Yachting World
- Digital Edition


Baltic 67 review: Finnish superyacht yard goes back to its roots with no-compromise cruiser
- Toby Hodges
- March 28, 2019
When a renowned superyacht yard builds a 67-footer for short-handed cruising you can be sure the result will be something special

Were money no object and you wanted the ultimate yacht for long-term cruising, what would you choose? How large could you go without needing a paid crew? What do you really need length and space for and how important is displacement and potential speed to you?
These were the sort of questions crowding into my head on first viewing the sensational new Baltic 67 at the Cannes Yachting Festival . It is truly striking. The quality of the yacht is undeniably world class, but it’s the precision of design and engineering that soon absorbs you.
The owner of this first boat is a highly experienced cruising sailor, boat owner and navigator, so joining him for a 24-hour trial from Mallorca proved the ideal way to get under the gleaming composite skin of this athletic new model.
The concept is about combining the pleasure of pure sailing with ease of handling for long-distance cruising at high average speeds. It is the alternative to a full custom yacht – all the engineering is already calculated – but a great deal of flexibility has been worked into the design, with options including single or twin rudders, a fixed or telescopic keel, multiple cabin layouts, and a carbon or epoxy sandwich hull.
Wanting to return to its mid-size fast cruiser roots, Baltic Yachts teamed up with designers and fellow in-demand superyacht specialists Judel Vrolijk and Design Unlimited. The result is this exceedingly attractive, modern-looking sloop, with a powerful hull shape, a flush foredeck and a low-profile coachroof.

Powered sail handling systems means Manyeleti can be sailed by just two
The Baltic 67 is very much at the luxury and custom end of the production yacht scale, so our light wind trial of the boat focused more on the various choices and details aboard and how they might be relevant to sailors in general. Hull number one in particular had a lot of owner input.
Manyeleti , the first 67, belongs to Erik Lindgren. It is his fifth yacht from Baltic after a string of upgrades that started with a used 39 in 1989. “It’s very different to design and build your own boat – in my case using nearly 30 years of offshore sailing experience,” Lindgren explains.
Swede Lindgren travelled to the yard once a month and was in daily contact with the project manager, Kjell Vesto.
The Lindgrens’ plan is to head off on another world cruise in a couple of years time, when Erik’s teenage children have finished school. His shakedown sail involved a 5,000-mile trip from Finland to and around the Mediterranean.
“Not a single thing broke,” he reports, saluting Baltic’s build quality. “I could literally go to El Corte Inglés, stock up, fuel up and sail across the Atlantic.”

CNB 76 boat test – more boat for your money
It may sound daunting, but it seems 60ft is no longer a big boat. In typical Philippe Briand fashion the…

Walk the course with Mike Broughton- navigator onboard the brand new Baltic 115 Nikata
Start date: Monday 22nd February 2016 Course: Approx. 600nm non-stop around 11 Caribbean Islands Organised by: The Royal Ocean Racing…
The Baltic 67 is as big as you can go without needing a pro crew, argues Erik Lindgren. “I’ve spent a lot of time on World ARC boats… it’s the details that make living on board easier. This is a technical boat, but is less dependent on systems than our old Baltic 56. On the other hand it’s great to have aircon and a lifting keel.
“Half the time spent aboard will be for long distance stuff and holidays for the two of us, but a lot of the time will be spent with friends and family too.”
Privacy at this size is a big benefit. “I have no need to have a big boat for show,” says Lindgren, “but I wanted to have the things I need.”

The retractable arm for the anchor roller is an engineering masterpiece. It rises from the anchor locker at the touch of a button
The most important features he wanted, which help explain the jump in size from his previous 56, were a furling boom, a large, practical galley, four cabins and a tender garage large enough to house a forward-facing dinghy. While his yachts have grown and become more complex, Lindgren maintains that the methodical way Baltic builds boats results in a lot fewer problems.
A carbon furling boom is an eye-watering investment, but it does make the hoisting, reefing and lowering of sails a quick and largely hassle-free procedure. It can make the difference to whether you go sailing or not. Within minutes of leaving Palma’s breakwaters, we had main and jib unfurled and were matching the 8 knot wind speeds.
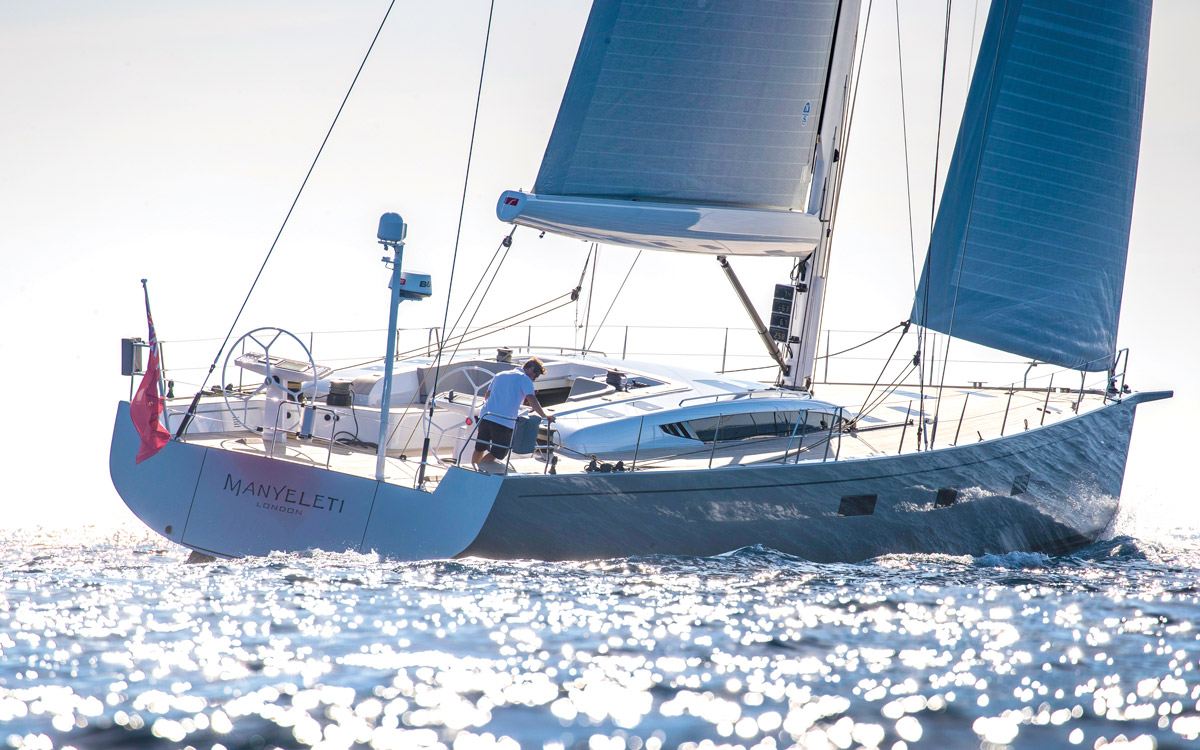

Manyeleti is hull number one in the Baltic 67 series
Easy performance
The Hall carbon boom uses an electric mandrel motor that is synchronised with the halyard to avoid too much sail spilling out during a hoist. The traveller is also electric, while the sheet car pullers, backstay, vang and furlers are hydraulically-operated. The result is the ease of push-button sailing typically used on modern performance superyachts.
We spent the first few hours reaching across Palma Bay. Despite having 24 hours aboard, the most breeze we found was 11 knots, which translated to 9.5 knots boatspeed – very respectable under white sails only (fully battened main and non-overlapping jib). The majority of the time was spent close-hauled, matching the single-figure wind, even exceeding it when it dropped below 6 knots.

