- BOAT OF THE YEAR
- Newsletters
- Sailboat Reviews
- Boating Safety
- Sailing Totem
- Charter Resources
- Destinations
- Galley Recipes
- Living Aboard
- Sails and Rigging
- Maintenance
- Best Marine Electronics & Technology
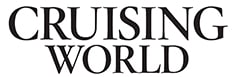

40 Best Sailboats
- By Cruising World Editors
- Updated: April 18, 2019

Sailors are certainly passionate about their boats, and if you doubt that bold statement, try posting an article dubbed “ 40 Best Sailboats ” and see what happens.
Barely had the list gone live, when one reader responded, “Where do I begin? So many glaring omissions!” Like scores of others, he listed a number of sailboats and brands that we were too stupid to think of, but unlike some, he did sign off on a somewhat upbeat note: “If it weren’t for the presence of the Bermuda 40 in Cruising World’s list, I wouldn’t even have bothered to vote.”
By vote, he means that he, like hundreds of other readers, took the time to click through to an accompanying page where we asked you to help us reshuffle our alphabetical listing of noteworthy production sailboats so that we could rank them instead by popularity. So we ask you to keep in mind that this list of the best sailboats was created by our readers.
The quest to building this list all began with such a simple question, one that’s probably been posed at one time or another in any bar where sailors meet to raise a glass or two: If you had to pick, what’re the best sailboats ever built?
In no time, a dozen or more from a variety of sailboat manufacturers were on the table and the debate was on. And so, having fun with it, we decided to put the same question to a handful of CW ‘s friends: writers and sailors and designers and builders whose opinions we value. Their favorites poured in and soon an inkling of a list began to take shape. To corral things a bit and avoid going all the way back to Joshua Slocum and his venerable Spray —Hell, to Noah and his infamous Ark —we decided to focus our concentration on production monohull sailboats, which literally opened up the sport to anyone who wanted to get out on the water. And since CW is on the verge or turning 40, we decided that would be a nice round number at which to draw the line and usher in our coming ruby anniversary.
If you enjoy scrolling through this list, which includes all types of sailboats, then perhaps you would also be interested in browsing our list of the Best Cruising Sailboats . Check it out and, of course, feel free to add your favorite boat, too. Here at Cruising World , we like nothing better than talking about boats, and it turns out, so do you.

