aft mast is shorter than the forward mast. A schooner can also have up to six masts (although two are the most common). These are the main differences between the two.
This one is quite similar to a ketch mast configuration (mentioned above). The only real difference between them is that the mizzen mast is put directly behind the sailboat’s rudder post in a yawl.
A cat sail will have one mast and one sail. The mast is put at the bow of the sailboat. This kind of mast configuration is often found on smaller boats, more specifically on dingy boats. Boats with the cat mast configuration are also often called catboats.
Final Verdict
Having the appropriate kind of sail on your sailboat is incredibly important. At the same time, being aware of the kinds of sails that there are and the kind of sail and mast configuration can make you into a more well-rounded and informed sailor. With that in mind, we hope that you leave this article feeling more confident in your skills when you are out at sea.

Boatsetter empowers people to explore with confidence by showing them a world of possibility on the water. Rent a boat, list your boat, or become a Boatsetter captain today.
Browse by experience

Explore articles

Florida senate approves new boating law, drops anchor on governor’s desk

10 Incredible Beach Camping Sites in the US

Boating Etiquette Part 2: A few more boating tips for beginners

Why Cape Coral Needs to be Your December Destination

- Find A School
- Certifications
- North U Sail Trim
- Inside Sailing with Peter Isler
- Docking Made Easy
- Study Quizzes
- Bite-sized Lessons
- Fun Quizzes
- Sailing Challenge

From Landlubber to Old Salt: Beginner Sailing Tips
By: Zeke Quezada, ASA Learn To Sail

Getting started with sailing is not as difficult as it may seem. When you get ready to head out onto the water you’ll want a little bit of information to ease your mind. Here are some beginner sailing tips for making sure you have a safe, fun, and successful voyage.
1. Pick a day with favorable conditions and dress appropriately. Depending on your area, good conditions come in a variety of shapes and sizes. Generally, you want fairly calm seas and lighter rather than stronger winds. Sunshine and 0% chance of precipitation is a plus! Remember that it is often windier and cooler out on the water than it is on shore, so dress appropriately.
The Art of Sailing
- Understanding Points of Sail The direction of the wind dictates the direction a sailboat can sail. The Points of Sail describe the range of courses a sailboat can and cannot travel.
- Understanding the Sails The sail is the driving force of the boat. A sailboat is only as good as its sails when you consider that capturing the wind’s energy is the premise behind what sailors do to propel their boats in a forward direction.
- Understanding the Wind A sailor’s world revolves around the wind and staying aware of the wind’s direction is crucial. Your ability to accurately sense changes in the wind, its speed and its direction will improve as you learn.
2. Have the right boat. When you’re learning, a smaller, more responsive boat makes it easier to understand the dynamics of sailing. ASA 101 courses are taught on 22′ keelboats, which are bigger and sturdier than a dinghy, but small enough that you can really feel the forces of wind and water acting on the boat.

3. Be aware of the boom. The boom is the big, heavy bar at the foot of the mainsail. It swings across the boat whenever you tack or gybe, and you really don’t want it to hit you. It can injure you and even knock you overboard, but it’s easy to avoid as long as you’re paying attention. Whenever you hear talk of tacking or jibing, make sure you’re down in the cockpit, well out of the way. Experienced sailors also know how to control the movement of the boom, mainly by “sheeting in” when preparing for a tack or gybe, as allowing it to move freely causes unnecessary wear on the boat. By a combination of common-sense safety and good sail-handling, you can ensure that there’s no danger or unpleasantness.

Learn to sail right on your mobile device. This easy to use sailing tool will get you started on your sailing education.
4. Go with someone who knows what they’re doing. We recommend an ASA instructor. An experienced, trained teacher of sailing will make a world of difference–the difference between a frustrating, unfulfilling experience, and a safe, fun, highly educational experience.
5. Know some basic sailing terms before you go. ( We’ve previously covered important sailing terms here. ) Learning basic terms such as “tack” and “gybe,” the difference between port and starboard, and the points of sail, is recommended. This will make it easier for you to contribute to sailing the vessel. Once you’re safely back at the dock you can expand your nautical vocabulary to include key phrases such as “beer,” “rum,” and “more beer and rum, please.”
If you do these five things, you’re setting yourself up to have a great time sailing, whether you’re a beginner or a seasoned plougher of the high seas. The best way to combine them all into one experience is to sign up for an ASA sailing course at one of our 300 schools nationwide. Find a sailing school near you here.
Learning to Sail
- ASA 101: What You’ll Learn ASA 101 is your in troduction to Basic Keelboat Sailboat and is your key to a lifetime of sailing.
- How To Sail Sailing a boat is part art and part skill but few activities offer such a variety of pleasures as sailing. Something special occurs when you cast off the lines and leave your cares at the dock.
- 7 Tips For The Beginning Sailor There are the obvious things you need when you go sailing, sunscreen, a hat, a windbreaker, non-skid shoes, and wind. However, what do you really need to be ready to head out on the water?
- How To Learn To Sail You won’t have to buy a boat or learn a new language or buy a new wardrobe to get a taste for sailing. You can dictate how much you want to experience.
- Learning To Sail Is Just The Beginning Sailing means different things to different people. At ASA we understand that learning to sail is just the beginning of a relationship with a lifestyle that is infectious. Where will sailing take you? We have a few ideas but how you view sailing is the most important.
- What Is Your Role on a Boat? What type of sailor are you and what role do you take on the boat? Your ASA sailing education will prepare you to be a skipper on a sailing vessel and with that comes the responsibility of keeping your crew safe and ensuring the safety of the vessel you are sailing.
Related Posts:

- Learn To Sail
- Mobile Apps
- Online Courses
- Upcoming Courses
- Sailor Resources
- ASA Log Book
- Bite Sized Lessons
- Knots Made Easy
- Catamaran Challenge
- Sailing Vacations
- Sailing Cruises
- Charter Resources
- International Proficiency Certificate
- Find A Charter
- All Articles
- Sailing Tips
- Sailing Terms
- Destinations
- Environmental
- Initiatives
- Instructor Resources
- Become An Instructor
- Become An ASA School
- Member / Instructor Login
- Affiliate Login
Better Sailing

Names of Sails on a Sailboat
Are you a beginner sailor and want to get acquainted with the names of the sails? Are you an experienced sailor and want to learn more details about the sails on a sailboat? Then this article is written for you! Sails form a crucial part of the sailboat because without them, there’s no starting up. For that reason, there are many details about different types of sails concerning their utility, functionality, fabrication materials, and performance. Simply put, each sail serves different purposes when out on the water. Since the sail is the engine of your sailboat, in terms of it being the basic source of propulsion, it’s important to know when best to use either type of sail and why.
Types of Sails on a Sailboat
So, in order to better explain the types of sails, let’s look at their characteristics. The first important distinction between sails is their placement. Generally, the mainsail is placed aft of the mast , which means behind. On the contrary, the headsail is in front of the mast. There are also other sorts of sails that are used for specific conditions. These can be the spinnakers or balloon-shaped sails for downwind use. The second important distinction for the sails is their functionality. The specialized sails have different functionalities and are used in different sailing circumstances and weather conditions. A rule about sails is that large sails are appropriate for downwind use, whereas small sails are good for upwind use. Moreover, large sails perform better on weak winds while small sails are good for strong winds.
The Parts of a Sail and its Shapes
- Head: This is the top of the sail.
- Luff: The forward edge of the sail.
- Leech: Back edge of the sail.
- Tack: The lower front corner of the sail.
- Clew: The bottom back corner of the sail.
- Foot: Bottom of the sail.
There are two sail shapes, the fore-and-aft rigged sails, and square-rigged sails. Nowadays, fore-and-aft sails are more popular, have better performance and maneuverability. To grasp the idea square sails are the ones that Vikings had on their ships and are good at sailing downwind because they run from side to side. But they’re not suitable at all when sailing upwind. On the other hand, a fore-and-aft sail is tied from the front of the mast to the stern and is much better at sailing upwind.

Also Read: What is Sailboat Rigging?
Types and Names of Sails
There are a lot of reasons why you’d want to put one sail over another, but the most important thing to remember has to do with the point of your sail and the wind strength. These points help you understand how your sailboat generates wind power. These points of sail include: into the wind (in irons), beam-reaching, broad-reaching, close-hauled, close-reaching, and running. They all go from windward to leeward and are symmetric from port to starboard . So, let’s get to the point and see the names and explanation of each sail:
- Mainsail : The large sail behind the mast which is attached to the mast and the boom, is called the mainsail. Mainsails cover a lot of surface area concerning incoming winds and by doing that they don’t need very strong winds to provide forward propulsion on a sailboat.
- Headsail or Jib : The small sail placed in front of the mast, attached to the mast and forestay (ie. jib or genoa), is called the headsail. Headsails are smaller than mainsails, thus their surface area is smaller. As a result, they can’t catch the same wind as a mainsail does. However, this is important because in case that the current wind is strong and the mainsail has been enough trimmed, being able to remove the mainsail and depend on the headsail alone, is a good strategy in order to reduce speed.
- Genoa : A genoa is like a large jib and it’s attached to the front of the forestay, like a headsail. When you use a genoa sail then you are expecting light to medium winds. Also, your sailboat would be somehow in a rush point of sail, meaning that the wind comes directly from the rear. Moreover, the surface area of a genoa sail is quite large, so it’s important to use it when winds are relatively low.
- Spinnaker : These downwind sails are symmetrical which makes them more sensitive to the reaching points of the sail and therefore more suitable for the running point of sail. Spinakkers are lighter than other types of jibs, and they don’t cover the mast like a genoa sail. Moreover, they remain unattached to the forestay and stretch out toward and past the bow of a sailboat.
- Gennaker : Gennakers are a mixture of genoa and spinnaker sails. There are small and big gennakers and both are downwind sails. They aren’t as symmetric as a spinnaker and aren’t attached to the forestay like a headsail. Furthermore, the gennaker sail is able to take on a more flexible point of sail while taking advantage of softer winds.
- Drifter Reacher : A drifter is a light air sail, and it’s basically a larger genoa for use in light winds. Its extra sail area offers better downwind performance than a genoa. It’s mostly made from lightweight nylon.
- Code Zero Reacher : This sail is a type of spinnaker, but it looks like a large genoa. However, code zero is designed for better reaching which makes it much flatter than the spinnaker.
- Windseeker : This sail is small, and it’s designed to guide light air onto the lee side of the mainsail. Moreover, it’s tall and thin and ensures a smoother flow of air.
Sail and Mast Configurations
Now that you got an idea of the different types of sails on a sailboat, it would also be an advantage to know how these types of sails are related to the configuration of a sailboat’s mast. There are numerous combinations when it comes to sails and mast configurations, let’s see some of them!
- Cat: A cat is similar to a dinghy and has one mast and one sail. The mast is located at the bow of the sailboat.
- Sloop: The sloop has the classic single mast and a double sail setup. The headsail can be different kinds of jibs, is connected with the forestay on the mast, and runs all the way up to the mast.
- Fractional Rig Sloop: A fractional rig sloop is different from the sloop because its forestay doesn’t reach the top of the mast. Its headsail is restricted to a fractional amount of space and this means that less wind can be captured, therefore the speed of the sailboat is reduced.
- Cutter: Having two forestays on the mast and cutters that are able to house two headsails this setup allows easy cruising because it offers a wide combination of points of sail for different strengths of wind.
- Ketch: Just like a sloop the ketch has a mast that enables the mainsail and headsail to a full range forestay. However, it also has a smaller mast between the mainmast and the stern of the sailboat.
- Schooner: A schooner is when a sailboat has two or more masts but it has a couple of sails to manage. A schooner’s aft mast is taller than the forward mast and sometimes a schooner can have up to six masts.
Names of Sails on a Sailboat – Summary
So, how many types of sails are there? In general, sailboats have one mainsail and one headsail. The rigging also affects the types of sails you can use. As we’ve explained before, the mainsail is a fore-and-aft Bermuda rig. Then, for a headsail, we use a jib or genoa. Most experienced sailors use extra sails to ensure better performance for their sailboat. For example, the spinnaker (a common downwind sail), the gennaker, the code zero (for upwind use), and the storm sail. Keep in mind that every sail has its own use and performance. Want to go downwind fast? Use a spinnaker. Don’t just raise any sail you think suits you best and go for it! It’s of great importance to understand the functionality, use, and performance of each sail.
Peter is the editor of Better Sailing. He has sailed for countless hours and has maintained his own boats and sailboats for years. After years of trial and error, he decided to start this website to share the knowledge.
Related Posts