Neat details: the forward end of the jib car puller, which is hydraulically powered
I found myself gravitating to the side deck to sit and steer, instinctively wanting to sail the Baltic 67 like a cruiser-racer. There are good views over the low coachroof and flush foredeck, but nothing except freeboard height to prevent a wet backside if the decks ship green water.
The helmsman can also sit forward of the wheel and reach the two winches. I like the way the primary is mounted inboard, though the positioning of the turning block for the jib sheet creates an obstacle on the side deck. Baltic reasons that it helps provide the option to use either winch for the sheet.
Speed for oceans
A flying sail would have helped to get the most out of the conditions, but Lindgren was still awaiting delivery of a Code 0 and A3, both on top-down furlers. However, even when the evening breeze died to around 4-5 knots, the Baltic 67 still provided an enjoyable experience on the helm. It’s rare that you can say such a thing while only using main and jib.
The 67 is designed for potent offwind performance, to limit engine use on transocean voyages. The aggressive sail area to displacement ratio of 30.9 is possibly taking things too far: the boat has so much power to weight that it will need to be treated as a real performance cruiser and tamed accordingly (i.e. reefed early). But what our trial sail did show was how well the Baltic 67 fulfils its brief of being able to offer enjoyable sailing in light wind.
“Bluewater boats don’t usually sail in 10-15 knots downwind – and we had a lot of that,” Lindgren points out, with reference to their previous Pacific crossing. “At 150º true, this boat is sailing at 8-9 knots, which is a big difference. As long as you are over 8 knots you are properly moving through the water,” he reasons. “Below that you’re in the swell and not in control.”

The twin pedestals are well designed to site plotter screens and remote controls for powered deck functions and sail handling
With the relatively low coachroof and cockpit backrests and aft positioning of the helms, protection from the elements may be a concern. When you look at Baltic’s large new designs in build, the 142 and 146, both have lengthy deckhouses that provide plenty of protection. But it chose the more in-vogue deck design for this semi-custom size, so its solutions for cockpit protection depend largely on a retractable sprayhood and bimini. These can remain in place while sailing and have already been tested in up to 40 knots.
The cockpit area on this first Baltic 67 has been adapted according to the owners’ wishes, including a narrower space between benches and no fixed table. The Lindgrens like to be able to brace feet between benches and to be able to sleep on the sole between them when offshore. The table and carbon legs stow beneath the central saloon soleboards.
We anchored at dusk at Es Trenc beach, 25 miles to the south-east of Palma, in water so clear we could pick the spot to drop the hook between weed patches. The ability to anchor in less than 4m amply demonstrated the appeal of a lifting keel. The keel system, from the highly reputable Italian brand APM, raises the T-keel hydraulically up to 2.5m.
The anchor arrangement is another fine piece of engineering: the arm is concealed in a shallow locker and rotates over and into place at the push of a button. The roller then extends out to keep it clear of the stem. The second Baltic 67 will have a fixed roller incorporated into the bowsprit.

The furling jib and powered padeye are recessed neatly
Open transom choice
The garage houses a 3.2m dinghy stowed longitudinally, with the engine mounted, between the dual rudders. Lindgren chose an AB tender with aluminium hull (53kg). It has a 20hp outboard so can plane with four adults yet is light enough to be dragged up the beach. He also opted for an open transom that, although an unconventional choice for ocean cruising, gives easy access to the swim platform and dinghy.
There is copious stowage space throughout the Baltic 67. In addition to the tall sail locker in the forepeak, the aft quarter lockers easily swallow electric bikes, inflatable paddleboards, snorkel gear, waterskis, spare fuel and a liferaft valise. Here there’s also access to the steering gear with independent autopilots used on both quadrants.
I particularly like the way multiple Antal T-lock fittings are flush-mounted along the toerail and in the cockpit. These enable quick and easy swivelling toggles to be inserted for loops and blocks, or for harness attachments.
Weight versus noise
The following morning was windless, leaving us with a three-hour motor back to Palma. The 150hp six-cylinder Steyr was specified for its low noise and emissions, and drives a four-blade Bruntons prop via a standard shaft.
E-glass was chosen over the standard carbon hull. Lindgren’s previous Baltic 56 was carbon and he wanted the better noise insulation over the weight difference (up to one tonne). The 67 is a very quiet, relaxing boat under motor, with no need to raise voices under power.

The spacious saloon has enough room for both dining and coffee tables
Down below the Baltic is an aircon-cooled haven of charm and exquisite quality. The more time I spent aboard and the more I learned of the systems and engineering, the more I began to appreciate what sets this boat apart.
The Design Unlimited styling is elegant and tasteful, with a mahogany finish on this first boat. With four different layout configurations plenty of scope is allowed for owner customisation. But behind the scenes is what you really pay for with the Baltic. It’s the telling result of what happens when a yard goes down in model size – this 67 is built like a superyacht.
For example, the engine room, used for hot items like engine, genset and water-heater, links through to a proper mechanical/utility room abaft the galley, where equipment is mounted on three walls for easy access (including chargers, inverters, pumps, watermaker and compressors).
“The thinking is that everything should be in reach and that you should be able to maintain it easily,” says Lindgren, pointing to the Spectra watermaker (his fourth) mounted on one bulkhead.

The boat’s systems are beautifully laid out for ease of inspection and maintenance
Stowage throughout has been brilliantly conceived. The 2,000lt of water and diesel tanks, plus the batteries, are all mounted centrally, under the saloon, leaving cavernous practical stowage under the berths. Custom-made fabric bags are used under the saloon seats to maximise useable volume.
Lifting the carbon sandwich soleboards at the base of the companionway reveals the sea chests and main manifolds for fuel and water, a prime example of the meticulous and practical systems layout. The 1,440Ah of lithium gel batteries further forward have a reservoir surrounding them, which can cool the cells if necessary without flooding them. And there are custom-made drip trays below any filters to prevent mess or corrosion.
The keel uses a Programmable Logic Controller (PLC) to activate the hydraulics, the cylinders for which can be replaced from within the boat. All other electrics are on manual relays. The fuse locker is a work of art and opens out for full access to the wiring, with every wire and fuse numbered and labelled.
Smart cabin choice
Manyeleti ’s owner’s cabin, with adjoining heads and shower in the forwardmost section, has an offset double berth positioned aft by the main bulkhead, a relatively central area of the boat to sleep. However, on passage, Lindgren says he sleeps on deck, or in the single cabin amidships. There are also leecloths on the saloon berths, a comfortable option if guests don’t want to share the twins.

The owner’s cabin is (purposefully) the only one aboard Manyeleti to feature a double bed
There is a good reason why there is only one double bed. Lindgren often sails with male friends, hence twin and single berths are a pragmatic choice. The use of a split heads and shower shared between the twin and single cabins is also sensible.
The central section of the interior is superb, with a traditional lower saloon, a navstation beside the companionway and a formidable U-shaped galley. It was important to the Lindgrens that the galley was large enough for two to work in yet still be seamanlike. The result is a very practical area with superb chilled, dried goods and crockery stowage. Ventilation ducts keep it nice and cool, though personally I’d want to have a hatch through to the cockpit.
Lindgren swears by the dishwasher, reasoning that it uses less water than washing up and helps keep the galley tidy. This and an induction cooker would be sensible options if you had sufficient power, and would avoid the need for gas.
The exemplary finish and smaller details help furnish the boat with a top quality feel. From the hinges, light switches and showerheads to the gas sprung hatches and overall joiner work, the Baltic 67 oozes quality.

The Baltic 67 has been designed with short-handed sailing in mind
Baltic 67: the verdict
Baltic has spent the last decade building some of the finest performance superyachts. You don’t receive commissions for yachts such as Hetairos , Pink Gin VI , or My Song without a top reputation, and to get that sort of quality on a 67-footer is truly special. Attention to detail and class of engineering and finish are hallmarks of this new model.
The Baltic 67 has the performance in light airs to match her on-trend looks and is a joy to helm. The choice of a comparatively unprotected cockpit and an open transom may not sit well with conventional bluewater sailors, but times are changing and this design is aimed as much at port-hopping from Portofino as at Pacific passagemaking . It is the solutions, stowage and systems employed throughout that help make it a valid option for distance cruising.
The Baltic 67 has the legs to outrun virtually any other cruising monohull and to keep sailing fast in light apparent winds. To know you’re buying the best in terms of design and composite build – and created by the same team involved in a yacht that costs tens of millions – must help compensate for the significant initial outlay. For the rest of us, we can but dream.
Specification
LOA: 20.52m (67ft 4in)
LWL: 19.20m (62ft 12in)
Beam (max): 5.45m (17ft 11in)
Draught (max): 3.90m (12ft 10in)
Draught (telescopic): 2.50m (8ft 2in)
Displacement (lightship): 24,400kg (53,792lb)
Ballast: 9,000kg (19,841lb)
Sail Area: 255.6m2 (2,751ft2)
Berths: 7-8