40. Moore 24
39. Pearson Vanguard

38. Dufour Arpege 30

37. Alerion Express 28

36. Mason 43/44
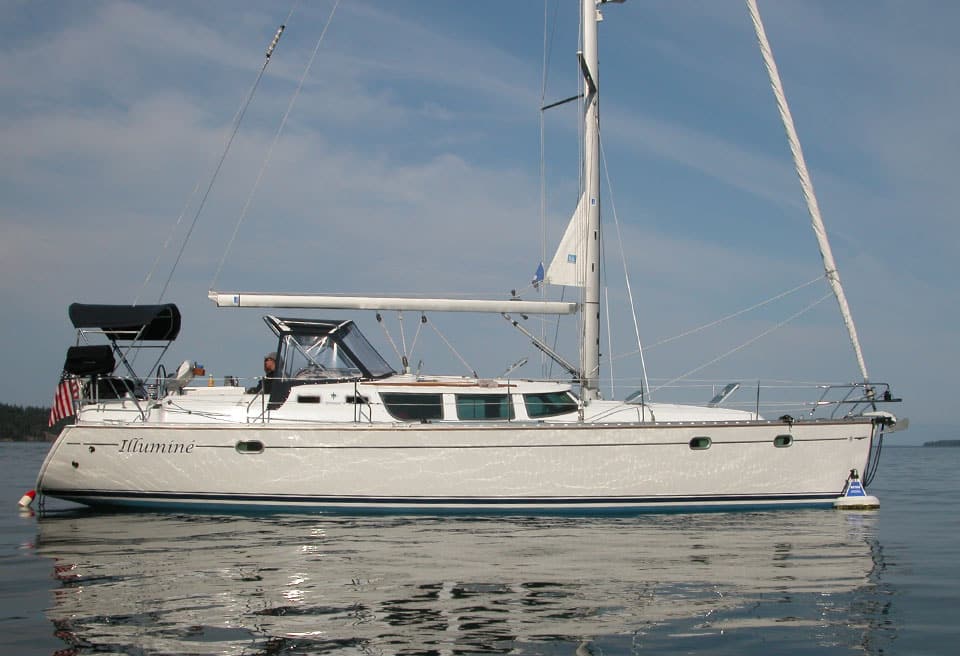

35. Jeanneau Sun Odyssey 43DS
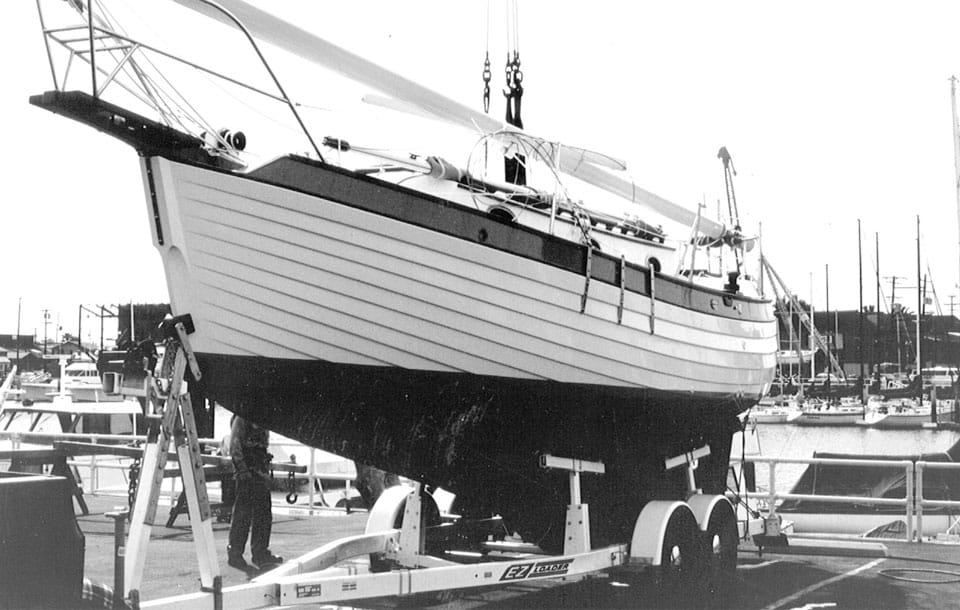

34. Nor’Sea 27
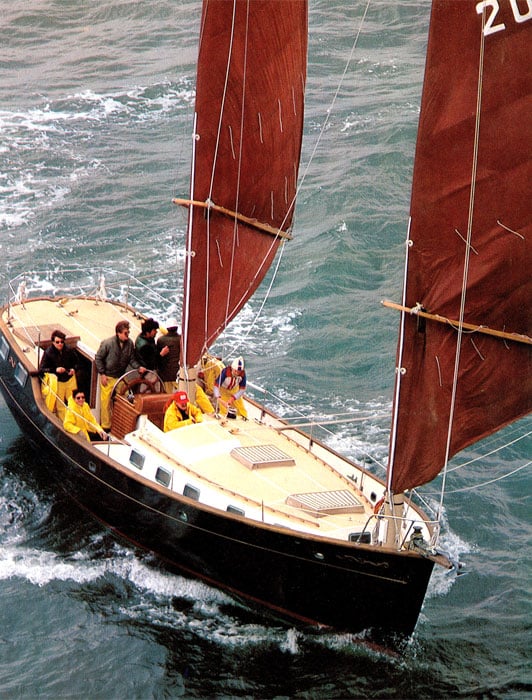

33. Freedom 40
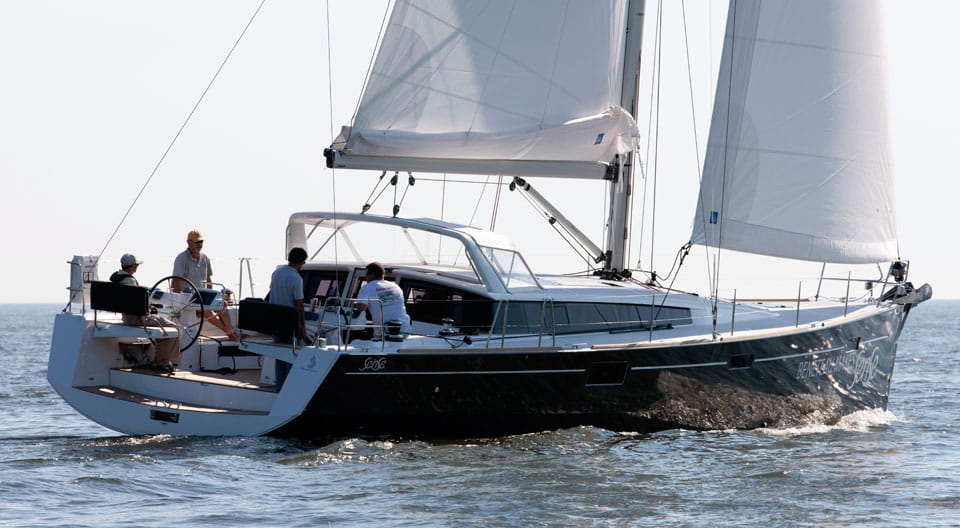

32. Beneteau Sense 50
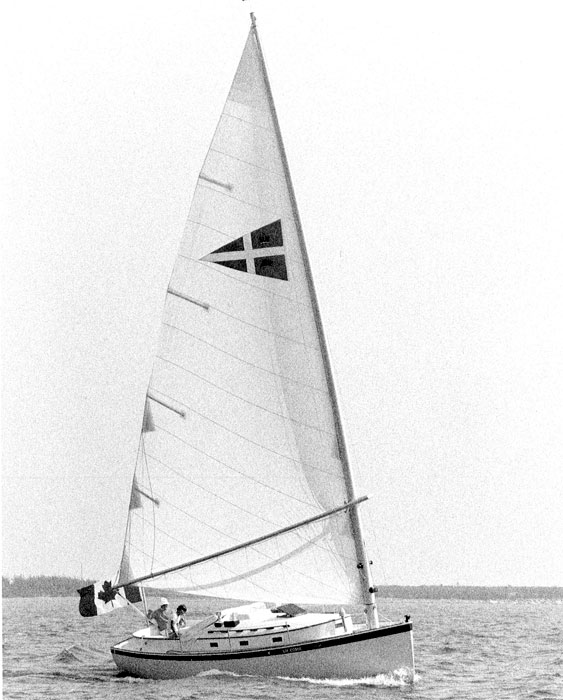

31. Nonsuch 30
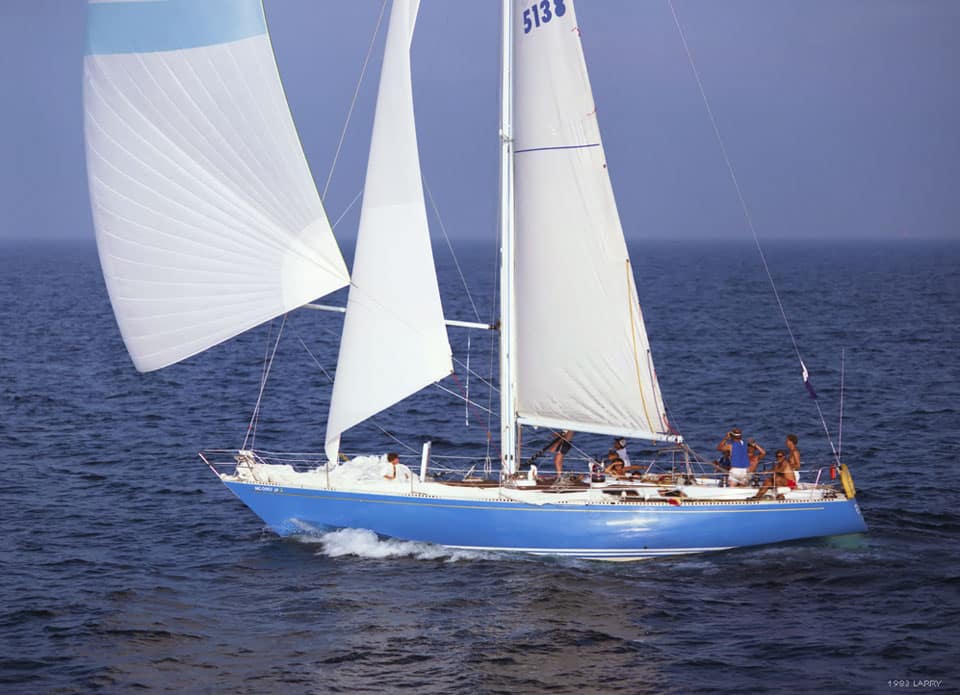

30. Swan 44

29. C&C Landfall 38
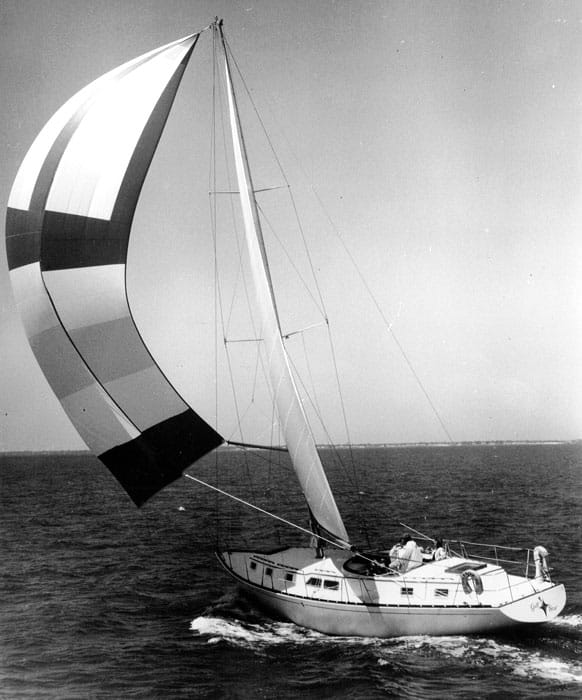

28. Gulfstar 50
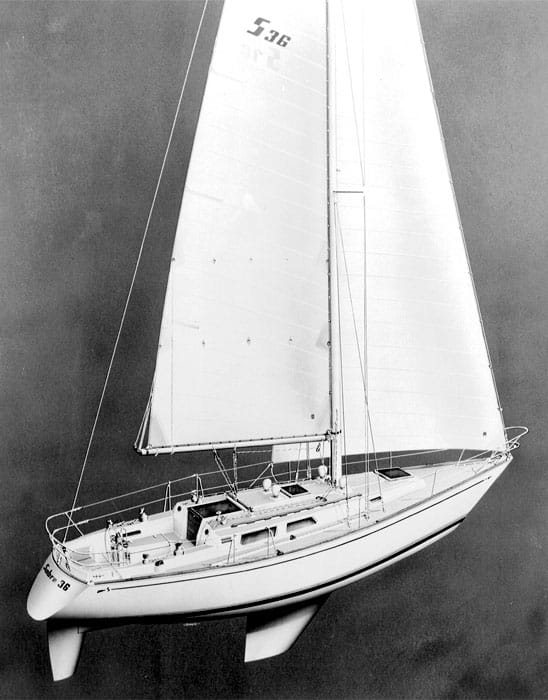

27. Sabre 36