Lagoon Catamaran Review: Are Lagoon Catamarans Good?

Best Inboard Boat Engine Brands

Are O’Day Sailboats Good? A Closer Look at a Classic Brand

Why Do Sailboats Lean?
- Buyer's Guide
- Destinations
- Maintenance
- Sailing Info
Hit enter to search or ESC to close.
Yachting Monthly
- Digital edition

How do solo sailors sleep at sea? Experts share their tips and advice
- February 27, 2024
When Andy Pag was planning a 450-mile solo passage, sleep was the biggest source of worry. Here’s how he created an effective solo sleep routine

When I was planning my first solo offshore sail on my Lagoon 410 Cushla , from Grenada to Bonaire, my biggest concern was not the risk of pirates off the coast of Trinidad, or the night-time squalls that might sneak up unseen in the trade winds. Even the risk of falling overboard and watching the boat sail away as I drifted alone in the current wasn’t giving me restless nights. The concern I was losing sleep over was sleep, and how I could ensure I’d get enough sleep when stewarding the boat on the four-night passage.
I know I don’t function well when suffering from a lack of sleep. I get irritable and make bad decisions. More specifically, I struggle to distil the relevant factors from everything going on around me when making vital decisions. My forward-planning goes out of the window and my actions become reactions to the most obvious and immediate factors. It’s not a good mental state to be in when the wrong decision can be costly, cause injury and sometimes be fatal.
Coincidentally, the Grenada Hash, an orienteering event held weekly around the island, was useful training. During the first weeks of participating on the run, I found the combination of being physically tired and having to make navigation decisions very frustrating, but over time I developed the skill of dedicating bodily energy and time to thinking and decision-making. Practising that mental shift was very useful when tired at sea.

Professional sailors, like 2018-19 Golden Globe Race winner Jean-Luc Van Den Heede, know that prioritising sleep is essential when making vital decisions. Photo: Christophe Favreau/PPL/GGR
Short naps when solo sailing
I do find it easy and beneficial to nap, and on the advice of a friend I downloaded an app called Interval Timer onto the boat’s tablet. It sounds regular alarms throughout the day. I set this to go off every 15, 30 or 45 minutes, depending on the circumstances, but importantly I let it run day and night so whenever I felt I could sleep I would just lie down, knowing I’d be woken within the given timeframe.
With clear skies, no traffic and far from land I set it to a longer interval, and shortened it when circumstances changed.
I tried to make life easier for myself and simplify processes I’d need to do when I knew I’d be tired by making checklists on post-it notes stuck around the boat.

Keep your energy levels up with decent meals, hot drinks and plentiful snacks. Photo: Yachting Monthly
Fuel yourself properly
Food and water are important ingredients for getting good sleep. My sleep is light and fitful on an empty stomach, and my decision making is also affected when I’m hungry or dehydrated. I made sure I had easy access to water with bottles dotted around the boat in easy reach. I didn’t drink coffee, and instead of brewing a cup of tea whenever I felt sleepy, I’d just take a nap.
I created a big snack basket that lived in the companionway containing mixed nuts, biscuits and fruit, and I kept chocolate in the fridge to give me an energy hit whenever I felt foggy or lethargic. I also made a habit of cooking meals in advance that would just need reheating or could be eaten cold from the fridge.
Article continues below…

Man overboard: tactics that really work for couples
The YM team get wet to see how well the MOB process works for shorthanded sailing. Here are our findings...