Engine: 150hp
Water: 1,000lt (220gal)
Fuel: 900lt (198gal)
Sail Area/disp ratio: 30.9
Disp/LWL ratio: 96
Price: €3.95 million (ex. VAT)
Design: Judel/Vrolijk & Co and Design Unlimited
Great choice! Your favorites are temporarily saved for this session. Sign in to save them permanently, access them on any device, and receive relevant alerts.
- Sailboat Guide
Baltic 33 is a 33 ′ 0 ″ / 10.1 m monohull sailboat designed by C&C Design and built by Baltic Yachts between 1975 and 1980.
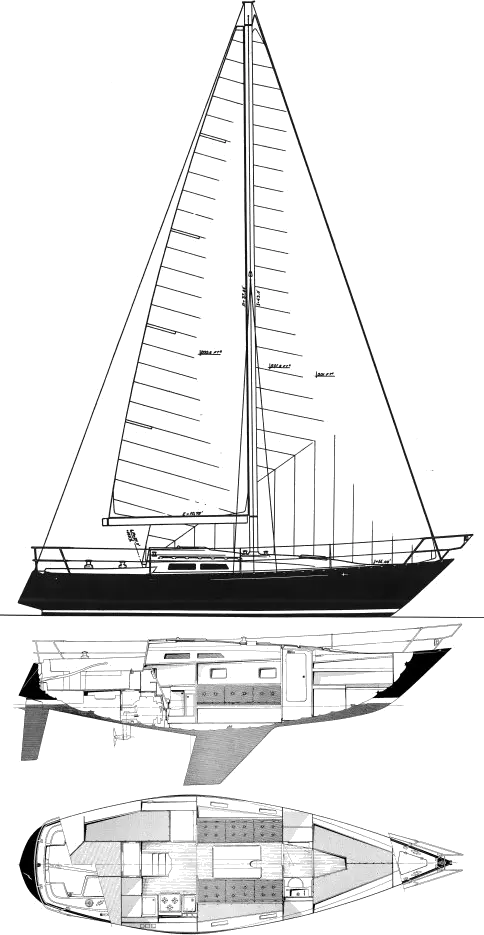
Rig and Sails
Auxilary power, accomodations, calculations.
The theoretical maximum speed that a displacement hull can move efficiently through the water is determined by it's waterline length and displacement. It may be unable to reach this speed if the boat is underpowered or heavily loaded, though it may exceed this speed given enough power. Read more.
Classic hull speed formula:
Hull Speed = 1.34 x √LWL
Max Speed/Length ratio = 8.26 ÷ Displacement/Length ratio .311 Hull Speed = Max Speed/Length ratio x √LWL
Sail Area / Displacement Ratio
A measure of the power of the sails relative to the weight of the boat. The higher the number, the higher the performance, but the harder the boat will be to handle. This ratio is a "non-dimensional" value that facilitates comparisons between boats of different types and sizes. Read more.
SA/D = SA ÷ (D ÷ 64) 2/3
- SA : Sail area in square feet, derived by adding the mainsail area to 100% of the foretriangle area (the lateral area above the deck between the mast and the forestay).
- D : Displacement in pounds.
Ballast / Displacement Ratio
A measure of the stability of a boat's hull that suggests how well a monohull will stand up to its sails. The ballast displacement ratio indicates how much of the weight of a boat is placed for maximum stability against capsizing and is an indicator of stiffness and resistance to capsize.
Ballast / Displacement * 100
Displacement / Length Ratio
A measure of the weight of the boat relative to it's length at the waterline. The higher a boat’s D/L ratio, the more easily it will carry a load and the more comfortable its motion will be. The lower a boat's ratio is, the less power it takes to drive the boat to its nominal hull speed or beyond. Read more.
D/L = (D ÷ 2240) ÷ (0.01 x LWL)³
- D: Displacement of the boat in pounds.
- LWL: Waterline length in feet
Comfort Ratio
This ratio assess how quickly and abruptly a boat’s hull reacts to waves in a significant seaway, these being the elements of a boat’s motion most likely to cause seasickness. Read more.
Comfort ratio = D ÷ (.65 x (.7 LWL + .3 LOA) x Beam 1.33 )
- D: Displacement of the boat in pounds
- LOA: Length overall in feet
- Beam: Width of boat at the widest point in feet
Capsize Screening Formula
This formula attempts to indicate whether a given boat might be too wide and light to readily right itself after being overturned in extreme conditions. Read more.
CSV = Beam ÷ ³√(D / 64)
Same hull design as C&C 33. Updated keel on later boats.
Embed this page on your own website by copying and pasting this code.
Discover Related Sailboats
- About Sailboat Guide
©2024 Sea Time Tech, LLC
This site is protected by reCAPTCHA and the Google Privacy Policy and Terms of Service apply.
Baltic 42 dp
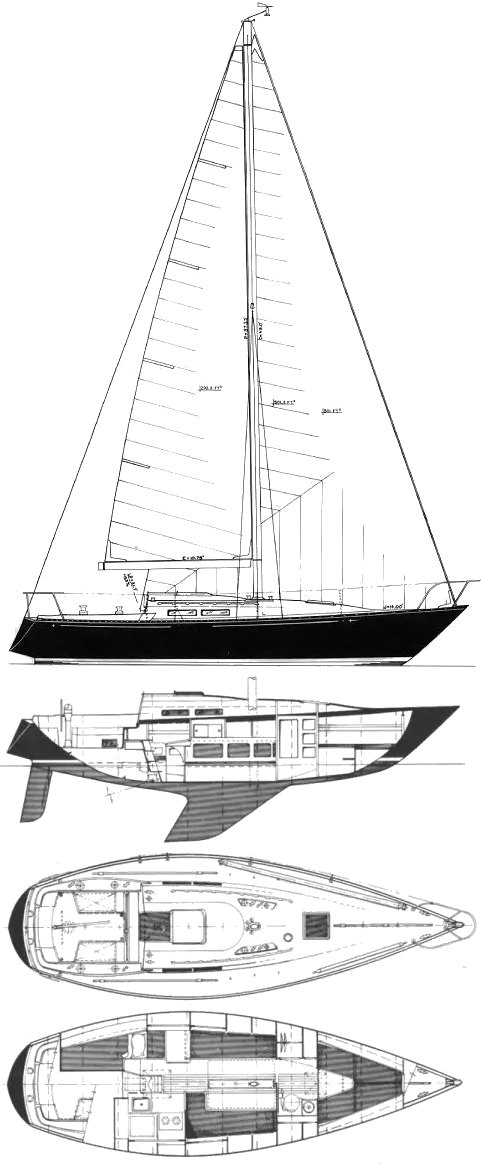
The baltic 42 dp is a 41.92ft masthead sloop designed by doug peterson and built in fiberglass by baltic yachts between 1981 and 1985., 30 units have been built..
The Baltic 42 dp is a moderate weight sailboat which is a good performer. It is very stable / stiff and has a low righting capability if capsized. It is best suited as a coastal cruiser. The fuel capacity is originally small. There is a short water supply range.

Baltic 42 dp for sale elsewhere on the web:

Main features
Login or register to personnalize this screen.
You will be able to pin external links of your choice.
See how Sailboatlab works in video

We help you build your own hydraulic steering system - Lecomble & Schmitt
Accommodations
Builder data, other photos.
Modal Title
The content of your modal.
Personalize your sailboat data sheet