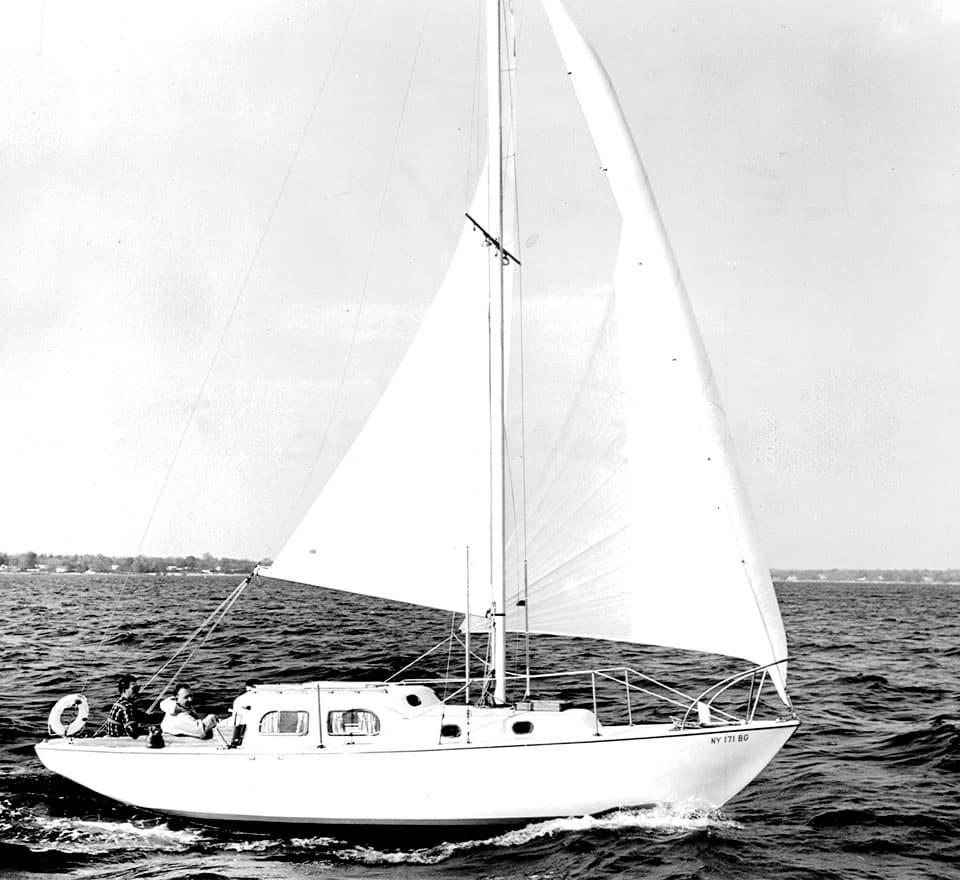

26. Pearson Triton
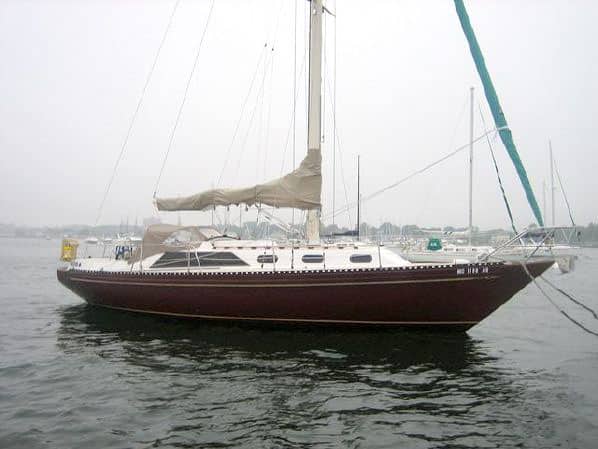

25. Islander 36
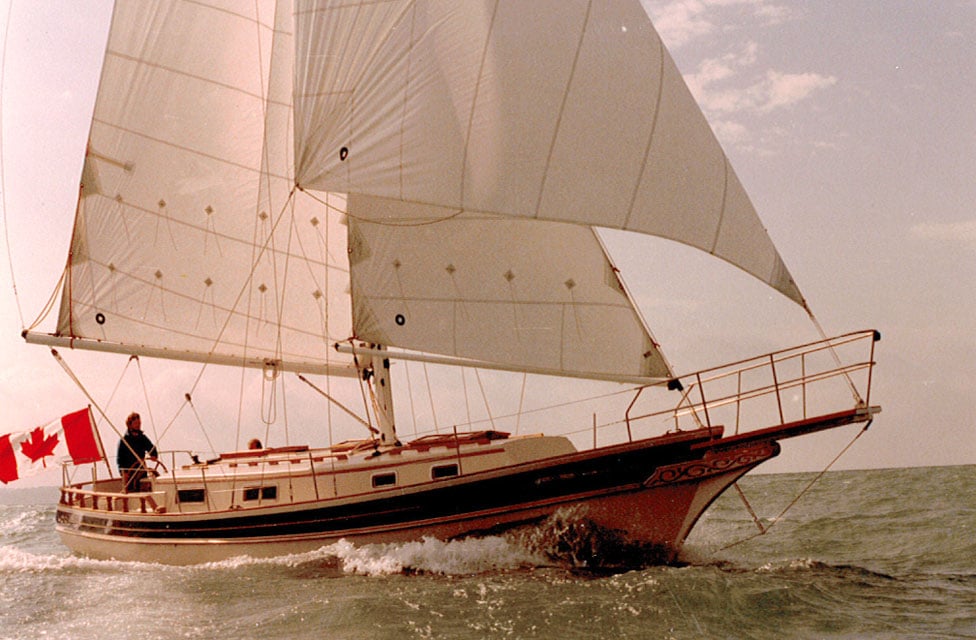

24. Gozzard 36
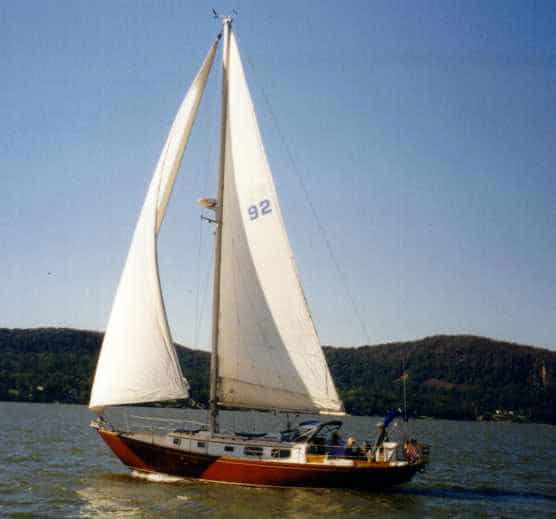

23. Bristol 40
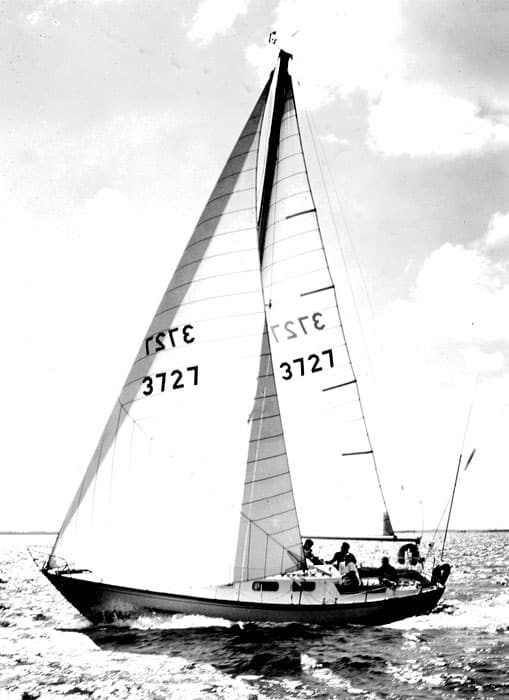

22. Tartan 34

21. Morgan Out Island 41
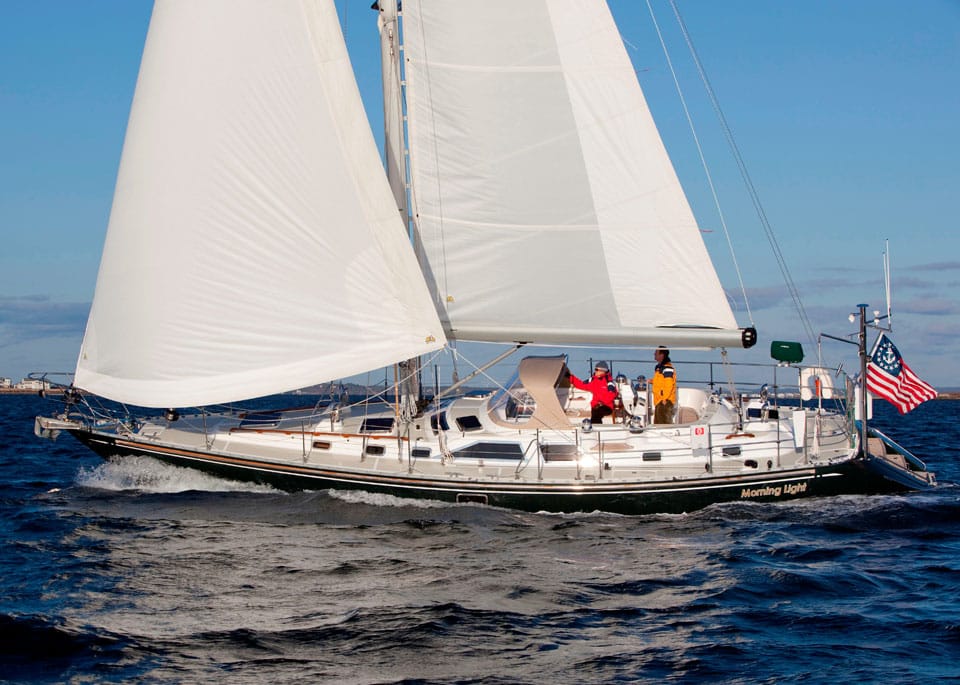

20. Hylas 49
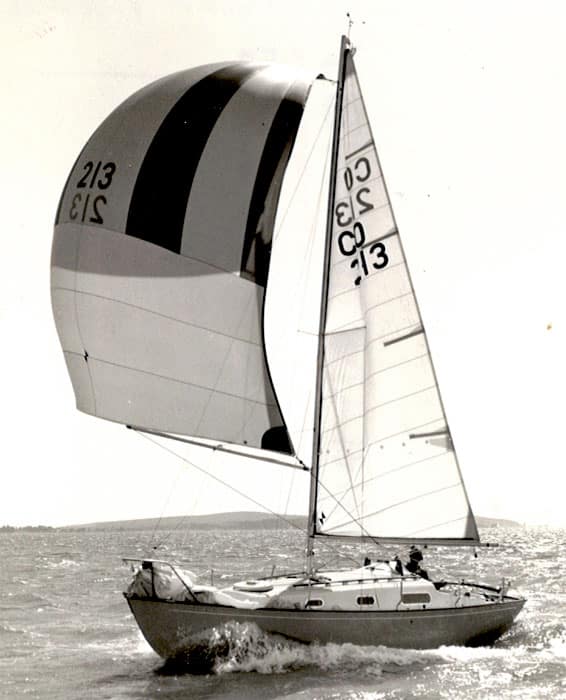

19. Contessa 26
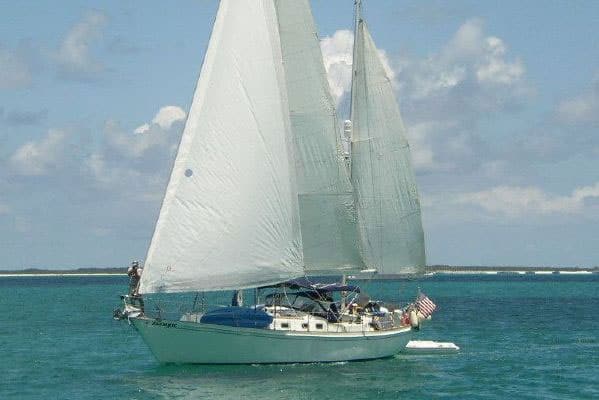

18. Whitby 42
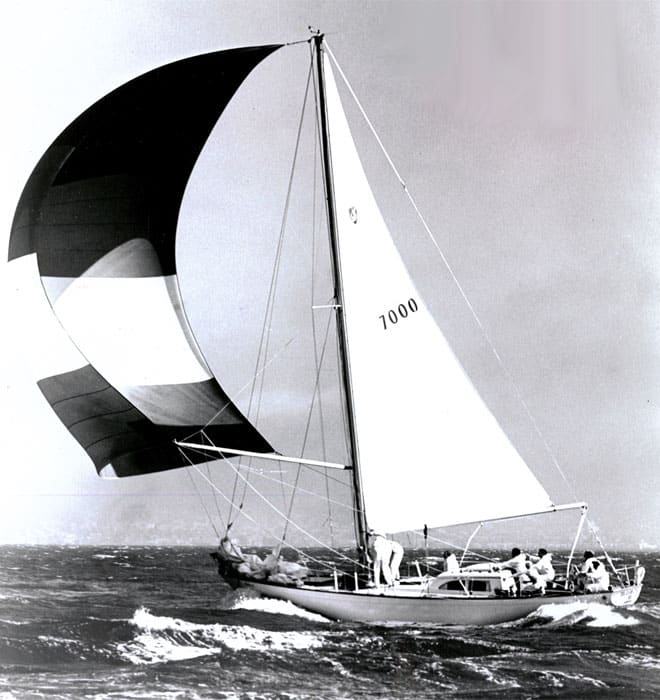

17. Columbia 50
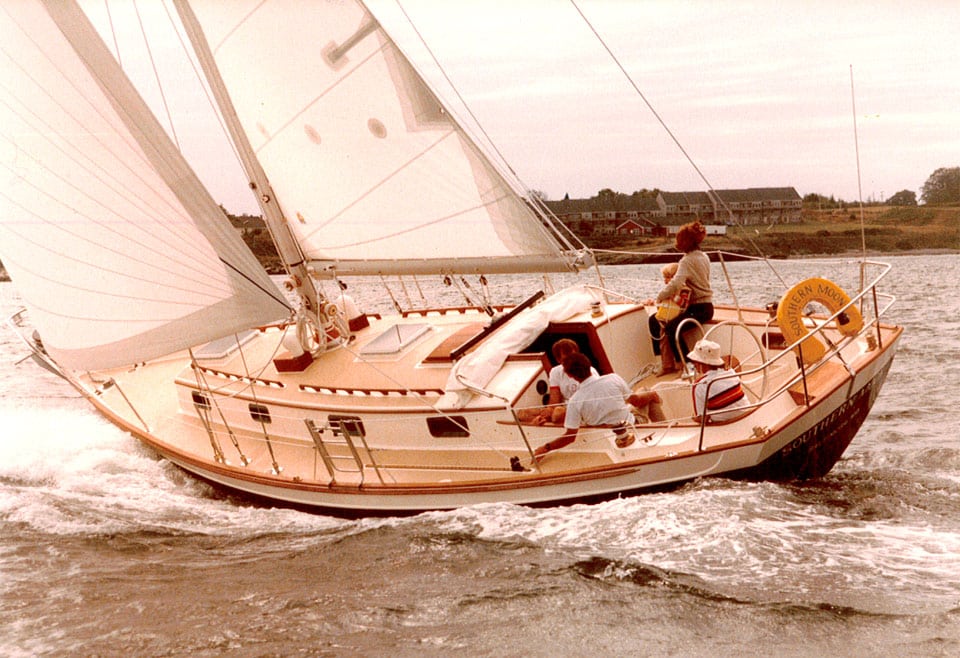