How To Climb A Mast Solo And Short Handed
How to climb a mast solo: Step by step guide If you’re here because you want to know how to…
Clutter-free sleep zone
Having a comfy place to sleep also helped. I find it tempting to share the bed with whatever clutter I can’t be bothered to put away, but I put a mattress in the cockpit and kept it clear of mess to remove distractions from sleep. Away from an internet signal it was easy to resist the temptation for screen time when lying down.
An eye mask also helped prolong sleep at dawn, and made it easier to doze off in the middle of the day. I developed a Pavlovian response to the snugness of the mask which helped trigger a deep sleep whenever I grabbed it and put it on.

Reduce backlighting on your instruments, and turn off any that you don’t need. Photo: Graham Snook/Yachting Monthly
Power is instrumental
As well as keeping your own batteries charged, the boat batteries also need to have reliable charge. As the power drains, the autopilot can become unreliable, disconnecting at low voltage. Cushla, our 1998 Lagoon 410, has 1kW of solar panels and although we can, we’ve never needed to charge the house batteries from the engines or shore power. But overnight passages are the toughest test of the system.
The sails can create shading on the panels for several hours of the day, and running the instruments 24/7 is a significant drain, especially the radar which can draw three or four amps when operating, and even draws a couple of amps when in standby mode.

Make yourself sort problems straight away, rather than leaving them for later when they can compound. Photo: Andy Pag
The boat has an AIS transponder, and offshore I felt pretty confident that other traffic would also be transmitting an AIS signal to fire my proximity alarm. Radar is useful for spotting rain squalls at night or when low cloud masks approaching rain.
I made the mistake of not learning how to set the proximity alarm on my Raymarine C80 chart plotter in advance, and when I came to do it for the first time, I found it frustratingly unintuitive. Lesson learned; become familiar and practiced with the menu functions you will need before setting off.
Don’t put things off
If anything was niggling on my mind it would stop me falling asleep so I’d make sure to deal with anything that could cause me anxiety; tidying the lines, checking the course heading, and a final, slow 360° sweep for traffic or weather. Picking a weather window where squalls would be less likely and using a modest sail plan that was easy to manage also reduced my anxieties.
I felt exhausted as I finally pulled in to the moorings of Bonaire, but not as tired as I thought I would be. The satisfaction of self-reliance, completing 440 miles solo, and the connection with the sea I experienced alone offshore are all highlights of my time as a solo skipper, and the sail will remain a formative experience.

Jean-Luc Van Den Heede
Jean-Luc Van Den Heede’s solo sailor sleep advice
Jean-Luc Van Den Heede holds the record for the fastest westward circumnavigation, sailing it solo, faster than any crewed boat. He is 77.
‘I always try to sleep enough. I sleep for 90mins and wake to check everything’s ok, and if there’s a job to do, I do it. Or I go back to sleep. ‘In 1991 researchers measured my sleep cycle with 16 electrodes over two days. People looked at me funny going around town with wires on my head.
‘But that’s how they came up with the 90-minute figure. I do it even when I have crew. It really works for me.
‘I can wake immediately and be able to do anything in two seconds. It’s a characteristic of mine, but it’s developed over time sailing alone. It wasn’t like that in the beginning when I started my first solo navigation. Now I can sleep at any time. In three to five minutes I’m sleeping, even at three in the afternoon. I just close my eyes, empty my head and that’s it.
‘In long races like the Golden Globe Race it’s good to have a good rest, and good sleep. Always be sure your mind is ok. The main problem on the GGR, was when the wind shifts, the boat changes heading.
‘If you’re cruising offshore, today with a good AIS alarm and a windspeed alarm, you can sleep a long time. Four hours is no problem. But if you’re close to shore, you have to be awake because of fishermen and sailing boats without AIS.
‘It’s important to stay optimistic. If you’re afraid of something you cannot sleep. It’s better to be in good shape at the end of the storm or low pressure, so it’s important to have a good rest before, and not to be tired when the wind is strong. I try to sleep at the start of storm, and to be in good shape when it is in the final phase.’

Laura Dekker
Laura Dekker’s solo sailor sleep advice
Laura Dekker sailed around the world solo aged just 14. She now teaches young people ocean sailing and personal development.
‘I am always very conscious of every action I take on board; every sound, every movement – anything strange. I try not to jump to conclusions before checking out all the factors.
‘If I am very sleep deprived my brain sort of fogs up and things go through my mind much slower then normal. But I do take heed to still go through the whole process before making a decision and not just jump ahead because it’s taking too long.
‘I sleep when I can, no matter what time of the day or how long it may be, including lots of 10-minute naps. I will always put rest and sleep ahead of anything “fun” I may have had in mind, so it goes ahead of reading or playing music, for example.
‘Never think “Oh I will sleep later,” if you can sleep now. Things change very quickly at sea and there’s a chance you may not be able to sleep for a long time.
‘Set multiple alarms for which you have to get out of bed to turn off. It’s just too easy to sleep through or fall asleep again.
‘There’s often only a need to check around quickly in between naps, so sleep for 30 mins, wake up, check the horizon, course and sails. At night, shine a torch around your rigging – this takes about 10 minutes, then sleep another 30 minutes.
‘The longest I ever slept in one stretch is one hour, that is with clear visibility on open sea. Big ships travel between 15-20 knots. Visibility at sea when it’s good is no more then 10 miles, so in theory, in 30 minutes you can go from not seeing it to being run over. Better to wake up more often and check quickly then go back to sleep. Close to shore this problem gets worse as there are often little boats with minimal lights that can only be seen from a mile.’