- Service & Refit
- Baltic Yachts Rendezvous

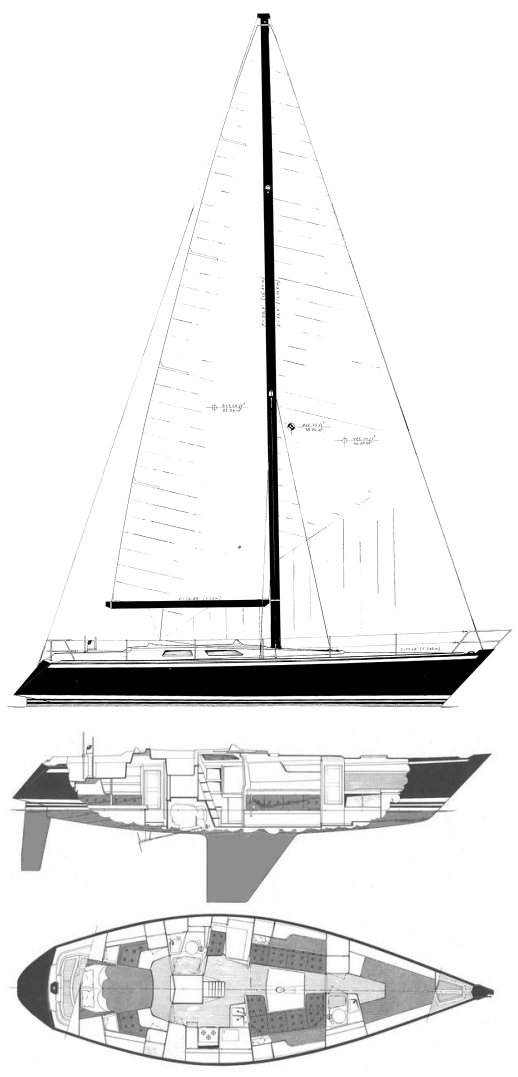
BALTIC 56-03
For the third hull of the Baltic 56 the owner wanted a multi-purpose yacht that would offer both good racing potentials as well as comfortable cruising, but without being too complex and too heavily loaded with equipment.
Functionality was an important factor when working on the layouts and specification for this project. The deck was of a twin cockpit type layout with entrances from both cockpits.
A good example of functionality was that the navigation station has been positioned just forward of the aft entrance, giving a superb communication between helm and navigation station.
This yacht was a good example of the high technology used on the majority of Baltic Yachts today. Typical example of this were vacuum infused Carbon/Epoxy laminates for both deck and hull, Carbon structural bulkheads and carbon mast among other things.
DELIVERY YEAR
MAIN SPECIFICATIONS
- L.O.A. 17.14 m
- D.W.L. 15.00 m
- BEAM 4.59 m
- DRAFT 3.10 m
- DISPLACEMENT 15,300 kg
- BALLAST 5,800 kg
- NAVAL ARCHITECT judel/vrolijk & co
We’re constantly updating our website to bring you news of launchings, new commissions and Baltic inspired innovation.

7 Major Ports in Russia
As the largest of all the landmasses in the entire world, Russia has an extensive coastline. It features on the periphery of the Arctic Ocean surrounding its entire North for trading prospects. The Barents Sea, with the South-Eastern side touching the Sea of Japan encompasses the major ports in Russia.
60% of the total cargo movement on the international scale for Russia takes place through the sea. This includes almost 722 million MT (2016) cargo movement through international vessel calls.
A staggering 67 thousand plus ship calls come through this busy network every year. However, the modern handling facilities ensure that the median handling time for these ships remains 1.45 days. This means the port facilities under the Russian Government’s reach are the best in the business!
As a shipping nation, the Russian seafarers are plenty in number across the globe. The country’s shipping strength boasts over 2820 vessel registrations and 98,000 seafarers under them.
Major Ports Of Russia
In this article, we review the major ports in Russia of inland and international importance. We highlight their share in building the 571 496 million current US$ shipping market in the country. The details also contain their accurate location, identity code, and other geographical information.
1. Port of Novorossiysk (Krasnodar Krai, Russia)
UN/Locode: RUNVS Latitude: 44.720065° Longitude: 37.81373°

The port of Novorossiysk has a 3.4 sq. km harbour area with a land area worth 2.7 sq. km. This includes a total of 89 functioning berths for vessels of all sizes. It features as the biggest seagoing port for Russia for over decades with almost 50% higher turnover.
The establishment of the port of Novorossiysk dates back to 1829, with major exchanges since 1846. The port’s range of services recorded 143 million MT of cargo handling for 2020. It includes one of the first Timber wood handling facilities to feature across the Black Sea ports.
Cargo Handling
A total of 11 berths are important in handling timber and other bulk cargo. 4 separate berths over a quay length of 570 meters handle the container operations. The sheer size of the facility allows maximum handling limits of 208 million MT every year.
Network and Layout
The timber operations across the 4 berths (31, 32, 31/A, 31/5) are the most advanced facility across Europe. Their throughput every year crosses figures between 400 thousand to 600 thousand.
This connects with direct railway and loading facilities, reaching out to 70% of timber industries. Meanwhile, 180 thousand and more TEU capacity of container handling adds to the port’s large-scale profits.

2. Port of Saint Petersburg (St. Petersburg, Russia)
UN/Locode: RULED Latitude: 59.91933° Longitude: 30.327035°
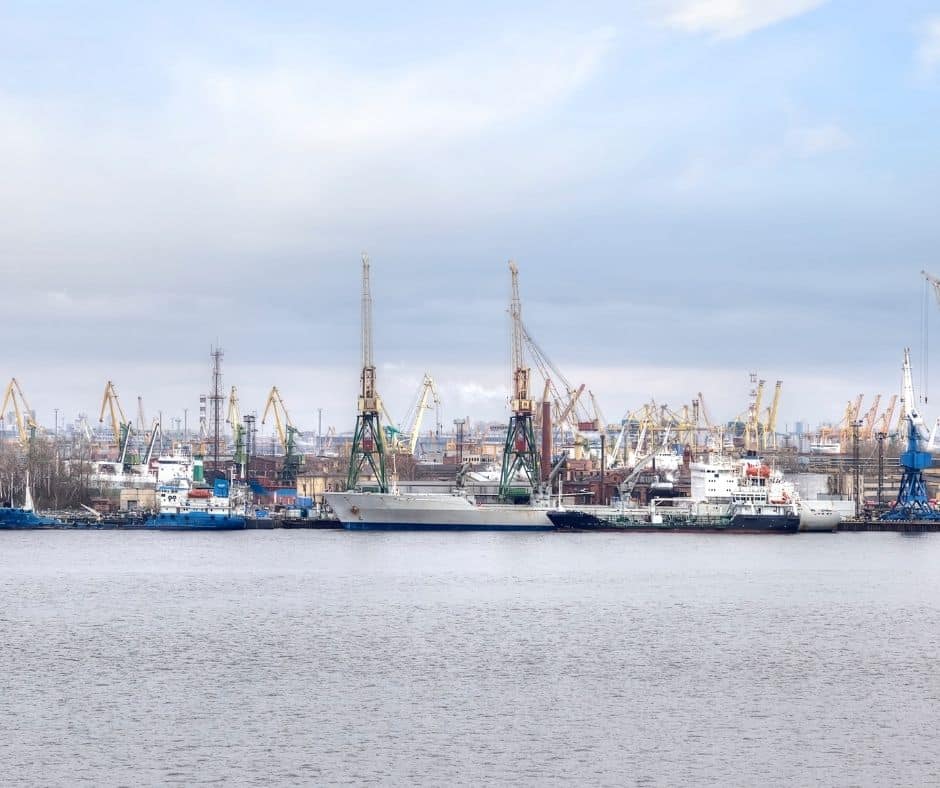