16. Morris 36
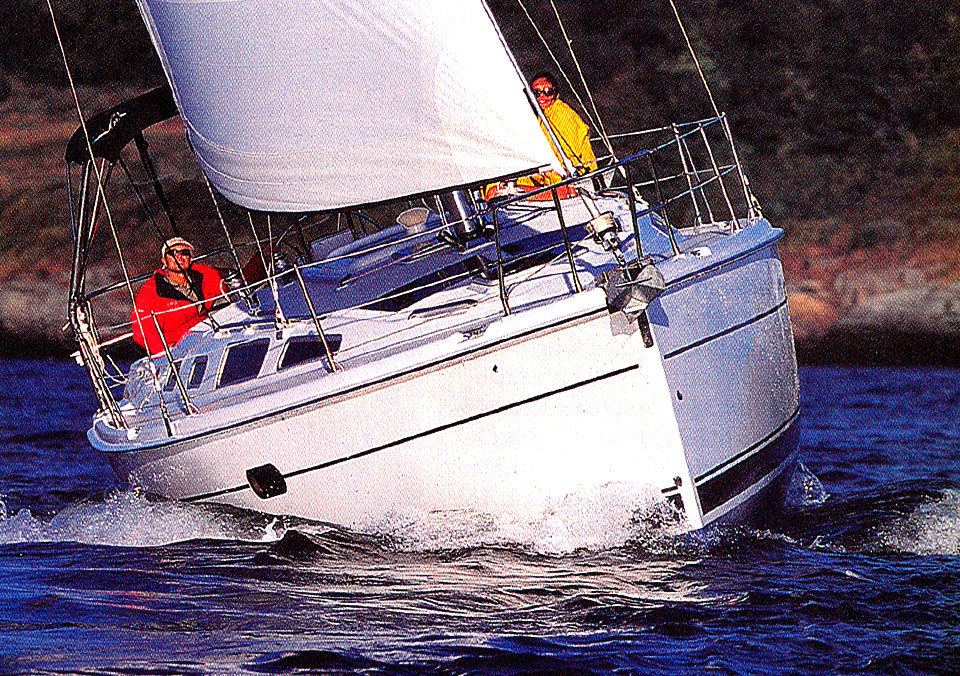

15. Hunter 356
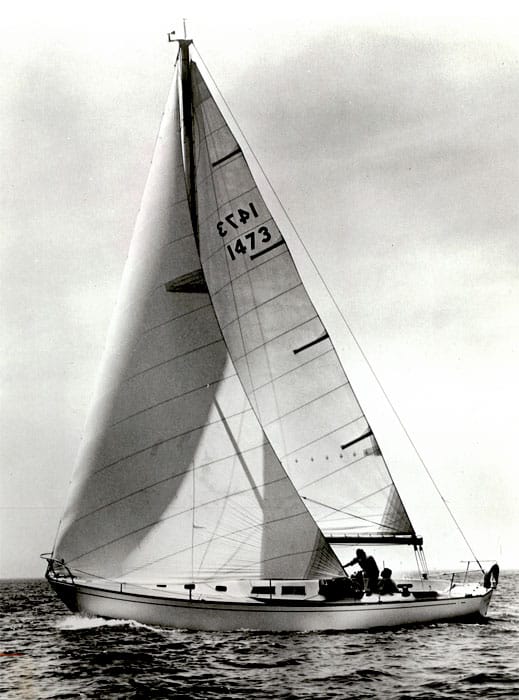

13. Beneteau 423
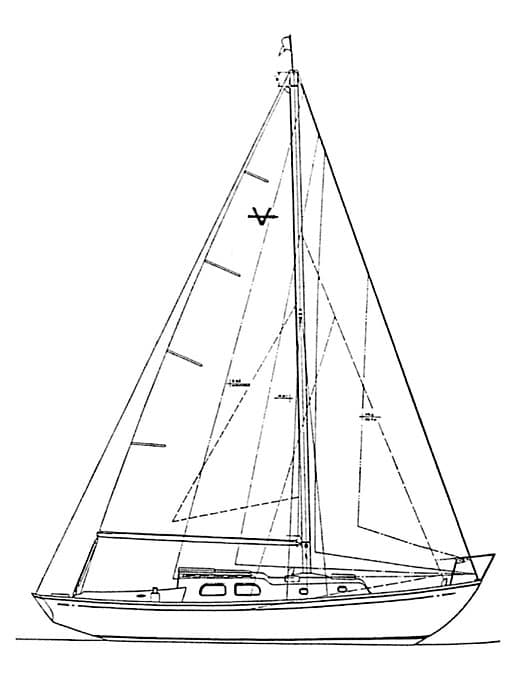
12. Westsail 32
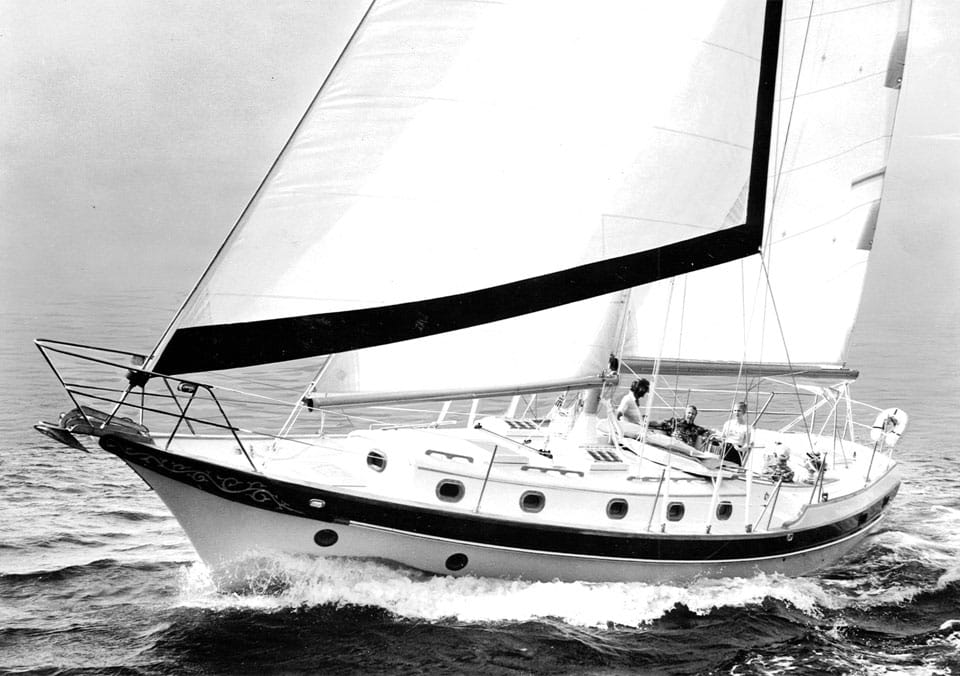

10. Alberg 30
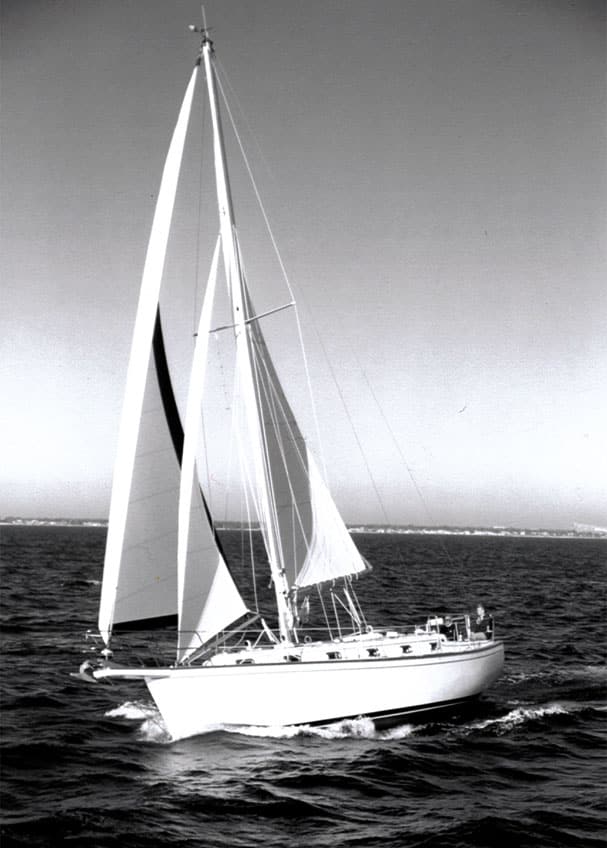

9. Island Packet 38
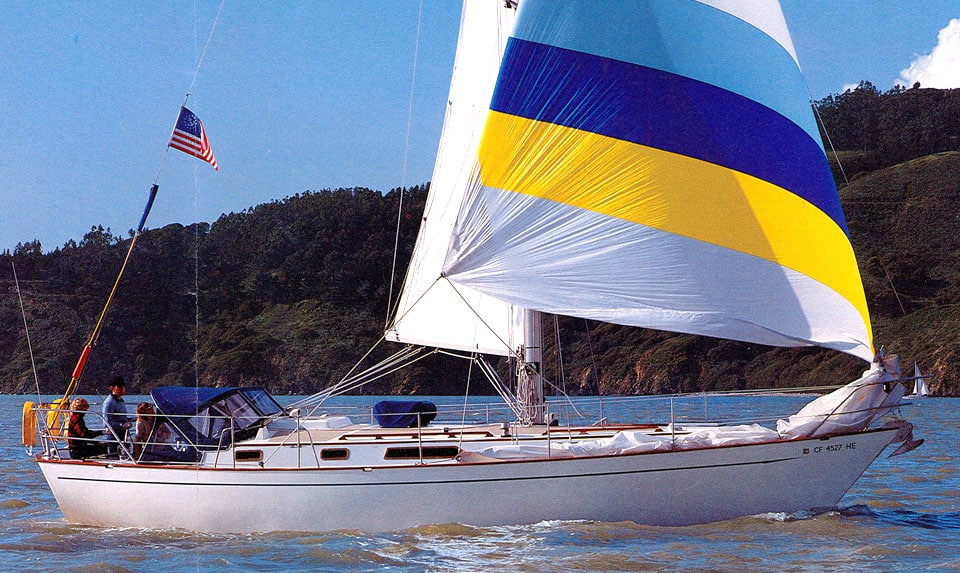

8. Passport 40
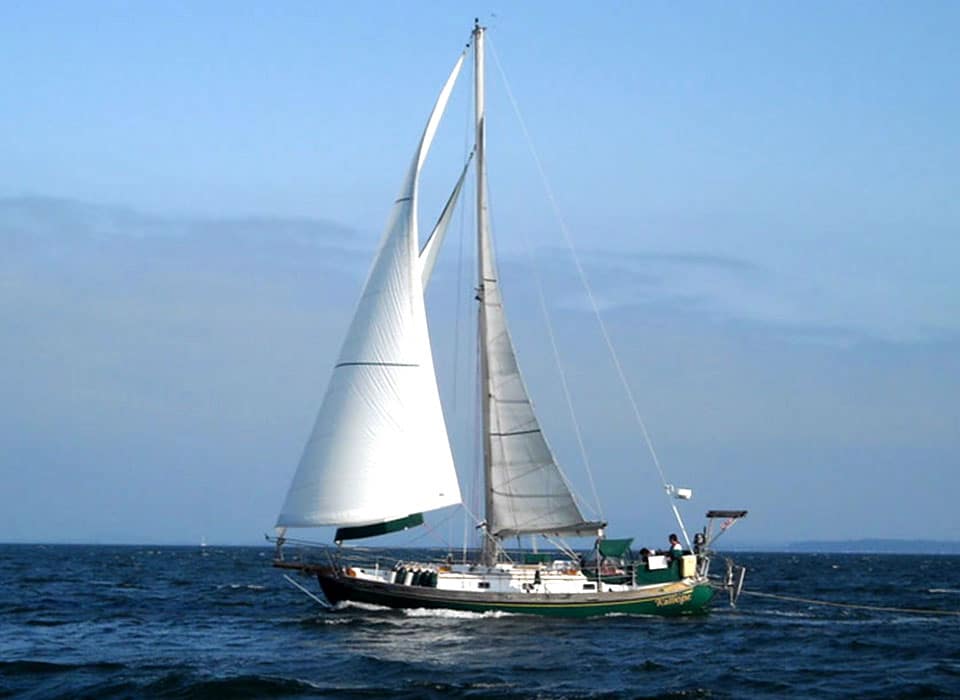

7. Tayana 37

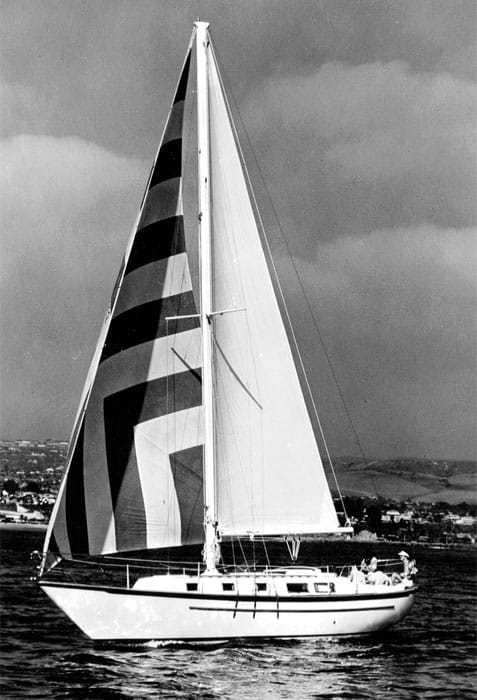
6. Peterson 44

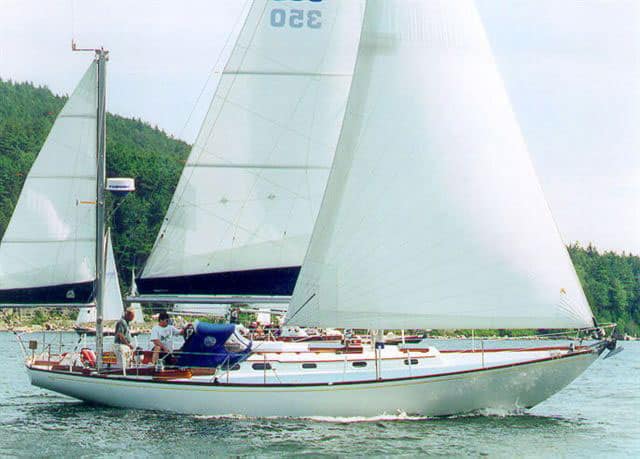
5. Pacific Seacraft 37
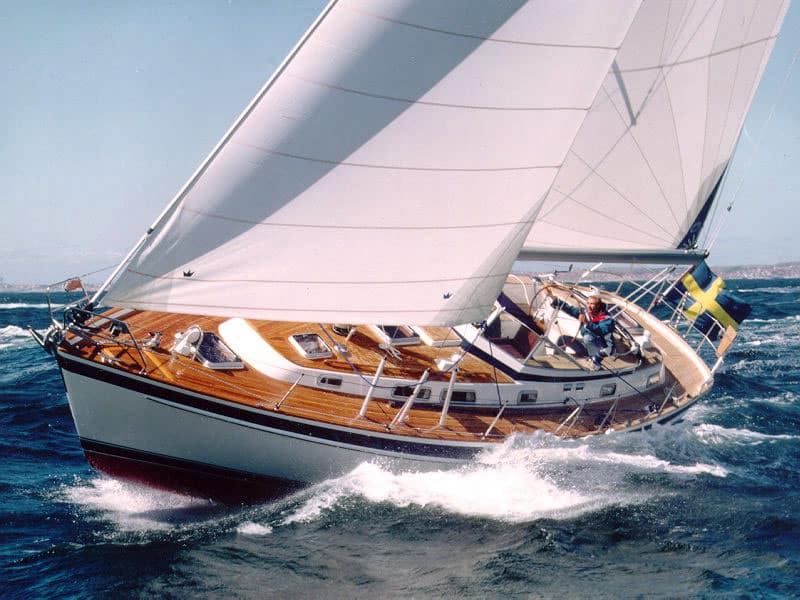