Understanding sleep cycles helps when planning how long to sleep for. Photo: Andy Pag
What the scientists say
When you’re asleep you cycle through four stages of sleep. Three non-REM phases (N1, N2 and N3) and REM sleep. The first one, N1 is nodding off, the second is preparing you for deep sleep, and N3 is where the brain, bones and muscles fully relax and do their healing and get reset for the next period of wakefulness.
In N3 you are hardest to wake and can even sleep through loud noises or the boat jolting. If you are woken from N3, you may feel foggy for up to half an hour. REM sleep is a lighter stage of sleep but it’s when you dream. Your body immobilises itself so you don’t physically act out those dreams.
During an uninterrupted night’s sleep most people cycle through the four stages every 90-110 mins.
Research published in 2007 showed being sleep-deprived leads to riskier decision making and a more blasé attitude to things going wrong.
What the law says about solo sailing
Colregs Rule 5 states: ‘Every vessel shall at all times maintain a proper look-out by sight and hearing as well as by all available means appropriate in the prevailing circumstances and conditions so as to make a full appraisal of the situation and of the risk of collision.’
So ask yourself, if something went wrong, and you were asleep or sleep-deprived, could you justify your actions as appropriate for the circumstances?
If you enjoyed this….
Yachting World is the world’s leading magazine for bluewater cruisers and offshore sailors. Every month we have inspirational adventures and practical features to help you realise your sailing dreams. Build your knowledge with a subscription delivered to your door. See our latest offers and save at least 30% off the cover price.
trending now in World News

Girl, 11, loses her entire family in horror car crash after...

3-fingered 'alien mummies' found in Peru have fingerprints that...

Jose Cuervo tequila factory explosion kills at least six,...

First male rape survivor of Hamas' October 7 attack describes...

IDF recovers body of kindergarten teacher kidnapped by Hamas on...

Harrowing CCTV shows woman hiding inside shop after alleged gang...

Surfer's leg washes up after shark attack, doctors scramble to...

Monday broke record for hottest day on Earth ever
Bodies of thrill-seeking couple mysteriously found in life raft after duo set sail on cross-ocean voyage in yacht over a month ago.
- View Author Archive
- Email the Author
- Get author RSS feed
Contact The Author
Thanks for contacting us. We've received your submission.
Thanks for contacting us. We've received your submission.
The bodies of a thrill-seeking Canadian couple were found in a life raft Wednesday — nearly six weeks after they left on a sailing trip across the Atlantic Ocean, according to a report.
Brett Clibbery, 70, and Sarah Justine Packwood, 54, apparently abandoned their yacht and perished on a life raft before washing up on Sable Island, nicknamed the “Graveyard of the Atlantic,” the Vancouver Sun reported.
Canadian authorities have not officially identified the tragic pair as the victims, but told the outlet that the 10-foot life raft was believed to be from a larger vessel named Theros — the same eco-friendly boat the couple had routinely documented on their travel blog account.

Clibbery and Packwood set sail on the 39-foot yacht from Halifax on June 11 with plans to cross the Atlantic to the Azores, a series of islands 900 miles west of Portugal, by July 2.
The pair were documenting their journey on their YouTube channel “Theros Adventures,” which they used to demonstrate how to travel the world via electric-, wind- and solar-powered vessels.
Their trip to the Azores was meant to be the first fully “green” journey on Theros, which the couple dubbed the Green Odyssey after they removed its diesel engine.
They had tried to cross the Atlantic in the boat once before in 2019, but were stopped by a forecast of storms.

On the day of their journey, Clibbery and Packwood shared a video that put them 16 nautical miles off the coast of Nova Scotia with fair winds and calm seas.
The video was their last. They were reported missing one week later.
Sable Island is about 175 miles south of Halifax.
Theros is still missing, the Times Colonist reported.

What went wrong and why the couple abandoned their beloved boat is still a mystery.
The pair got married on the yacht in 2016, one year after they met during a chance encounter at a bus stop in London, England.
Packwood was preparing to donate a kidney to her sister when she met Clibbery, who was visiting from Canada — a heartwarming story that was the center of a 2020 “How We Met” piece in The Guardian.
“We have been traveling and co-creating adventures ever since,” Packwood previously posted on YouTube.