The Port of Saint Petersburg has one of the deepest drafts for any Russian facility. The inner anchorage ranges between 23 to 25 meters while the channel draft is approx. 18.5 to 23 meters.
As one of the major ports in Russia, its water area spreads over an expanse of 164 sq. km. Meanwhile, the beginning of its establishment dates back to 1869. At present, the facility uses 470 vessels for in-house operations along their coast.
The passenger terminal at St. Petersburg handles over 450 vessels annually. This happens over a dozen of berths, with 2 major terminals having the alongside the extent of 360 meters.
The total mooring size capacity of this facility is over 30 kilometres. This includes the working capacity of more than 200 berths of various sizes in this facility.
St. Petersburg famously works with 8 major cranes of Panamax capacity. This couples with 3 RMG and 20 gantry nature cranes for handling container goods. This rounds off to the port’s annual handling figures to well over 2 million every year.
The facility connects with major cargo shipping destinations through 2 dozen operating lines. It acts as the major gateway for providing shipping access to the Russian interiors. The neighbouring ports like Rotterdam, Bremerhaven, etc. act as the feeder terminals for the super container ships .
Over 122 tugs and 3 dozen oil barges are resident for berthing and bunkering operations. The rail line operates through the container segment of the port, handling container transport.
3. Port of Ust-Luga (Kingiseppsky District, Russia)
UN/Locode: RUULU Latitude: 59.68294° Longitude: 28.329515°
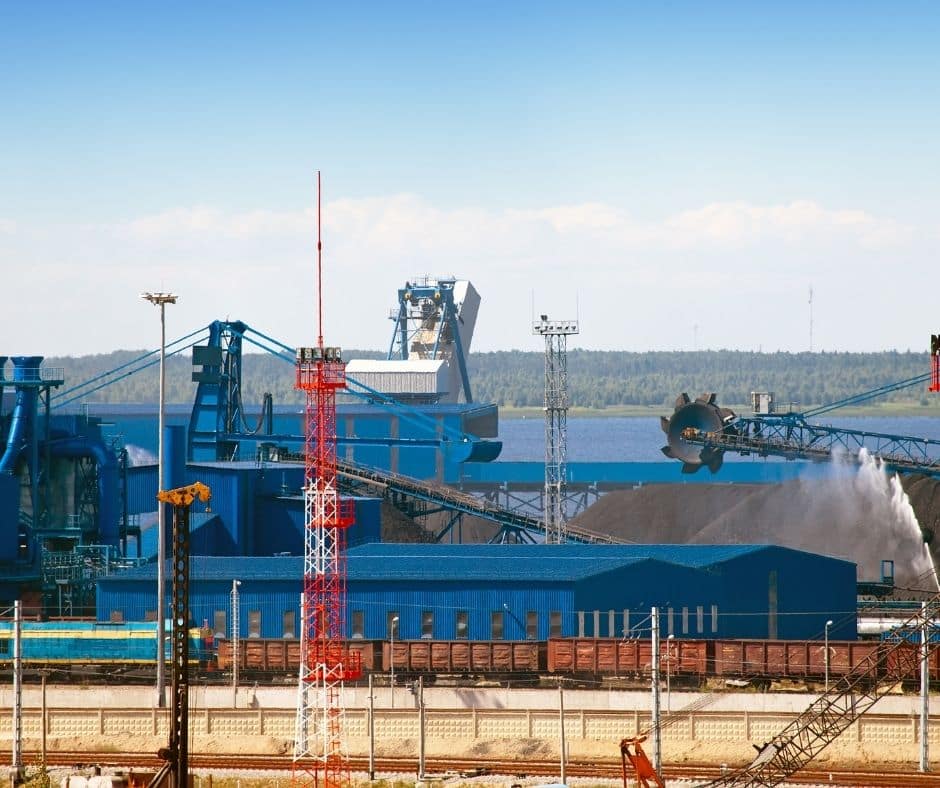

The port of Ust-Luga stands only behind Novorossiysk in terms of cargo handling volume for 2020. It has the biggest handling facility for coal bulk operations in the Northern part of Russia. The additional expansion plans provide this facility with a total area of 30 sq. km.
Ust-Luga has 5 major berths that operate for round the year operation in severe temperatures. These handle over 30 vessels at once with anchorage facilities over 20 meters and higher depth.
The state-of-art coal loading facilities handle export abilities up to 20 million MT annually. It also is one of the newest facilities in Russia, dating back to 2011 for its establishment.
The loading conveyors for the coal handle up to 500 MT every hour on average. This facility accommodates vessels ranging up to 60,000MT of DWT for coal loading.
In addition, Ust-Luga also handles livestock, liquid, and general cargo operations. The overall cargo operations have figures worth 102.6 million MT for 2020. 2 mega cranes of 104 MT capacity and 1 of 80 MT capacity operate simultaneously with the conveyor system.
The berthing network contains a ramp bridge terminal and 7 deep berths spread across 1500 meters. Their operations handle 1000 to 1450 vessels up to 1,20,000 MT DWT.
The layout also has a warehouse for final goods handling, spread over 2800 sq. meters. This facility connects with the Ust-Luga railway terminal that has a special station for the port. The plan is for expanding the facility for over 26 train arrivals every day in the next decade.
4. Port of Vostochny (Nakhodka Bay, Russia)
UN/Locode: RUVYP Latitude: 42.762495° Longitude: 133.0514°
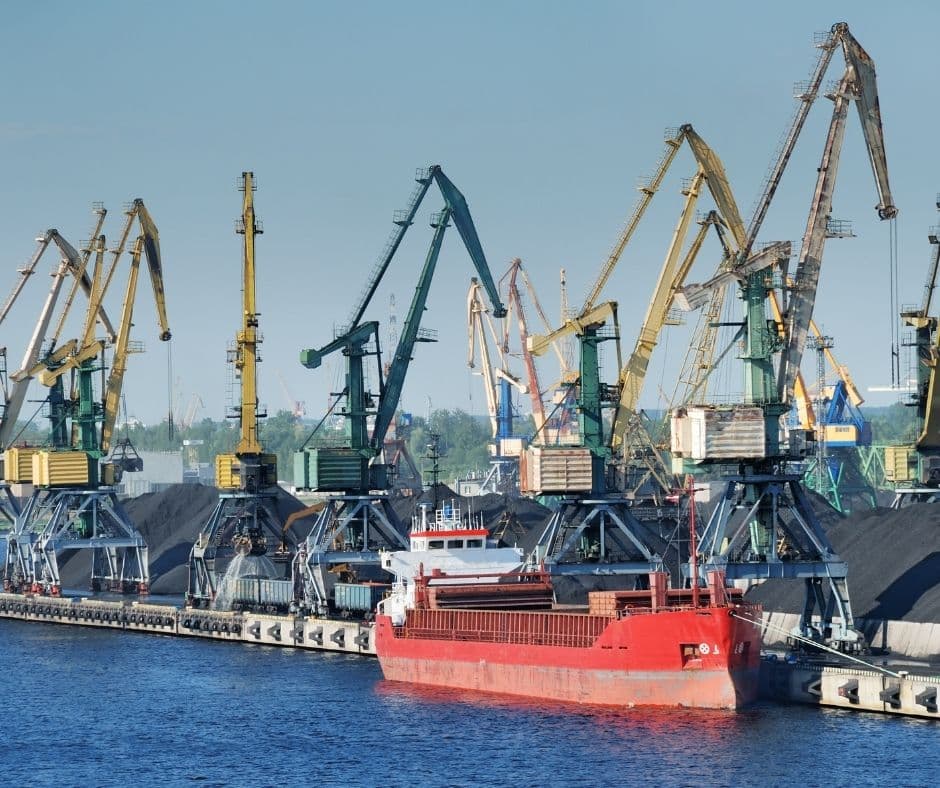

The port of Vostochny operates with two major terminals for a handling capacity of 80 million MT. In 2020, the facility shows stats worth 77 million MT including the export. In the internodal structure, the coal loading takes place at the special coal terminal.
The facility is amongst the oldest in the major ports in Russia, dating back to 1974. The trans-Siberian railway connects the terminal to the most prominent end-user plants. Vostochny’s major exports connect with the Asian countries, with Japan and Korea using up to 60%.
Over 550 vessel arrivals for the year 2019 have mostly bulk carriers of different sizes. The facility accommodates vessels up to 1,80,000 MT DWT for bulk coal operations.
The general handling facilities show 300,000 units of rail cars carrying the cargo for this period. The discharge to these rails uses the conveyor mechanism with automatic operations.
The Vostochny terminal employs over 1700 people for the cargo and operational routines. The spreading layout uses 98% of mechanical and electrical automation for operations.
With the progressive development of their phase 3, the handling capacities will touch over 100 million MT. As a result, the net income of the facility amounts to an annual figure of 125 million USD.
5. Port of Primorsk (Vyborgsky District, Russia)
UN/Locode: RUPRI Latitude: 60.3463° Longitude: 28.67096°
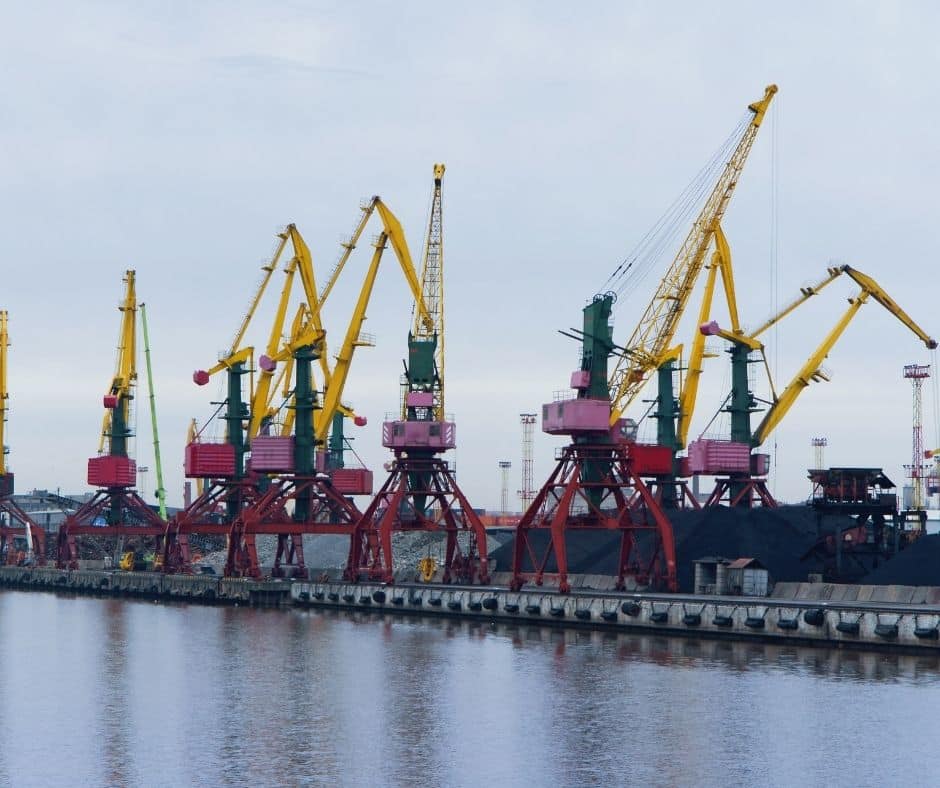