4. Hallberg-Rassy 42

3. Catalina 30

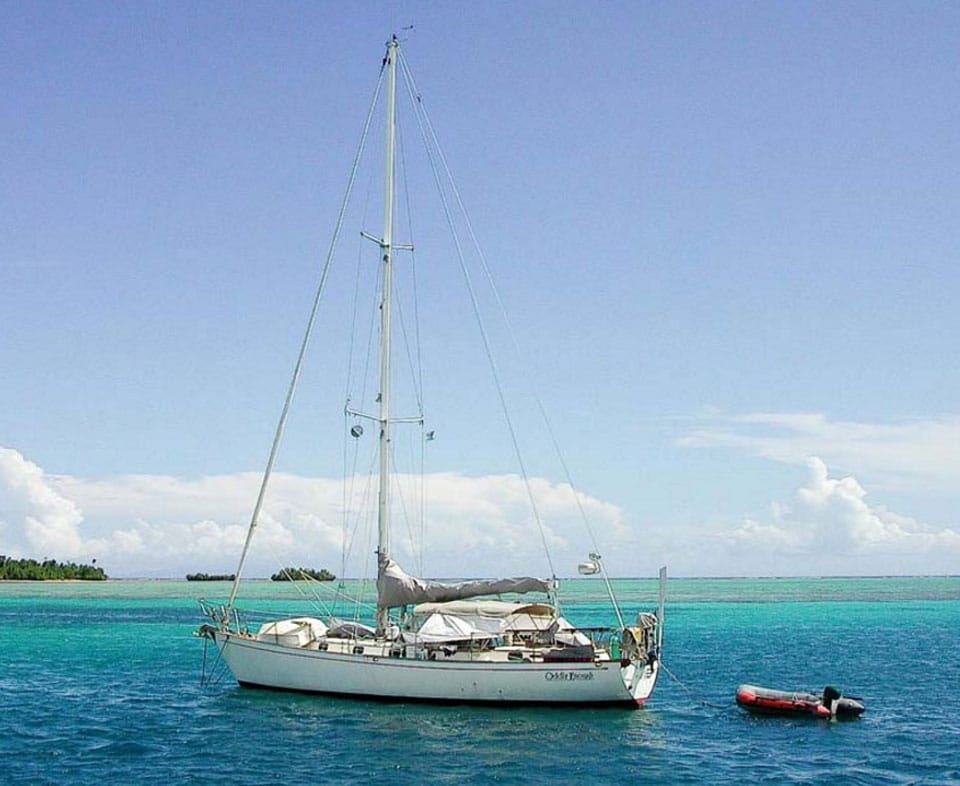
2. Hinckley Bermuda 40

1. Valiant 40
- More: monohull , Sailboats
- More Sailboats

Meet the Bali 5.8

Celebrating a Classic

New to the Fleet: Italia Yachts 12.98

Leopard 40 Prelude Listed For Sale

The Moorings Expands in Croatia
C-Map Updates North America Charts

St. Vincent Court Orders Deportation For Hijacking Suspects
- Digital Edition
- Customer Service
- Privacy Policy
- Terms of Use
- Email Newsletters
- Cruising World
- Florida Travel + Life
- Sailing World
- Salt Water Sportsman
- Sport Fishing
- Wakeboarding
Many products featured on this site were editorially chosen. Cruising World may receive financial compensation for products purchased through this site.
Copyright © 2024 Cruising World. A Bonnier LLC Company . All rights reserved. Reproduction in whole or in part without permission is prohibited.
- New Sailboats
- Sailboats 21-30ft
- Sailboats 31-35ft
- Sailboats 36-40ft
- Sailboats Over 40ft
- Sailboats Under 21feet
- used_sailboats
- Apps and Computer Programs
- Communications
- Fishfinders
- Handheld Electronics
- Plotters MFDS Rradar
- Wind, Speed & Depth Instruments
- Anchoring Mooring
- Running Rigging
- Sails Canvas
- Standing Rigging
- Diesel Engines
- Off Grid Energy
- Cleaning Waxing
- DIY Projects
- Repair, Tools & Materials
- Spare Parts
- Tools & Gadgets
- Cabin Comfort
- Ventilation
- Footwear Apparel
- Foul Weather Gear
- Mailport & PS Advisor
- Inside Practical Sailor Blog
- Activate My Web Access
- Reset Password
- Pay My Bill
- Customer Service

- Free Newsletter
- Give a Gift

How to Sell Your Boat

Cal 2-46: A Venerable Lapworth Design Brought Up to Date

Rhumb Lines: Show Highlights from Annapolis

Open Transom Pros and Cons

Leaping Into Lithium

The Importance of Sea State in Weather Planning

Do-it-yourself Electrical System Survey and Inspection

Install a Standalone Sounder Without Drilling

Rethinking MOB Prevention

Top-notch Wind Indicators

The Everlasting Multihull Trampoline

In Search of the Snag-free Clew

What’s Involved in Setting Up a Lithium Battery System?

Reducing Engine Room Noise

Breaking Point: What Can Go Wrong With Your Yanmar?

Mildew-resistant Caulks for Boats

Can We Trust Plastic Boat Parts?

Repairing Molded Plastics

Mailport: Marine plywood, fuel additives, through bolt options, winch handle holders

The Day Sailor’s First-Aid Kit

Choosing and Securing Seat Cushions

Cockpit Drains on Race Boats

Rhumb Lines: Livin’ the Wharf Rat Life

Resurrecting Slippery Boat Shoes

Shoe Goo’s Gift to Sailors

Tricks and Tips to Forming Do-it-yourself Rigging Terminals

Marine Toilet Maintenance Tips

Learning to Live with Plastic Boat Bits

The Ultimate Guide to Caring for Clear Plastic
- Sailboat Reviews
Practical Sailor Takes a Look at Trends in Modern Boat Design
Is the quest for speed and interior comfort trumping smart design in todays sailboats.

Practical Sailor editors have noticed the increasing tendency in newer-model sailboats to be ill-mannered in gusty conditions. Establishing balance between the sails and the hull is one of the main factors in quality boat design. For correct trim, many things must be considered: the ballast package location, the combined longitudinal center of gravity (LCG), and the longitudinal center of buoyancy. At the same time, to maintain a balanced helm, the keel must promote sufficient lead (the fore and aft distance between the center of effort and the center of lateral resistance). To highlight how these boat design principles play out, Practical Sailor looks at classic sailboats such as the Bill Shaw-designed Pearson 32, Ericson 41, Valiant 40, and Peterson 44, and compares their keel/sail ratios and lead values to more modern sailboat designs such as the Catalina, Hunter, Tartan, and Beneteau.
In the course of taking out boats for testing, Practical Sailor editors have observed an increased tendency for new-model sailboats to be ill-mannered in gusty conditions. We have been watching this trend for several years, and it seems to be becoming more usual than unusual.
In a typical situation, we will be sailing the test boat on the wind in 12 or so knots of breeze and everything is fine. Then, the breeze picks up to about 15 knots and the helm loads up. OK, thats to be expected, so we flatten the main, drop down the traveler, and that takes care of it.
Then we get a puff. Were already on the point of needing to reef, so in the puff, were overcanvassed. Instead of just heeling farther, the boat begins to round up. Fighting it with the helm is hard work, and easing the main so it luffs doesn’t help much.

Photo by Ralph Naranjo
We take in a reef, which usually means we roll in a bit of the jib or a bit of the main, or both, and the helm lightens up. We trim to the new wind and sail along, a bit slower now in the light spots, but then the next gust comes along, and the helm immediately loads up again.
In the worst case weve experienced, the boat rounded up so quickly that it tacked, even though the helm was hard over in the opposite direction. To prove that wasnt a fluke caused by a temporary diversion into a parallel universe, it did the same thing on the other tack.
Practical Sailor editors are old enough to remember a generation of cruising boats that didnt behave in this manner. For sure, there have always been twitchy boats, but most, when hit by a gust, would heel a little more, put some pressure on the wheel or tiller, and once the boat picked up speed, the pressure would come right off. A boat like that will sail for a long time with a loose lashing on the helm.
So, where does this bad habit come from? Several trends in modern cruising yacht design can share the blame. One of them is builders inclination to tilt their designs toward the performance end of the cruisers spectrum. Many recent and current cruising boats, if suitably fitted out with racing sails and the hardware and software to tweak them, could put up an impressive show on the race course.
The sensitivity to trim that accompanies such potential isn’t always suited to cruising shorthanded or with a family, when balance and good manners are key both to enjoyment and, to a degree, safety.
Establishing Balance
Many factors contribute to the balance of a sailboat. The obvious and principal pair are the sails and the hull. When working up a new design, the architect develops these in close association, but both are in turn influenced by other aspects of the boats design as it evolves.
In the standard approach, the designer works up preliminary drawings to express the basic requirements of the design brief, which normally include a desired length, displacement, cabin arrangement, and sailplan to provide the desired performance.
He then sketches out the hull lines (the matrix of contours that define its three-dimensional shape and its volume) to enclose the interior and meet expressed performance goals. The preliminary lines also serve as a basis on which to perform a number of calculations, one of them being the location of the center of buoyancy (CB).
With everything roughed out, the designer then “weighs” every item that will go into the complete boat, from the hull laminate to the toothbrush holder, but excluding the ballast. He combines these weights and their locations on the three axes, X, Y, and Z, to calculate the center of gravity (CG) of the whole package. Computer programs have helped to speed up this process and make volume calculations more accurate, but the process hasn’t changed much.
For the boat to float on its desired lines, the ballast package must then be designed and located to bring the combined longitudinal CG (LCG) of hull and ballast to the same fore-and-aft location as the CB (LCB). Once everything has been resolved satisfactorily, the designer can finalize the lines, carry out the necessary calculations, and establish shape and locations for the keel and the sailplan.
On most boats of current design, the ballast also constitutes the fin keel, and in that role, its location determines the center of lateral resistance (CLR), which in conjunction with the center of effort (CE) of the sailplan, influences how the boat balances under sail.
Even as boat design procedures have evolved from three-dimensional modeling using half hulls, through two-dimensional modeling using pen on vellum, to three-dimensional virtual modeling on computers, the fundamental principles have remained constant. One of the fundamental values used for predicting the proclivities of a boats helm is the dimension termed “lead.” Lead, pronounced “leed,” is the fore and aft distance between the CE and the CLR, expressed as a percentage of the waterline length (DWL).
“Skenes Elements of Yacht Design,” as revised by Francis S. Kinney, and other references for yacht design provide rules of thumb for calculating lead from the sailplan and the hull profile. (See illustration above).
Looking at the diagram, its easy to see how lead is an elusive quantity. First of all, no boat sails with the sailplan as shown-the sails are never flat and on centerline. The traditional range for lead places the CE forward of the CLR by 14 to 19 percent of DWL. This value is lifted from “Skenes,” for years the first reference for any designer. Since that book was written and updated, hull forms have changed, and with them, optimum values for lead.
On designs with fin keels, lead is often calculated with reference to the keel alone. One feature remains constant whatever the design. Moving the centers closer together-reducing lead-increases the tendency to weather helm. Moving them apart reduces that tendency. If the lead is too great, the result may be lee helm, which is generally considered undesirable-and is in fact, rare.
In Kinneys prime years, the 1960s to the 1980s, the basic working sailplan of a sloop included a 150-percent genoa, which would have the effect of moving the CE closer to the CLR. Many designs today have headsails with short or even no overlap and very often a full-battened mainsail with lots of roach. The different aerodynamic characteristics of such rigs might well affect optimum lead, something which designers can only determine through experience. (If a boatbuilder offers an in-mast furling mainsail as an option, its effect on lead will differ from that of the “classic” sailboat.)
The effective CLR can also be very different from that calculated. On a deep-bodied, full-keel hull, that difference simply might be the difference between the geometric center and the center of hydrodynamic pressure of the whole profile.
A sharp bow with a pronounced “chin” might well move the effective CLR forward. On a modern, fin-keeled boat with a shallow, broad canoe body like that of a dinghy, the keel makes a proportionately larger contribution to lateral resistance, so the location of the keel will strongly influence where that resistance operates.
Obviously the rudder, too, is part of the lateral plane, but if our objective is to sail with light to neutral pressure on the helm, under normal conditions, it should not be making a significant contribution to lateral resistance. Its role is to provide a means to change the boats direction and to compensate for the constant fluctuations in the forces applied to the boat in the normal course of sailing. A certain amount of pressure in the form of weather helm helps by providing positive feedback to the helmsman on the state of balance. That said, on many racing hulls, the rudder is designed to contribute lift and has an active role in driving the boat to windward. (It is worth noting that those wide-bodied race boats also tend to have twin rudders.)
Then and Now
Even in the age of computer modeling, yacht design remains a series of compromises. At the moment, it seems the pendulum has swung to a point where high-volume, wide-beam shapes dominate. With them come large rigs to overcome skin drag and its negative effect in light air. As a result, theres a need to sail the vessel as flat as possible or suffer the consequences.
The sailplan and outboard profiles of boats from different eras represent the shift in yacht design that has occurred during recent decades. The modern boats have longer proportional waterlines, indicating higher potential speed. It also means that the boats immersed volume, or displacement, has been distributed over a greater length.
Given two boats of similar displacement like the classic Pearson 32 and the modern Tartan 3400 (above), the Tartan winds up with a shallower canoe body. This also contributes to its being potentially faster and, if both boats had the same draft, would give the keel a slight advantage in span, and therefore effectiveness to windward.
So far so good, but a shallower canoe body forces the cabin sole upward, especially if the belowdecks accommodations are to take full advantage of the wide beam favored in the modern hull. To achieve comparable headroom with its older counterpart, the cabintop has to go up, too, and to ensure sitting headroom on the settees under the sidedeck, so does the freeboard.
Ultimately, the whole deck moves upward. To ensure the boom doesn’t sweep everybody out of the cockpit during an unplanned jibe, the boom too goes up. If sail area is not to be compromised, the entire mainsail goes up, and with it, its center of effort. The bigger the boat, the less pronounced these differences become as the proportions become more relaxed.
Differences are visible, too, between the boats keels; the modern Tartans is smaller in area. While it might be claimed that less wetted surface promises higher sailing speeds in light air, some builders accept a smaller keel to simplify the manufacture of the hull.
In a perfect world, the designer draws a keel to suit the boats sail area and other characteristics, places it to obtain the desired sailing performance, then massages the needed ballast to both fit the keel and trim the boat correctly. The volume of the ballast is usually less than that of the keel, and the builder has to do some intricate laminating work to mold a keel to receive ballast internally or a stub to which to bolt it externally.
On many production boats today, the keels are bolted directly to the bottom of a fair canoe body, a practice which eliminates much labor. The consequence is that the area of the keel is determined by the weight, and therefore the volume, of the ballast. To achieve the desired hydrodynamic properties and mechanical strength-it mustnt bend under the influence of normal sailing loads-a given volume of ballast can be formed into a limited range of shapes. Placing ballast in a bulb at the bottom aids the keels efficiency by creating an endplate effect and raises stiffness by placing ballast low, but it means that the keels lateral plane is sharply reduced.
For a more dramatic representation of how changes in keel design can affect helm balance, compare a Cruising Club of America (CCA) design like the Ericson 41 above, to a modern equivalent with comparable sail area like the Beneteau 46.