Advertisement

Couple in homemade yacht who died and washed ashore in a life raft could have been hit by larger ship, experts suggest
E xperts have offered theories about how a thrill-seeking Canadian couple’s attempted transatlantic sailing expedition turned tragic last month, positing their homemade vessel may have been struck by a much larger ship soon after they departed Halifax on the country’s North East coast.
Earlier this month, the bodies of Brett Clibbery, 70, and Sarah Justine Packwood, 54, were found on a life raft washed up on Sable Island, Nova Scotia.
The area is ominously nicknamed the “Graveyard of the Atlantic” due to the large number of shipwrecks that wind up on its shores.
An official investigation is underway, and although no concrete answers have yet come to light, one leading theory is that their boat was badly damaged by a much larger vessel, forcing the couple to seek refuge in the life raft.
“While they do not have conclusive proof, [investigators] suspect the sailboat … was struck by a bulk carrier likely only a few days after departing Halifax,” a source close to the investigation revealed to Saltwire .
Investigators have reportedly inspected a carrier ship that was in the same area as the couple’s boat — named Theros — at the outset of its voyage, but the results of the probe have not been released to the public.
“The crew of the carrier ship told investigators there were no signs of damage and they were unaware of any collision with a smaller vessel,” the Daily Mirror writes.
The source surmised that the ship’s homemade additions might have presented additional problems, and veteran sailors told the outlet the excessive ballast from batteries and solar panels could have destabilized the boat.
The pair set sail June 11 on a journey that was supposed to take them across the Atlantic Ocean from Halifax to the Azores in their 42-foot yacht, which the couple built themselves.
The eco-friendly boat, which operated without a diesel engine, was due to arrive at its destination by July 2, to serve as a demonstration of how it’s possible to travel the world with electric, wind and solar-powered vessels.
The excursion was to be the couple’s first fully “green” journey on Theros, the building of which the couple chronicled on their YouTube channel, “Theros Adventures.”
Despite the swirling theories about how the doomed voyage turned deadly, the Canadian transportation safety board has not made any formal announcements indicating what happened
“At this time, we cannot say with complete certainty that the sailing vessel was struck by a ship, as we are still gathering information regarding the overdue sailing vessel Theros,” a spokesman said.
Clibbery and Packwood married on the yacht in 2016, one year after they met during a chance encounter at a bus stop in London, England.
Packwood was preparing to donate a kidney to her sister when she met Clibbery, who was visiting from Canada — a heartwarming story that was the center of a 2020 “How We Met” piece in The Guardian.
“We have been traveling and co-creating adventures ever since,” Packwood previously posted on YouTube.
Clibbery’s son, Brett, posted a loving tribute to the couple on Facebook, acknowledging the last few days had been really hard for the family, and news to emerge from the investigation has left it “hard to remain hopeful.”
He continued, “They were amazing people, and there isn’t anything that will fill the hole that has been left by their, so far, unexplained passing.
“Living will not be the same without your wisdom, and your wife was quickly becoming a beacon of knowledge, and kindness. I miss your smiles. I miss your voices. You will be forever missed.”

Orcas sink sailing yacht in Strait of Gibraltar
An unknown number of orcas have sunk a sailing yacht after ramming it in Moroccan waters in the Strait of Gibraltar, Spain’s maritime rescue service said on Monday, a new attack in what has become a trend in the past four years.
The vessel Alboran Cognac, which measured 15 metres (49 feet) in length and carried two people, encountered the highly social apex predators, also known as killer whales, at 9 a.m. local time (0700 GMT) on Sunday, the service said.
The passengers reported feeling sudden blows to the hull and rudder before water started seeping into the ship. After alerting the rescue services, a nearby oil tanker took them onboard and transported them to Gibraltar.
The yacht was left adrift and eventually sank.
The incident is the latest example of recurring orca rammings around the Gibraltar Strait that separates Europe from Africa and off the Atlantic coast of Portugal and northwestern Spain.
Experts believe them to involve a subpopulation of about 15 individuals given the designation “Gladis.”
According to the research group GTOA, which tracks populations of the Iberian orca sub-species, there have been nearly 700 interactions since orca attacks on ships in the region were first reported in May 2020.
Researchers are unsure about the causes for the behaviour, with leading theories including it being a playful manifestation of the mammals’ curiosity, a social fad or the intentional targeting of what they perceive as competitors for their favourite prey, the local bluefin tuna.
Although known as killer whales, endangered orcas are part of the dolphin family. They can measure up to eight metres and weigh up to six tonnes as adults.
Couple Who Set Sail In Self-Built Eco-Friendly Yacht Found Dead In Lifeboat
Brett clibbery and sarah packwood embarked across the atlantic ocean, sailing from halifax to the azores in their self-built, eco-friendly yacht, theros..

The couple had left Halifax Harbour on June 11 aboard their yacht. (File)
A British-Canadian couple, who set sail across the Atlantic Ocean roughly six weeks ago, were found dead in a lifeboat off the coast of Canada. The bodies of Brett Clibbery and Sarah Packwood were discovered after their raft washed ashore on Sable Island, off the coast of Nova Scotia, reported the NY Post .
The pair had embarked on an ambitious journey across the Atlantic Ocean, sailing from Halifax to the Azores in their self-built, eco-friendly yacht, Theros. The 42-foot vessel, powered solely by electric, wind, and solar energy, was intended to demonstrate the feasibility of sustainable travel. The couple had been posting about the construction of Theros on their YouTube channel, "Theros Adventures," and this voyage was to be their inaugural fully "green" journey.
They left Halifax Harbour on June 11 aboard their yacht bound for the Azores region of Portugal. They were reported missing on June 18 and found three weeks later on July 10.
While initially reported to be from British Columbia, it is believed that Ms Packwood was from the UK and Mr Clibbery was from Canada. Formal identification is still pending.
The cause of death is not yet known. The Royal Canadian Mounted Police are investigating the incident.
Their sailboat, Theros, was severely damaged, and investigators suspected that it was struck by a larger vessel.
The area they were sailing in is notoriously known as the "Graveyard of the Atlantic" due to the large number of shipwrecks that occurred there. The exact circumstances of the incident are still unknown, but investigators are exploring several theories.
One leading theory is that Theros was hit by a bulk carrier, which may have caused significant damage to the sailboat. Investigators have inspected a carrier ship, which was in the same area as Theros at the time of the incident, but they have not released their findings, as per the Saltwire .
Promoted Listen to the latest songs, only on JioSaavn.com
The crew of the carrier ship reported that they did not notice any damage or collision, the Mirror reported. Some veteran sailors have suggested the homemade additions to Theros may have contributed to the tragedy, particularly the excessive weight of batteries and solar panels, which may have destabilised the boat.
Brett Clibbery and Sarah Packwood met by chance in 2015 at a bus stop in London. At the time, Ms Packwood was preparing to donate a kidney to her sister, while Mr Clibbery was visiting from Canada. This chance encounter led to them eventually falling in love and getting married on their yacht, Theros, in 2016.