The Port of Primorsk is spread across a land piece of 5.4 sq. km area for cargo operation. This is in addition to the 32 sq. km of water limits within their expanse. It features amongst the top Russian ports by volume, handling 50 million MT+ cargo annually.
The initial operations at the facility date back to the year 2001, with a further increase in 2004. The facility operates 6 major berths that spread across a length of 2.8 km alongside. The deepest tanker-handling terminals allow drafts up to 17.8 meters for convenient loading.
An annual handling capacity of 60 million MT and more of liquid cargo allows major export relations. The Primorsk port also stands out as the highest contributor to oil exports in Russia.
The operations include 50 major oil extraction firms for direct loading transfers. All loading arms connect for a throughput of 2800 cubic meters loading rate for bigger tankers. This allows tankers of 1,50,000 DWT capacity to arrive with better draft features.
The wide oil handling range connects with the Baltic Pipeline and serves at its one end. This comes with a specific terminal for gas loading operations that operates 8-24hrs for cargo.
The 2 phases of pipeline extending onwards span over 1000 kilometres for oil handling. These terminals involve 250 regular employees with camera surveillance measures.
6. Port of Murmansk (Kola Bay, Russia)
UN/Locode: RUMMK Latitude: 68.984125° Longitude: 33.061°
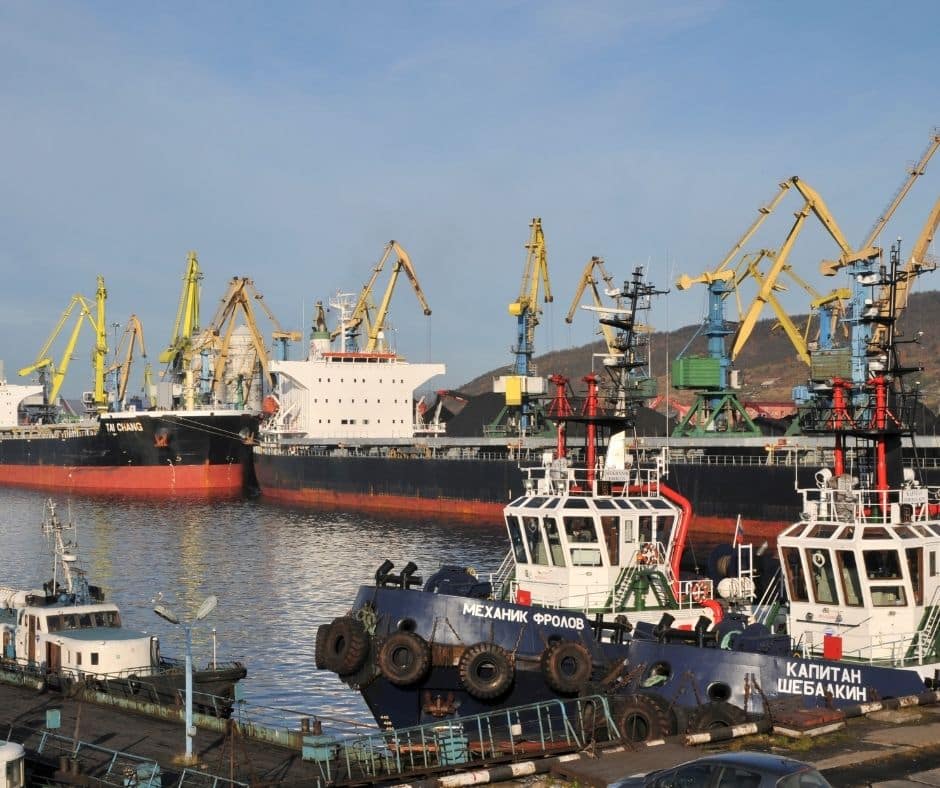

With its location on the northern end of the Arctic circle, Murmansk is the coldest Russian port. It also is the largest to lie on the North of this geography. It is also the geographical North-most amongst the major ports in Russia.
The port helps to house the ice-breaking vessels assisting the larger vessels passing through the Arctic. Its establishment owing to this reason is also quite old, dating back to 1917.
The port operates through its 15 berths, 11 of which are for solid cargo. These berths divide into 2 major port districts or nodes for operation. The general berths operate over 1.5 km in length, while the oil terminals operate on half the figure.
In 2021, Murmansk has figures worth 56 million MT of cargo through its facility. All major bulk cargo operations take place through the gantries at a steady rate. The operates to switch between 16 and 32 MT per hour operation capacity for these.
Meanwhile, the bulk liquid berths vary between 10 to 15 meters in depth. The 3 terminals that use the roadways facility operate the majority of bulk operations.
Despite its challenging location, Murmansk operates round the year. Its expanse has an additional third node for car and container handling tasks. It is the only node with length restrictions, with vessels coming up to 220 meters long.
Major bulk cargo storage facility houses more than 25000 MT in this area. The facility houses over 200 operators for cargo, and less than 100 for ice-breaking requirements.
7. Port of Vladivostok (Vladivostok, Russia)
UN/Locode: RUVVO Latitude: 43.087445° Longitude: 131.9022°
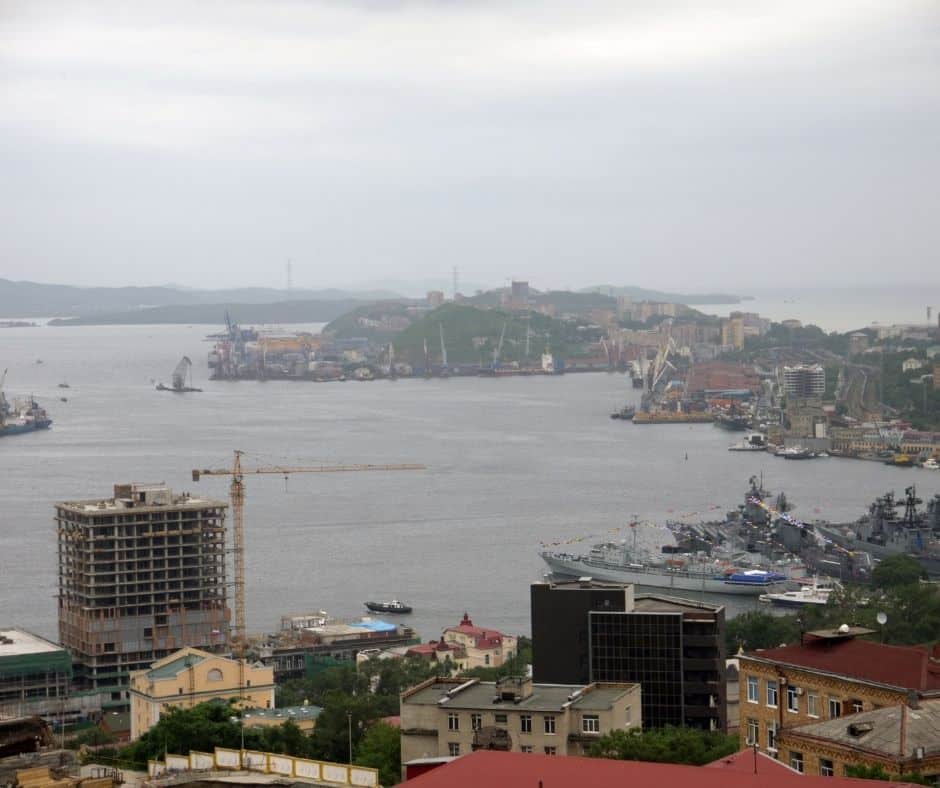