When sailing, two boats are subjected to similar forces on the sails. Resisting that side force are the immersed hull, the keel, and the rudder. If the hulls offer similar resistance, the remaining force is shared between the keel and rudder. If one keel is smaller than the other (as is clearly the case here), the effect is to increase the share taken by the rudder.
When the sails are trimmed properly and all is in balance, the rudder will carry a small load. If however, you hit a gust, the rudder must pick up a high proportion of the added side thrust until balance is restored, usually by some adjustment to sail trim.
Simply put, boats of the general modern type are not forgiving in changeable conditions, say, for example when the apparent wind is in the 12- to 18-knot range. At the higher end, youd want to be reefed; at the lower end, probably not.
On a day when you expect the wind to soften rather than harden, youd rather not put in the reef, so that you can maintain speed in the lulls. In the puffs, you want your hands free to ease the traveler and flatten the jib, which is hard to do if the helm is a handful. Compounding the problem on most boats, the mainsail controls are usually not within reach of the helm.
On racing boats, such sensitivity isn’t an issue. On the contrary, sufficient crew are on hand to make adjustments on the fly as quickly and often as needed to keep the boat sailing at her fastest.
Cruising boats are often sailed shorthanded and by crews who are not looking for a constant physical workout. An autopilot might be doing most of the steering, and good balance is helpful in protecting it from having to work too hard-or from being overpowered.
Another striking difference between the older and newer designs is visible in the plan (overhead) view. By 1980, cruising-boat hulls were already becoming beamy relative to boats of the 1960s and 1970s. The current trend is to carry the beam aft, so that in the region of the rudder, its as much as 85 percent of the maximum beam, far wider than the 55 percent to 60 percent once considered acceptable. The principal beneficiary of this extra breadth is the boats interior-builders often offer twin double cabins aft where a generation ago they might have squeezed in a quarter berth and a cockpit locker. The cockpit, too, becomes roomier, and the transom, scooped and sculpted, is transformed into a swim platform and dinghy dock.

Photo by Jarrod Scanlon
All this additional boat aft adds weight aft, in both construction materials and outfit. To compensate, the ballast-that is to say, the keel-has to be fitted farther forward.
The full beam aft does provide a significant boost to the boats ability to carry sail. As the boat heels, the center of buoyancy moves quickly outboard, away from the center of gravity. This lengthens the righting arm, giving a positive contribution toward stability, but it also moves the immersed centerline of the hull away from the static centerline along which both the keel and the rudder are attached. Depending on the hulls shape, this can create a distortion in the immersed volume, which can in turn affect the dynamics acting on it.
Effect of Keel Area
Another factor entering the equation is the area of the keel. This, too, is apparent when comparing the drawings of the older and newer generation boats. Many of the standard tracts on the design of sailing yachts are, lets say, vague on what keel area is adequate or even desirable, although many designers have come up with their own formulas.
Because the keel is reacting in the water to forces generated on the sails by the wind, it makes sense that the area of a fin keel should be related in some way to sail area.
When naval architect Dave Gerr took over as director of the Westlawn Institute of Marine Technology, he found the course materials for sailing yacht design had little detailed explanation on this topic, a gap he subsequently filled. Briefly, he recommends no fin keel should be less that 2.5 percent of the sail area (mainsail 100 percent foretriangle) and need be no more than 5 percent. The smaller value is appropriate for a racing boat with a full crew aboard to trim and tweak the sails to every change in the wind. The larger area is suited to cruising boats, which need to be more forgiving to shorthanded crews.
Current Design Trends
In the past, racing measurement rules have been criticized because the boats designed to compete under them have become type-formed, sometimes with unwelcome consequences in how they handle. We might just as easily level criticism at present-day marketing and manufacturing methods for doing the same to cruising boats.
Lets face it, but for a few differences in sailplans and keel shapes, modern cruising sailboats are quite generic below the sheerline. They are all beamy; they carry their beam aft; they have long waterlines; they have dinghy-like underbodies; and they have spade rudders. The forces that have created this shape have at least as much to do with how many people can sleep and shower in them comfortably as with how the boats will sail.
Dishing out the hull shape in this manner makes it fairly easy to push through the water, but arranging the keel, rudder, and sails so they work in concert has become a more complex problem, exacerbated by having to compensate for extra weight of accommodations aft, something thats less of an issue in raceboats.
The byproduct of these design parameters is zesty performance, a bonus for the marketing department, but speed for its own sake is not the first priority of cruising sailors. In the brochure for the Beneteau 37, the boats polar diagram shows a maximum theoretical sailing speed of over 12 knots in 30 knots of wind. When cruising sailors encounter 30-knot winds, they are more likely to hunker down in the expectation it will blow even harder than they are to set the chute to go surfing. What they want is a boat that will take readily to hunkering, and all the signs indicate those boats are getting fewer in number . . . and they are mostly older designs.
- The Balancing Act
- Pearson 32 vs. Tartan 3400
- Ericson 41 vs. Beneteau 46
- Practical Sailor Design Guide
- The Modern Hull and Helm Balance
RELATED ARTICLES MORE FROM AUTHOR
Leave a reply cancel reply.
Log in to leave a comment
Latest Videos

Catalina 380: What You Should Know | Boat Review
- Privacy Policy
- Do Not Sell My Personal Information
- Online Account Activation
- Privacy Manager

- SPECIFICATIONS

In 2016, we spent the winter and spring months working closely with Paul Waring and Robert Stephens of Stephens Waring Yacht Design and Martha Coolidge of Martha Coolidge Design , together with the owners, to fine-tune the design and construction of Anna , a cold-molded 65′ modern classic sloop. As is customary with our custom projects, we built a full-scale mockup of the boat in March, plus an alternative mockup of the master stateroom and guest cabin. This set-up enabled us to walk through a couple of different layouts of the project to further fine tune the cockpit and interior layout according to the owners’ wishes.
Anna was launched on a brisk April afternoon in Thomaston, and after a few weeks of commissioning at Lyman-Morse’s facilities in both Thomaston and Camden, we delivered her to her owner in Newport, Rhode Island. She quickly earned a name for herself on the classic yacht racing circuit in New England, including first-place finishes. After a summer of sailing from Rhode Island to Maine and Nova Scotia, her owner delivered this stunning yacht back to Lyman-Morse for storage and seasonal service.
Specifications
- displacement 57,000 pounds
- fuel capacity 250 gallons
- water capacity 200 gallons
- type Sailing
- designed by Stephens Waring Yacht Design
- builder Lyman-Morse
- model 65' Cold Molded Sailing Yacht
- construction Composite cold-molded wood
- hull material Wood
- configuration Sloop
- boat engine SteyrMO164 Diesel
- horsepower 160
- Sail Area approx 2000
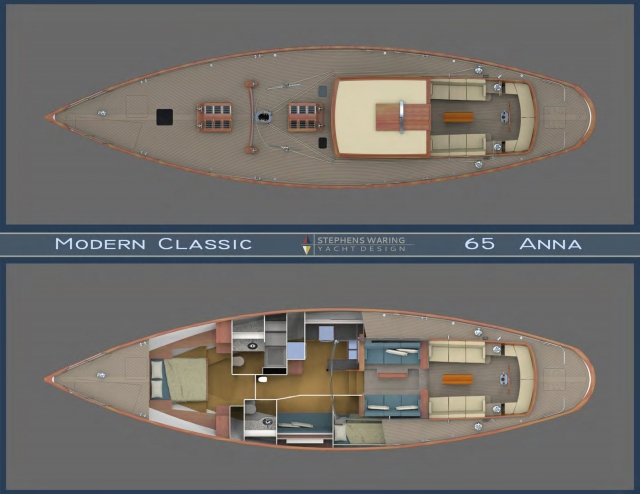

Under Sail: S/Y Anna
The fusion of design, technology, and craftsmanship that created Anna has resulted in a powerful, and yet ultimately gorgeous, yacht — precisely what her owner, designer, and builder had envisioned.
Acclaimed photographer/videographer Alison Langley documented every step of Anna ‘s construction. Scroll down for a six-part series of videos chronicling her construction.
Layout and Design
The mission of this modern classic sloop is to provide easy day-sailing to have fun with friends and family. The roomy cockpit flows into the raised saloon that features large, drop windows in the aft bulkhead for easy socializing and communications between exterior and interior spaces. Accommodations provide for 6, though overnights and cruising are not top priorities for the owners. However, purposeful crew accommodations for delivery up and down the eastern seaboard were specified. And the owners cabin forward has all the creature comforts commensurate with a yacht of this caliber.
While the owners’ racing agenda is light, this boat will no doubt perform well around the buoys or make efficient passagemaking the norm. The sloop-rigged yacht is fitted with a large main and self-tacking jib for easy everyday sailing. The yacht is made race ready by switching to the manually tacked 105% working jib along with downwind sails and cruising spinnaker to help round out the inventory in races or sailing on lighter days.
The talent of every LM department was tapped in the construction of this yacht. Precision on every front is required in such a highly engineered boat. The cold molded hull construction is a transparent one in that the hull and structure is left exposed on the interior rather than being covered up with ceiling and hull panels. Douglas fir deck beams, traditional raised and v-groove paneling, bright varnish and white painted surfaces make it a light, airy enclave. LM Fabrication manufactured the gorgeous gleaming, custom designed deck hardware including the rail systems, butterfly hatch hardware, amidships boarding step, and various structural components. Martha Coolidge Design has worked closely with the owners to fine-tune the meticulously designed interior spaces.
Our systems team stepped up to the task with high-tech push button hydraulic systems, including the amidships boarding platform and the anchor launching system. To deploy the anchor, one simply opens the hatch and presses a button, the custom hydraulic anchor launching system deploys and hoists the anchor hands free. While underway the anchor stows neatly and flush below the teak deck hatch. Once at anchor, the amidships board platform can also be deployed. The platform is operated by push-button hydraulics. A stainless steel stair folds automatically into position as the platform is lowered. This all-in-one platform with stainless swim ladder provides for the easiest access to tenders, docks, and whatever waters invite you for a swim.
Part 1: Planking Anna
Lyman-Morse’s newest sailboat, designed by Stephens Waring Yacht Design, is the embodiment of a Spirit of Tradition yacht, perfect for both day sailing and racing. The work of Lyman-Morse’s in-house production-design team made the planking of the first three layers of the cold-molded hull a seamless endeavor.
Part 2: The Whiskey Plank
The whiskey plank is the last plank fastened into the hull and is typically marked by a celebration, according to WoodenBoat Magazine. Who are we to argue!
Part 3: Rolling the Hull
The process of rolling over a large hull is always an interesting affair for any boatbuilder, but the Lyman-Morse team made it look easy. Once upright, the hull is ready for installation of the interior modules, deck, and final commissioning.
Part 4: Making the Modules
Utilizing our CNC machining capabilities and the latest CAD software, the Lyman-Morse team was able to design and build each of Anna’s interior modules in its entirely and then install it directly into the hull, dramatically increasing accuracy and efficiency.
Part 5: Measure Once, Cut Once
Lyman-Morse’s in-house use of technology dramatically increased efficiency in the building of Anna, a 65′ cold-molded modern classic sailboat, and resulted in a better final product.
Part 6: Launching Anna
After two years of design, technology, and craftsmanship, Lyman-Morse launched the 65′ sloop Anna on brisk April afternoon.
- Name * First Last
- Add me to your mailing list
- Email This field is for validation purposes and should be left unchanged.
- Motorcycles
- Car of the Month
- Destinations
- Men’s Fashion
- Watch Collector
- Art & Collectibles
- Vacation Homes
- Celebrity Homes
- New Construction
- Home Design
- Electronics
- Fine Dining
- Baja Bay Club
- Costa Palmas
- Fairmont Doha
- Four Seasons
- Four Seasons Private Residences Dominican Republic at Tropicalia
- Jacob Cohën
- Reynolds Lake Oconee
- Wilson Audio
- 672 Wine Club
- Sports & Leisure
- Health & Wellness
- Best of the Best
- The Ultimate Gift Guide
8 Fascinating Facts About ‘Kokomo,’ the Lightning-Fast 192-Foot Sailing Superyacht
The 192-footer has a 242-foot-high mast and spinnaker half the size of a football field. but it's so automated it can be sailed by two people., julia zaltzman, julia zaltzman's most recent stories.
- This Boatmaker Builds 1960s-Inspired Cruisers With a Modern Twist. Here’s How.
- This 150-Foot Fishing Trawler Was Transformed Into a Rugged Explorer Yacht
- These 3 Miniature Explorer Yachts Are Ready to Take You Off-Grid
- Share This Article