Track Budget 2023 and get Latest News Live on NDTV.com.
Track Latest News Live on NDTV.com and get news updates from India and around the world .
India Elections | Read Latest News on Lok Sabha Elections 2024 Live on NDTV.com . Get Election Schedule , information on candidates, in-depth ground reports and more - #ElectionsWithNDTV
Watch Live News:
- Share full article
Advertisement
Supported by
Couple Who Attempted to Cross Atlantic Found Dead in Lifeboat
James Brett Clibbery and his wife, Sarah Justine Packwood, had left Nova Scotia on June 11, bound for the Azores. The authorities recovered remains believed to be theirs earlier this month.

By Derrick Bryson Taylor
The bodies of two sailors who planned to sail from Nova Scotia to the Azores using green energy were found washed ashore at a Canadian national park this month, four weeks after they were last seen, the authorities said.
The Royal Canadian Mounted Police responded to calls on July 10 that a 10-foot inflatable lifeboat containing human remains had been discovered on Sable Island National Park Reserve, according to a news release from the agency .
The authorities did not identify the remains, but said they believed they were those of a 70-year-old man and a 60-year-old woman from British Columbia. A Facebook post by the man’s son, James Clibbery, later identified them as James Brett Clibbery and his wife, Sarah Justine Packwood, who had left Halifax Harbor in Nova Scotia on June 11 bound for the Azores. They were reported missing on June 18.
“The past few days have been very hard,” the younger Mr. Clibbery said in the post, adding that DNA tests would be carried out to confirm their identities. “With all the news, it is hard to remain hopeful.”
“There isn’t anything that will fill the hole that has been left by their, so far unexplained, passing,” he said.
The Royal Canadian Mounted Police said it was investigating the deaths. A spokesman for the agency did not immediately return a request for comment on Monday.
Sable Island is a “thin crescent of shifting sand” that is about 180 miles southeast of Halifax, Nova Scotia, the Canadian government said , adding that the area is widely known for its variety of wildlife and its proximity to more than 350 shipwrecks.
The couple had chronicled much of their sailing activities and travels on social media.
In a video on their YouTube channel , Theros Adventures, the elder Mr. Clibbery said they had named their trip to the Azores “The Green Odyssey” to show it was possible to travel without burning fossil fuels. Their 42-foot GibSea sailboat was powered by electricity and solar energy, the couple said.
“It is to show that you can travel, and you can do long distances without burning fossil fuels, without climbing onto a plane and filling the air with carbon dioxide,” Mr. Clibbery said.
In their final post on social media on June 11, Mr. Clibbery, wearing a bright orange jacket with his silver hair tossing in the wind, described how the trip was just beginning.
With his hands steady on the helm, he took note of their speed and the distance they had so far traveled. Mr. Clibbery then looked at the camera and said with a smile, “We’re sailing.”
Derrick Bryson Taylor covers breaking and trending news and is based in London. More about Derrick Bryson Taylor