The port of Vladivostok provides Russia with an opportunity to explore the Pacific. It extends towards the south-eastern end and touches the Sea of Japan for the bulk Asian traffic. This facility spreads across 55 hectares and also provides a cultural significance for the Russian landmass.
Vladivostok has a record of handling 24 million MT of cargo for 2021. It is significantly higher than its 13.9 million MT average across the decade. The port’s establishment starts in the 1800s, with free status existence in between.
The terminal operates through its range of 15 berths for general operations. Each of these varies between 10 to 15 meters for depth. The approach through the channel gives a depth of up to 25 meters.
A collection of 200 automatic and semi-automatic loading resources are available overall. This includes the STS, RMG, and RTG facilities operating alongside. The container handling facilities operate round the year for efficient discharging.
Being the south-eastern tip, the Vladivostok network has major relation with Asian ports. 45% and more of their trade flow through Korea, Japan, and China in combination. The layout divides into the universal and the container-specific terminals for operation.
An area of 450,000 sq. meters is available for the warehouse storage and handling of goods. The inter-port handling facilities feature a train map and 2 major truck checkpoints.
Russian Shipping Riches
The sea transport shares a stake worth 112 087 million current USD for the Russian trade. This creates a significant impact for managing international trade, despite the large land area. The concentration of land does not have too big inland waterways, leading to major ocean ports.
Moreover, the testing conditions while operating in the Arctic do not make the cargo movement easier. In such situations, the Russian authorities focus highly on developing the ice-breaking fleet for year-long operations.
With a diverse portfolio, the major ports in Russia handle cargo of every significant use. The country’s latest focus on developing a green corridor is in line with the shipping requirement and future.
You might also like to read:
- 7 Major Ports of South Africa
- 7 Major Ports of the United States
- 7 Major Ports in The United Kingdom
- 10 Major Ports In Brazil
- Top 14 Major Ports in Italy
Disclaimer: The authors’ views expressed in this article do not necessarily reflect the views of Marine Insight. Data and charts, if used, in the article have been sourced from available information and have not been authenticated by any statutory authority. The author and Marine Insight do not claim it to be accurate nor accept any responsibility for the same. The views constitute only the opinions and do not constitute any guidelines or recommendations on any course of action to be followed by the reader.
Do you have info to share with us ? Suggest a correction
Latest Maritime Knowledge Articles You Would Like :

7 Amazing Makassar Strait Facts

10 Amazing Beaufort Sea Facts

4 Major Ports in Micronesia

12 Interesting Facts About the PNS Ghazi Submarine

Differences Between Marines And Navy

10 Interesting Bali Sea Facts

Subscribe To Our Newsletters
By subscribing, you agree to our Privacy Policy and may receive occasional deal communications; you can unsubscribe anytime.
Web Stories
Leave a Reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Subscribe to Marine Insight Daily Newsletter
" * " indicates required fields
Marine Engineering
Marine Engine Air Compressor Marine Boiler Oily Water Separator Marine Electrical Ship Generator Ship Stabilizer
Nautical Science
Mooring Bridge Watchkeeping Ship Manoeuvring Nautical Charts Anchoring Nautical Equipment Shipboard Guidelines
Explore
Free Maritime eBooks Premium Maritime eBooks Marine Safety Financial Planning Marine Careers Maritime Law Ship Dry Dock
Shipping News Maritime Reports Videos Maritime Piracy Offshore Safety Of Life At Sea (SOLAS) MARPOL
- Guided tour
River Cruise on Luxurious Radisson Boat
- Description
- Choose date

Equipped with ice-breaking technology, these huge fancy yachts are the only river cruisers running all year around. The round trip journey takes two and a half hours and floats past all the big sights like the White House, Novodevichy monastery and the Kremlin. There’s a large open air observation deck up top, while the main body of the ship houses a restaurant with a dance floor for a romantic post dinner dance. For a particularly romantic experience take one of the evening boats and admire the bright lights of the city skyline at night.
The most relaxing and picturesque tour that Moscow can offer: a great way to see the city center and its main attractions. This is a perfect alternative to exploring the city by car, if you only have time to do sightseeing during weekday rush hours.
Your English-speaking guide is eager to share every bit of their knowledge about the surrounding landscape, the architecture and historical details.
We conduct Moscow river tour on Radisson Flotilla boats all year around! It’s warm inside during winter months, while there’s air conditioning during hot summer days. You may also treat yourself to drinks, lunch or dinner on board (drinks and food are not included in tour price).
The cost of an excursion with a personal guide for 1 person
Quay at Radisson Collection Hotel
Government Headquarters ("the White House")
Kievsky Railway Central
Novodevichy Convent
Luzhniki Stadium
Academy of Sciences
Monument to Peter I
Cathedral of Christ the Saviour
Moscow Kremlin
St.Basil's Cathedral
Novospassky Monastery
U-turn and back to Quay at Radisson Royal Hotel
Choose your dates
Who's going.
- Excursion River Cruise on Luxurious Radisson Boat
- Date and time:
- Who's going:
See photo of the meeting point
NATO helicopters are shooting down and eliminating enemy drones in a rarer kind of Red Sea battle
- Houthi attack drones have mostly been intercepted by US and allied warships in the Red Sea.
- Air-to-air combat has been much less common, but last month, a French helicopter shot down a drone.
- A former US naval aviator said the engagement is not necessarily surprising.

The Houthis have launched a lot of deadly threats into the Red Sea, many of which have been shot down by US and allied warships operating in the region's dangerous waters.
One recent interception, however, was credited to a French helicopter crew, which blasted a Houthi attack drone out of the sky in air-to-air combat. Helicopter-versus-drone fights aren't the norm in this conflict.
Victories like these can be more difficult to achieve, given that they require hitting a moving target from another moving target in the air, but they aren't all that surprising because helicopters are capable assets and the crews likely would have trained for such scenarios in advance, a former US naval aviator told Business Insider.
Helicopters are 'pretty good' on defense
On March 20, a French frigate detected a Houthi drone while the ship was protecting a merchant vessel in the southern Red Sea as part of the European Union's security mission Operation Aspides .
A helicopter embarked onboard the warship was then deployed to locate the drone, which was deemed a threat, and destroy it. France didn't say exactly how the aircraft engaged the drone, but it was effectively eliminated.
"These actions directly contribute to maritime security," the French defense ministry said of the incident in an update on its operations around the world.
France also did not say what type of helicopter engaged the Houthi drone, but both of the French warships that have been in the Red Sea both carry NH90 aircraft, which can be equipped with air-to-surface missiles and machine guns. Because the drone was traveling in the air, the crew likely used the guns to take it down.
Nearly all of the drones and missiles launched by the Houthis since November, when the Iran-backed rebels began consistently attacking international shipping lanes off the coast of Yemen, have been shot down by US Navy warships or fighter jets , or coalition vessels like those party to Operation Aspides.
Helicopter engagements are rarer occurrences, and have only happened a handful of times. But Brynn Tannehill, who flew the SH-60 Seahawk, a multi-mission helicoptered used by the Navy that's based on the UH-60 Black Hawk, said France's success "is not particularly surprising."
"Helicopters can provide a relatively stable platform — they're relatively maneuverable," Tannehill, now a US Army Black Hawk aviator and a defense analyst, said. "The biggest thing against them is that they're slow, so against a faster target, they're going to be useless."
Related stories
After the Sept. 11, 2001 terror attacks, while in the Navy, Tannehill said she practiced simulated intercepts of small aircraft — something that would move at a speed similar to that of a one-way attack drone — and boats that a bad actor could theoretically pack with explosives.
The goal was to essentially figure out whether a SH-6o could maneuver into position, put a gunner in the door, and eliminate such threats with a .50 caliber machine gun, she said. The simulations demonstrated that helicopters were, indeed, very effective.
"What they found was that helicopters are pretty good at shooting down non-maneuvering, slow targets out the door," Tannehill said. "And because you're shooting sideways out of them, the debris doesn't even come back at you."
These training simulations have ultimately been brought to life during the ongoing conflict between the Houthis and the US and its allies.
On December 31, four Houthi small boats attacked a container ship, prompting its crew to issue a distress call. Helicopters from the USS Dwight D. Eisenhower and USS Gravely — an American aircraft carrier and a destroyer, respectfully, that are deployed to the region — responded to the call.
When the responding Navy helicopters arrived on the scene, the Houthis opened fired on the American aircraft, which then returned fire in self-defense, sinking three of the four Houthi small boats and killing everyone on board, US Central Command said in a statement at the time. The fourth boat managed to flee the area.
Pilots are 'well-trained'
And the US hasn't been the only naval force to destroy Houthi threats in the Red Sea with embarked helicopters. A day after the French engagement, on March 21, a helicopter attached to the German frigate Hessen destroyed a Houthi surface drone that was identified as a threat to civilian ships.
A spokesman for the German Bundeswehr Joint Forces Operations Command told BI that the aircraft involved was a Sea Lynx, which is armed with torpedoes and a machine gun. It was not clear how, exactly, the helicopter engaged the surface drone, but guns are likely.
Tannehill said that these kinds of engagements require a considerable amount of training and knowledge of both the aircraft and its weapons systems, and also coordination with other allied ships operating in the area.
"You've got to be competent with your systems, you've got to be quick with them, you've got to be knowledgeable about them," she said. "The pilot's got to be good at communicating with the rest of the crew and making sure that you're setting up for shot after shot after shot."
There are limitations, however, as for how fast the helicopter can travel, when the doors can open, and when the gunners can open fire. The pilots also have to make sure they're operating at a safe distance such that a drone that gets hit and explodes doesn't send shrapnel flying into the aircraft.
"The pilots are well-trained," Tannehill said, adding: "This is something that you probably would've practiced with the task force beforehand to make sure that when it does happen, that everybody knows what they're supposed to do and gets it done — including permission to fire in an amount of time that allows you to do it before the target presents a real threat to somebody. "
Watch: See the hectic flight deck of a US warship fighting Houthis in the Red Sea
- Main content