The 192-foot Kokomo was the second largest sloop in the world when it launched from New Zealand’s Alloy Yachts shipyard in 2010. It remains the largest fast-cruising sloop available for charter. The yacht’s commissioning owner Lang Walker (who died in January 2024) was a seasoned sailor who gave all three of his yachts the same name.
The first was a 131-foot sloop, which Walker replaced five years later with a 171-footer. The same day he took delivery of his 171-foot sloop, he placed an order for the third and final 192-foot Kokomo, which he planned to use for racing and cruising around the world. He also kept the same design team for all three yachts, with exterior and naval architecture by Ed Dubois and interior by UK’s RWD.
The reference to the yacht’s name has had different explanations over the years, ranging from the pseudonym of a composer whose music Walker played as a child to a nod to the Beach Boys’s song from their 1988 album Still Cruisin’ , which references a fictional utopian island called Kokomo. The island fantasy was brought to life in 2011 when Walker acquired a private island in Fiji’s Great Astrolabe Reef and named it Kokomo .
Here are eight unknown facts about one of the most game-changing sailing yachts on the water.
You’re Going to Need a Bigger Boom

When Kokomo was launched, she was the second-largest sloop in the world and carried the largest set of sails made by Doyle Sails in New Zealand. The 23,971-square-foot asymmetric spinnaker is half the size of a professional football field, while the 9,688-square-foot mainsail needs a crane to lift it. Because of the gargantuan size of the sails, the designers entered a new era of spar and winch design, having to “reinvent” the deck equipment—winches, mast, boom, rigging and sails—to cope with the 31.6-ton load on the genoa sheet and 32-ton load on the main sheet clew. The 244-foot carbon mast is the largest ever made by Southern Spars.
A Hidden Lifting Keel

The yacht’s 130-ton lifting keel is one of its most impressive features, though it’s largely left to the imagination. The interior layout is carefully designed so that the keel structure remains hidden. Dubois Naval Architects positioned the keel box to come above the main deck, serving as a partial separation between the bridge and the main salon (see inset). Kokomo was only the second yacht to be fitted with a lifting a keel, the first being 246-foot M5 (ex-Mirabella V), the world’s largest single-masted sailing yacht. This innovative design shortens Kokomo’s 28.5-foot draft when the keel is fully extended, to just 15 feet for shallow waters.
Fast-Track Sailing

Kokomo was one of the first yachts to be fitted with a hydraulic batt-car system for furling the mainsail, which has cars at each batten end that slot in an outer track on the mast. This alleviates a once-common issue where the luff tape or bolt rope on large sailing yachts became chaffed by the compression of the battens, which often caused the in-boom furling mainsails to fail. “When sailing Kokomo , especially when racing, I am completely impressed with the speed and efficiency of the hydraulic system,” says Kokomo ’s captain, Jeremy ‘Bear’ Wynne, who notes the yacht’s recorded top speed is a very impressive 22 knots. “The jib furlers are some of the fastest I have seen. There is absolutely no shortage of hydraulic power, even with multiple winches running on a jibe—a rarity on a big sailing yacht.”
Now You See It, Now You Don’t

Kokomo might be big on technology, but never at the expense of design. The wheelhouse has fold-down computer screens that conceal the navigation equipment when not in use, converting to beautiful carbon counter tops. This design sleight of hand transforms a highly technical area into a tony lounge. It’s a theme that extends to the foredeck, where the yacht’s two tenders are concealed in dedicated lockers. There’s also a fully retractable tender crane that launches the tenders from either side of the boat but disappears out of sight when guests are using the Jacuzzi. “The designated deck lockers were an advanced feature at the time of her launch,” says Wynne, adding that another bonus is that diesel tanks are fully available. “The tenders can be fueled onboard before launching.”
It Takes Just A Few Good Sailors

Kokomo can accommodate up to 10 crew in total, but theoretically it only takes two to sail—a helm person and a sail trimmer. That sounds almost impossible given the size and complexity of yacht. But all sails are controlled by joystick on the flybridge. And when the boat is in full-on racing mode, there are control stations on both sides, providing visibility of the sails. Thanks to the hydraulics system, the mainsail can be hoisted and lowered on a wireless remote control. Of course, maneuvers like stowing the massive genoa can never be automated. That’s a job for a half-dozen good sailors.
Art On Board

The hallway that leads to the owner’s cabin is lined with a mosaic tapestry made from sea glass woven together with wire. Backlit to create an unusual effect, it’s just one of the eclectic works of art that decorates the interior. The main salon also has a stunning and colorful work of glass art as another example.
Interior Matters

Kokomo is not all tech features. The yacht’s modern interiors combine dark wood floors and calming cream furnishings start in the main salon and continue across the five guest cabins. Penned by British studio Redman Whiteley Dixon, the design carefully wraps around the lifting keel without sacrificing or impeding on any interior guest space. The yacht accommodates up to 10 guests in a master suite, VIP, one double cabin and two twins. There are other accommodations for up to 10 crew. On the foredeck, the Jacuzzi brings another element of outdoor entertainment, bolstered by a sunken cockpit.
World Traveler

The mandate issued by Walker was to create a yacht that was a “quantum leap forward” from his previous yachts, with superior sailing characteristics and guest comfort. The mast’s height is too tall to sail through the Panama or Suez Canals, which meant it would have to be designed to sail around Cape Horn and the Cape of Good Hope to reach the Caribbean and Mediterranean. The maiden voyage took the yacht from the New Zealand shipyard to Australia, New Caledonia, the Solomon Islands, and Fiji. It also spent time at Walker’s private island (pictured above), also named Kokomo. The vessel has since spent many years exploring the Caribbean and Med. It’s based in both regions during the respective cruising seasons, with charters available through Cecil Wright.
Read More On:
- Alloy Yachts
- New Zealand
- Superyachts
More Marine

This New 220-Foot Custom Superyacht Is Topped With an Epic Jacuzzi

This Custom 112-Foot Trideck Superyacht Feels Bigger Than It Actually Is

Azimut’s New 72-Foot Yacht Has One of the Largest Flybridges in Its Class. We Hopped Onboard.

You Can Charter Lürssen’s New 400-Foot Gigayacht for $3.3 Million a Week

Culinary Masters 2024
MAY 17 - 19 Join us for extraordinary meals from the nation’s brightest culinary minds.
Give the Gift of Luxury
Latest Galleries in Marine

‘Lady A’ Superyacht in Photos
More from our brands, buyers weigh in on hottest fall 2024 accessories seen across european fashion marathon, sportico transactions: moves and mergers roundup for march 15, ke huy quan action movie ‘with love’ gets 2025 release date from universal, artist says comments on palestine cost them a german museum show, the best yoga mats for any practice, according to instructors.

The Ultimate Guide to Sail Boat Designs: Exploring Sail Shape, Masts and Keel Types in 2023
- June 4, 2023