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
1. Attach the sails. Secure the bottom front ( tack) of the mainsail and jib to their respective shackles on the boom and the bow of the boat. There will be a small line ( outhaul) attaching the rear corner of the mainsail ( clew) to the end of the boom. Pull it so the foot of the main is taut, and cleat.
Join me on a comprehensive sailing lesson. I teach you the basics you need to know to begin sailing, from vocabulary and parts of the boat to getting underwa...
How to sail. Simple and practical demonstration of how to sail on a sailboat.http://www.alivesailing.com/https://www.instagram.com/skipper_igor/SUBSCRIBE to ...
Sailing a yacht, with its billowing sails and the gentle sound of water against the hull, is an enchanting experience that beckons adventurers and dreamers alike. Whether you've always been drawn to the allure of the open waters or you simply seek a new and exhilarating hobby, setting sail on a yacht is an extraordinary journey that awaits you. ...
A boat can't sail directly into the wind, but it can sail toward the wind, as close as about 45 degrees off the wind's direction. As you turn toward the wind from a beam reach to a close reach to close-hauled, you must gradually trim your sails to keep them from luffing. Once the sails are trimmed in all the way, your steering keeps them from ...
Sailing is the art of taking a boat, turning off the motor, and harnessing the power of the wind to make the boat go where you want it to go. It might seem difficult, but it is really very simple, provided you take the time to understand how the boat utilizes the power of the wind. More than likely your boat will also have a motor (for times ...
GYBE: (jibe) when sailing with the wind, to move the sails from one side of the boat to the other by moving the stern through the eye of the wind. WINDWARD: the direction that the wind is blowing from, also upwind. LEEWARD: the direction that the wind is blowing toward, also downwind. LINE: a rope on a boat.
When the wind passes across the stern of the boat, we jibe, and the sails switch to the other side of the boat. As the angle of the wind changes we need to adjust or "trim" our sails. A sail perfectly trimmed for a broad reach will luff when on a close reach. When sails luff, they stop propelling the boat forward.
Dock or Anchor the Boat. Now you're out there sailing and you've got the boat under control. Learn how to go faster, dock or anchor the boat and use some of the equipment you've ignored so far. Take a look at some of these additional sailing skills. Practice Tying Knots. For thousands of years, sailors have used times where it is cold or ...
Trim your sails accordingly (left). Tacking a boat is the act of changing course by swinging the bow of the boat through the direction of the wind. When sailing as close to the breeze as possible, at an angle of about 40 degrees, a boat is said to be "closehauled" or "hard on the breeze" (right). Illustration by Mark Smith.
Learn to Sail. Your dream to learn to sail is close to becoming reality. Find a school, take a course and set off on your new adventure. ASA has everything you need to sail confidently and safely and you can start right now. We have compiled a list of tools and resources that will help you learn the basics of sailing before you get out on the ...
Sloop. A sloop is by far the most popular configuration. It features a single mast, double sail (the mainsail and the headsail), and mast configuration. The headsail is located from the forestay on the mast to the top of it. The type of headsail used can also vary from a genoa, a spinnaker, or a gennaker sail.
Foot - The bottom edge of the sail. Tack - Between the luff and the foot is the tack. The tack is attached to the boat or a spar. Head - The corner at the top of the sail between the luff and the leech. Clew - The third triangle of a sail between the leech and the foot. Batten - Solid slats or rods to help maintain the desired airfoil ...
The Art of Sailing. Understanding Points of Sail The direction of the wind dictates the direction a sailboat can sail. The Points of Sail describe the range of courses a sailboat can and cannot travel. Understanding the Sails The sail is the driving force of the boat. A sailboat is only as good as its sails when you consider that capturing the wind's energy is the premise behind what sailors ...
A sailboat refers to any class and subclass of boat that is designed with one or more masts and rigging system as the main source of propulsion. Sailboats are available in a variety of models and rigs, including racing boats, sloops, schooners, catamarans, trimarans, sailing cruisers, and others. Some of the first sailboats on record date back ...
Learn to sail vacation for beginners. September 07, 2023 8 min. All around the world there are treasures to discover, hidden gems to uncover and lifelong memories to make. Going on a learn to sail vacation abroad gives you the unique opportunity to visit idyllic islands and experience the world in a completely new way.
Sailing is a fun activity for people of all experience levels. In fact, learning to sail a basic boat is relatively easy—in the right environment, you can start cruising with minimal experience. However, the idea of a beginner commanding a 55-foot ketch in the middle of the Atlantic Ocean is a bit ridiculous.
Luff: The forward edge of the sail. Leech: Back edge of the sail. Tack: The lower front corner of the sail. Clew: The bottom back corner of the sail. Foot: Bottom of the sail. There are two sail shapes, the fore-and-aft rigged sails, and square-rigged sails.
When I was planning my first solo offshore sail on my Lagoon 410 Cushla, from Grenada to Bonaire, my biggest concern was not the risk of pirates off the coast of Trinidad, or the night-time squalls that might sneak up unseen in the trade winds.Even the risk of falling overboard and watching the boat sail away as I drifted alone in the current wasn't giving me restless nights.
Find Sail boats for sale in United States. Offering the best selection of boats to choose from. ... United Yacht Sales - Pacific Northwest, Western Canada and BC | Billings, Montana. 2024 Yamaha Boats 255 FSH Sport H. US$97,399. Performance East Inc | Goldsboro, North Carolina. 2024 Yamaha Boats 252 FSH Sport. US$78,699.
There are many kinds of sailboats and they carry different rigs (masts, supporting shrouds and stay, and sail combinations). Sloops have one mast and generally two sails - a mainsail and a headsail called a jib or genoa. If there are two headsails, the boat is usually called a cutter rig.
Clibbery and Packwood set sail on the 39-foot yacht from Halifax on June 11 with plans to cross the Atlantic to the Azores, a series of islands 900 miles west of Portugal, by July 2.
On a sailboat, you may not have that luxury. 8. Material. Material matters, whether it is affecting the cost or the sturdiness, it is something to consider. A yacht will be made of fiberglass, carbon fiber, and metals such as titanium. A sailboat, on the other hand, will likely be made from wood or fiberglass.
The pair set sail June 11 on a journey that was supposed to take them across the Atlantic Ocean from Halifax to the Azores in their 42-foot yacht, which the couple built themselves.
Jeanneau Sun Odyssey 380. 2022 Jeanneau Sun Odyssey 380. Image credit: Jeanneau. While smaller than other sailboats on the market, the Jeanneau Sun Odyssey 380 shouldn't be written off when you're shopping. What this boat may lack in size, it makes up for in performance and features. One of the best aspects of having a smaller sailboat is ...
The vibrant buzz of the Minnesota Yacht Club Festival speaks to a tradition of community and celebration, a call to the masses to revel in shared experiences on the water.
An unknown number of orcas have sunk a sailing yacht after ramming it in Moroccan waters in the Strait of Gibraltar, Spain's maritime rescue service said on Monday, a new attack in what has ...
A British-Canadian couple, who set sail across the Atlantic Ocean roughly six weeks ago, were found dead in a lifeboat off the coast of Canada. The bodies of Brett Clibbery and Sarah Packwood were ...
The bodies of two sailors who planned to sail from Nova Scotia to the Azores using green energy were found washed ashore at a Canadian national park this month, four weeks after they were last ...
Video shows the moment a whale breaches onto a boat in Portsmouth Harbor, nearly sinking the vessel. 00:37 - Source: CNN. Trending Now 18 videos. Video Ad Feedback. Watch: Whale breaches water and ...