IMAGES
COMMENTS
Baltic Yachts Balticvagen 1 6855 Bosund Finland tel. +358-6-781-9200 fax +358-6-781-9222 www.balticyachts.fi [email protected]
BALTIC 67PC-03 FREEDOM. The judel/vrolijk-designed Baltic 67PC was conceived as a robust, fast, easy to handle long distance cruising yacht able to sail well in light to medium airs downwind conditions and maintain high daily mileage averages without recourse to the engine. The owner of the third 67PC is keen to sail short-handed, so in ...
Baltic boats for sale on YachtWorld are listed for a variety of prices from $29,769 on the moderate end of the spectrum, with costs up to $7,859,855 for the most luxurious yachts. What Baltic model is the best? Some of the most widely-known Baltic models presently listed include: 35, 42, 43, 46 and 51. Baltic models are available through yacht ...
LIGHTER, STIFFER, FASTER, GREENER - TOGETHER. Baltic Yachts is the world's leading builder of advanced composite yachts. Our highly skilled workforce uses leading edge marine technology and traditional craftsmanship to create award-winning yachts. Each yacht is unique, unmatched in its quality, unmatched in its performance.
Baltic Yachts is a shipyard specialized in sailing yachts. It is located in the municipality of Larsmo in Finland, where it is the largest employer. The shipyard was established in 1973 and now produces sailing yachts between 50 feet (15 m) and 197 feet (60 m) in length. Advanced and light materials, such as carbon fiber and Kevlar are used in ...
The Baltic 39 was one of the first serial production yachts that were designed and performance evaluated using computer programs. Full VPP studies were executed resulting in both polar plots and performance in numbers. In addition to producing a good basis for design optimizations, the result from the computer studies also gave racing clients ...
The Baltic 58 is a 58.5ft masthead sloop designed by Sparkman & Stephens and built in carbon fiber or composite by Baltic Yachts between 1992 and 2004. 4 units have been built. The Baltic 58 is a light sailboat which is a high performer. It is very stable / stiff and has a good righting capability if capsized. It is best suited as a fast cruiser.
The Baltic 67 is very much at the luxury and custom end of the production yacht scale, so our light wind trial of the boat focused more on the various choices and details aboard and how they might ...
The first yacht of this model was delivered in 1975. The Baltic 33 was designed as a high performance and responsive boat - easily handled - suitable for racing as well as family cruising. The displacement was moderate at 4455 kg and her performance was designed to do well in medium to light wind. The deck was designed for both cruising and ...
The Baltic 40 is a recreational keelboat, built predominantly of fiberglass with a balsa core, with wooden trim, including a teak deck. It has a masthead sloop rig with anodized aluminum spars and steel rod standing rigging for the three spreader mast. The design has a raked stem, a reverse transom, a spade-type rudder controlled by a wheel and ...
Finnish builder of the well known brand of high quality, performance cruisers.
The Baltic 51 is a 50.92ft masthead sloop designed by C & C Design Group and built in fiberglass by Baltic Yachts between 1979 and 1988. 24 units have been built. The Baltic 51 is a moderate weight sailboat which is a good performer. It is stable / stiff and has a good righting capability if capsized. It is best suited as a bluewater cruising boat.
The Baltic 37 is a 37.0ft masthead sloop designed by C&C Design Group and built in fiberglass by Baltic Yachts between 1978 and 1983. 51 units have been built. ... The data on this page has been derived from different sources but a significant part is attributed to sailboatdata.com. We thank them for their encouragements and friendly collaboration.
Baltic 33 is a 33 ′ 0 ″ / 10.1 m monohull sailboat designed by C&C Design and built by Baltic Yachts between 1975 and 1980. Designer C&C Design Builder Baltic Yachts Association Baltic Yachts # Built 42 Hull Monohull Keel Fin Rudder ... Source: sailboatdata.com / CC BY. Embed Embed. View Demo.
BALTIC 67. PERFORMANCE CRUISER. A fast, easy to handle cruising yacht benefitting from the highest quality carbon fibre construction, half a century of seamanlike design experience and the opportunity for owners to customise layout. This performance bluewater cruiser is designed to meet the demands of owners looking for a fast, easy to sail ...
The Baltic 42 dp is a 41.92ft masthead sloop designed by Doug Peterson and built in fiberglass by Baltic Yachts between 1981 and 1985. 30 units have been built. The Baltic 42 dp is a moderate weight sailboat which is a good performer. It is very stable / stiff and has a low righting capability if capsized. It is best suited as a coastal cruiser.
Baltic Yachts. www.balticyachts.fi. Finnish builder of the well known brand of high quality, performance cruisers.
BALTIC 56-03. For the third hull of the Baltic 56 the owner wanted a multi-purpose yacht that would offer both good racing potentials as well as comfortable cruising, but without being too complex and too heavily loaded with equipment. Functionality was an important factor when working on the layouts and specification for this project. The deck ...
The Volga-Baltic Waterway (Волгобалт), formerly known as the Mariinsk Canal System (Мариинская водная система), is a series of canals and rivers in Russia which link the Volga with the Baltic Sea via the Neva.Like the Volga-Don Canal, it connects the biggest lake on Earth, the Caspian Sea, to the World Ocean.Its overall length between Cherepovets and Lake ...
3. Port of Ust-Luga (Kingiseppsky District, Russia) UN/Locode: RUULU. Latitude: 59.68294°. Longitude: 28.329515°. The port of Ust-Luga stands only behind Novorossiysk in terms of cargo handling volume for 2020. It has the biggest handling facility for coal bulk operations in the Northern part of Russia.
Book. Guided tour. 2,5 hours. Популярные , Речные прогулки. Code: 10147. Equipped with ice-breaking technology, these huge fancy yachts are the only river cruisers running all year around. The round trip journey takes two and a half hours and floats past all the big sights like the White House, Novodevichy monastery and ...
NATO helicopters are shooting down and eliminating enemy drones in a rarer kind of Red Sea battle. Jake Epstein. Apr 8, 2024, 2:30 PM PDT. A Houthi attack drone (L) and a French NH90 helicopter (R ...
Nov. 6, 2023. Russia's Spasatel Karev repair vessel Wikimedia Commons. Finnish authorities said Monday that a Russian telecommunications cable in the Baltic Sea was discovered damaged in October ...