When it comes to sail boat designs, there is a wide array of options available, each with its own unique characteristics and advantages. From the shape of the sails to the number of masts and the type of keel, every aspect plays a crucial role in determining a sailboat’s performance, stability, and manoeuvrability. In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the fascinating world of sail boat designs, exploring the various elements and their significance.
Table of Contents
The sail shape is a fundamental aspect of sail boat design, directly impacting its speed, windward performance, and maneuverability. There are several types of sail shapes, including:
1. Bermuda Rig:
The Bermuda rig is a widely used sail shape known for its versatility and performance. It features a triangular mainsail and a jib, offering excellent maneuverability and the ability to sail close to the wind. The Bermuda rig’s design allows for efficient use of wind energy, enabling sailboats to achieve higher speeds. The tall, triangular mainsail provides a larger surface area for capturing the wind, while the jib helps to balance the sail plan and optimize performance. This rig is commonly found in modern recreational sailboats and racing yachts. Its sleek and streamlined appearance adds to its aesthetic appeal, making it a popular choice among sailors of all levels of experience.
2. Gaff Rig:
The Gaff rig is a classic sail shape that exudes elegance and nostalgia. It features a four-sided mainsail with a gaff and a topsail, distinguishing it from other sail designs. The gaff, a horizontal spar, extends diagonally from the mast, providing additional area for the mainsail. This configuration allows for a taller and more powerful sail, making the Gaff rig particularly suited for downwind sailing. The Gaff rig offers a traditional aesthetic and is often found in vintage and classic sailboats, evoking a sense of nostalgia for a bygone era of maritime exploration. The distinctive shape of the Gaff rig, with its graceful curves and intricate rigging, adds a touch of timeless charm to any sailboat that dons this rig.
3. Lateen Rig:
The Lateen rig is a unique and versatile sail design that has been used for centuries in various parts of the world. It features a triangular sail that is rigged on a long yard, extending diagonally from the mast. This configuration allows for easy adjustment of the sail’s angle to catch the wind efficiently, making the Lateen rig suitable for a wide range of wind conditions. The Lateen rig is known for its ability to provide both power and maneuverability, making it ideal for small to medium-sized sailboats and traditional vessels like dhow boats. Its versatility allows sailors to navigate narrow waterways and make tight turns with ease. The distinctive silhouette of a sailboat with a Lateen rig, with its sleek triangular sail and graceful curves, evokes a sense of adventure and a connection to seafaring traditions from around the world.
Number of Masts
The number of masts in a sail boat design affects its stability, sail area, and overall performance. Let’s explore a few common configurations:
1. Sloop Rig:
The sloop rig is one of the most popular and versatile sail boat designs, favoured by sailors around the world. It consists of a single mast and two sails—a mainsail and a jib. The sloop rig offers simplicity, ease of handling, and excellent performance across various wind conditions. The mainsail, situated behind the mast, provides the primary driving force, while the jib helps to balance the sail plan and improve manoeuvrability. This configuration allows for efficient upwind sailing, as the sails can be trimmed independently to optimize performance. The sloop rig is commonly found in modern recreational sailboats due to its versatility, enabling sailors to enjoy cruising, racing, or day sailing with ease. Its streamlined design and sleek appearance on the water make it both aesthetically pleasing and efficient, capturing the essence of the sailing experience.
2. Cutter Rig:
The cutter rig is a versatile and robust sail boat design that offers excellent performance, especially in challenging weather conditions. It features a single mast and multiple headsails, typically including a larger headsail forward of the mast, known as the cutter rig’s distinguishing feature. This configuration provides a wide range of sail combinations, enabling sailors to adjust the sail plan to suit varying wind strengths and directions. The larger headsail enhances the boat’s downwind performance, while the smaller headsails offer increased flexibility and improved balance. The cutter rig excels in heavy weather, as it allows for easy reefing and depowering by simply reducing or eliminating the headsails. This design is commonly found in offshore cruising sailboats and has a strong reputation for its reliability and seaworthiness. The cutter rig combines versatility, stability, and the ability to handle adverse conditions, making it a preferred choice for sailors seeking both performance and safety on their voyages.
3. Ketch Rig:
The Ketch rig is a sail boat design characterized by the presence of two masts, with the main mast being taller than the mizzen mast. This configuration offers a divided sail plan, providing sailors with increased flexibility, balance, and versatility. The main advantage of the Ketch rig is the ability to distribute the sail area across multiple sails, allowing for easier handling and reduced stress on each individual sail. The mizzen mast, positioned aft of the main mast, helps to improve the sailboat’s balance, especially in strong winds or when sailing downwind. The Ketch rig is often favoured by cruisers and long-distance sailors as it provides a range of sail combinations suitable for various wind conditions. With its distinctive double-mast appearance, the Ketch rig exudes a classic charm and is well-regarded for its stability, comfort, and suitability for extended journeys on the open seas.
The keel is the part of the sail boat that provides stability and prevents drifting sideways due to the force of the wind. Here are some common keel types:
1. Fin Keel:
The fin keel is a popular keel type in sail boat design known for its excellent upwind performance and stability. It is a long, narrow keel that extends vertically from the sailboat’s hull, providing a substantial amount of ballast to counterbalance the force of the wind. The fin keel’s streamlined shape minimizes drag and enables the sailboat to cut through the water with efficiency. This design enhances the sailboat’s ability to sail close to the wind, making it ideal for racing and performance-oriented sailboats. The fin keel also reduces leeway, which refers to the sideways movement of the boat caused by the wind. This improves the sailboat’s ability to maintain a straight course and enhances overall manoeuvrability. Sailboats with fin keels are commonly found in coastal and offshore racing as well as cruising vessels, where stability and responsiveness are valued. The fin keel’s combination of performance, stability, and reduced leeway makes it a preferred choice for sailors seeking speed and agility on the water.
2. Full Keel:
The full keel is a design known for its exceptional stability and seaworthiness. It extends along the entire length of the sailboat, providing a continuous surface that adds substantial weight and ballast. This configuration offers significant advantages in terms of tracking and resistance to drifting sideways. The full keel’s deep draft helps to prevent leeway and allows the sailboat to maintain a steady course even in adverse conditions. Its robust construction enhances the sailboat’s ability to handle heavy seas and provides a comfortable ride for sailors on extended journeys. While full keel sailboats may sacrifice some manoeuvrability, their stability and predictable handling make them a popular choice for offshore cruising and long-distance voyages. The full keel design has stood the test of time and is often associated with classic and traditional sailboat aesthetics, appealing to sailors seeking reliability, comfort, and the ability to tackle challenging ocean passages with confidence.
3. Wing Keel:
The wing keel is a unique keel design that offers a combination of reduced draft and improved stability. It features a bulbous extension or wings on the bottom of the keel, which effectively increases the keel’s surface area. This design allows sailboats to navigate in shallower waters without sacrificing stability and performance. The wings create additional lift and prevent excessive leeway, enhancing the sailboat’s upwind capabilities. The reduced draft of the wing keel enables sailors to explore coastal areas and anchor in shallower anchorages that would be inaccessible to sailboats with deeper keels. The wing keel is particularly well-suited for sailboats in areas with variable water depths or tidal ranges. This keel design offers the advantages of increased manoeuvrability and improved performance while maintaining stability, making it a popular choice for sailors seeking versatility in a range of sailing environments.
In the vast world of sail boat designs, sail shape, number of masts, and keel types play pivotal roles in determining a boat’s performance and handling characteristics. Whether you’re a recreational sailor, a racer, or a cruiser, understanding these design elements can help you make informed choices when selecting a sailboat.
Remember to consider your specific needs, preferences, and intended use of the boat when choosing a sail boat design. Each design has its strengths and weaknesses, and finding the perfect combination will greatly enhance your sailing experience.
By gaining a deeper understanding of sail boat designs, you can embark on your next sailing adventure with confidence and make the most of the wind’s power.
Related Posts

Sailing Navigation: Exploring Modern Techniques for Navigating the Seas in 2023
- June 10, 2023

Sailing in Different Directions: Harnessing the Wind’s Power in 2023

Sailing Terms Demystified: A Comprehensive Guide to 14 Common Sailing Terminology
- May 28, 2023
Sloop Rigged Sailboat: The Ultimate Guide
by Emma Sullivan | Aug 18, 2023 | Sailboat Maintenance

Short answer: Sloop rigged sailboat
A sloop rigged sailboat is a type of sailboat that features a single mast and two sails, namely a mainsail and a headsail. This popular rigging configuration allows for efficient sailing both upwind and downwind, making it widely used in recreational and racing boats. The sloop rig provides versatility and ease of handling, contributing to its popularity among sailors worldwide.
The Basics of a Sloop Rigged Sailboat: A Comprehensive Guide
Welcome aboard, sailing enthusiasts ! If you’re new to the world of sailboats or simply looking to expand your knowledge, you’ve come to the right place. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll delve into the intricacies of a sloop rigged sailboat – an iconic and versatile vessel that has captured the hearts and minds of sailors worldwide.
So, grab your nautical charts, put on your captain’s hat, and get ready to set sail on a journey through the basics of a sloop rigged sailboat.
1) What is a Sloop Rigged Sailboat? A sloop rigged sailboat refers to a popular type of sailing vessel with one mast and two sails – a mainsail located at the rear (aft) of the mast and a headsail at the front (forward). This configuration allows for efficient wind capture and provides great maneuverability in different wind conditions.
2) The Main Components: a) Mainsail: The mighty mainsail is typically the largest sail on the boat. Its purpose is to harness wind power and propel the vessel forward. Positioned behind the mast, it generates most of the driving force required for sailing.
b) Headsail: Also known as a jib or genoa, this smaller sail is located at the front part of the boat . It assists in catching additional wind and adds balance by counteracting some forces exerted by the mainsail. Headsails come in various sizes depending on wind conditions.
3) Benefits of a Sloop Rigged Sailboat: Why choose a sloop rig? Well, here are some compelling reasons:
a) Versatility: A sloop rig offers versatility across various wind conditions – from light breezes to stronger gusts. By adjusting or changing headsails, sailors can optimize their vessel’s performance without compromising control.
b) Maneuverability: Due to the simplicity of controlling two sails, a sloop rigged sailboat is more maneuverable compared to other sail setups. This means easier tacking (changing direction against the wind) and gybing (changing direction with the wind).
c) Efficiency: The streamlined design of a sloop rig maximizes efficiency by reducing drag and sail interference. It allows for better pointing ability (sailing closer into the wind) and improved upwind performance.
4) Additional Sailing Terms: To truly navigate the jargon-laden seas, it’s essential to familiarize yourself with key sailing terms related to sloop rigged sailboats. Here are a few important ones:
a) Halyards: Ropes used to raise or lower sails. The mainsail halyard raises the mainsail while the headsail halyard controls the headsail’s position.
b) Sheets: Lines used to control sail trim – one for the mainsail and another for the headsail. By adjusting these sheets, sailors can optimize their sail shape in different wind conditions.
c) Tacking and Gybing: As mentioned earlier, tacking involves turning a boat into the wind to change its direction, while gybing is turning away from the wind.
d) Reefing: The process of reducing a sail’s area by partially lowering it or rolling it up, often necessary in strong winds to maintain control.
5) Conclusion: Congratulations on completing this comprehensive guide ! By now, you understand what makes a sloop rigged sailboat such an appealing choice for sailors worldwide. From its versatility and maneuverability to enhancing efficiency in various wind conditions, this configuration is beloved by both seasoned mariners and newcomers alike.
So next time you set foot on a sloop rigged sailboat, confidently command your vessel using your newfound knowledge. Remember that sailing is not just about skill but also an art form that embraces nature’s elements; embrace them wholeheartedly as you embark on thrilling adventures across the open water.
Happy sailing!
How to Rig a Sloop Sailboat: Step-by-Step Instructions for Beginners
Title: Mastering the Art of Rigging a Sloop Sailboat: Comprehensive Step-by-Step Guide for Aspiring Seafarers
Introduction:
Embarking on a sailing adventure is an exhilarating experience, and rigging a sloop sailboat lays the foundation for an unforgettable voyage on the open waters. If you’re a beginner eager to unravel the secrets of this ancient art, we’ve got your back! In this guide, we’ll walk you through the step-by-step process of rigging a sloop sailboat like a seasoned sailor. So, hoist your sails, batten down the hatches, and let’s dive right in!
Section 1: Understanding the Basics
Before diving into the rigging process, it’s essential to grasp some fundamental concepts. A sloop sailboat typically consists of two sails—a mainsail and a headsail—hinged around one mast.
Section 2: Gathering Your Tools
To ensure smooth sailing during the rigging process, assemble these vital tools:
1. Sailors’ Bag: – Multitool with pliers, knife, and wrench attachments. – Marlin spike for untying knots. – Shackles and carabiners for attaching lines.
2. Safety Equipment: – Life jacket or personal flotation device (PFD). – High-quality sailing gloves.
3. Essential Lines: – Halyards to raise and lower sails. – Sheets that control sails’ trim .
Section 3: The Step-by-Step Process
Step 1: Prepare Your Boat Ensure your boat is docked securely before starting any rigging work. It’s crucial to maintain stability throughout the process by fixing your boat firmly using anchors or dock lines.
Step 2: Hoisting the Main Sail Attach each halyard—one from each side—to designated points on either side of the main sail near its head. Make sure the halyards run smoothly through blocks and do not twist or tangle. Raise the main sail steadily using a winch until it reaches its full height.
Step 3: Handling the Sheets Connect one end of each sheet—one from each side—to their respective clew points on the main sail . Ensure proper alignment without crossing lines. Lead both sheets aft through the boom, adjusting tension for optimal sail trim.
Step 4: Setting Up the Headsail Begin by attaching the halyard to a designated point near the head of your headsail, ensuring smooth running through blocks. Hoist it with moderate tension until it unfurls but remains manageable in low winds.
Step 5: Positioning Jib Sheets Securely connect each jib sheet—one from each side—to their appropriate clew points on your headsail, allowing free movement when adjusting trim. Remember to lead them back to a location where you can efficiently control and adjust their tension.
Section 4: Safety Precautions and Additional Tips
1. Always Wear a Life Jacket: Prioritize safety at all times by wearing a properly-fitted life jacket or PFD while rigging and sailing .
2. Familiarize Yourself with Nautical Knots: Understanding essential knots like reef knots, bowlines, and clove hitches will greatly aid you in securing lines during rigging processes.
3. Don’t Rush: Take your time during every step of rigging to avoid mistakes that could lead to accidents or improper sail function .
Conclusion:
As sailing enthusiasts ourselves, we understand how tempting it is to skip past crucial steps while rigging a sloop sailboat; however, mastering this process paves the way for blissful seafaring adventures in style. By following this comprehensive guide designed specifically for beginners, you’ll be well-equipped with both knowledge and practical skills needed to rig your sloop sailboat with finesse. So, grab your sailors’ bag, breathe in the salty air, and embark on your exciting sailing journey like a seasoned mariner!
Frequently Asked Questions About Sloop Rigged Sailboats, Answered!
Are you considering purchasing a sloop rigged sailboat? Do you have questions about its design, functionality, or performance on the water? Look no further! In this blog post, we will delve into some of the frequently asked questions about sloop rigged sailboats and provide you with insightful answers to aid in your decision-making process. So, let’s set sail on this nautical adventure and get those queries answered!
1. What is a sloop rig?
A sloop rig refers to a sailing boat that has one mast and two sails – a mainsail and a headsail (commonly known as a jib or genoa). The main characteristic of this configuration is versatility. With both sails working together, the boat can efficiently harness wind power across various wind conditions.
2. Why are sloop rigs so popular?
Sloop rigs have gained immense popularity among sailors due to their flexibility and ease of handling. The ability to balance the mainsail and headsail allows for fine-tuning depending on wind strength and direction. This adaptability makes sloop rigs suitable for diverse sailing adventures, from racing in challenging regattas to leisurely cruising with family and friends.
3. How do I know which size headsail is right for my sloop rig?
The choice of headsail size depends on several factors such as boat size, anticipated wind conditions, and personal preference. As a general rule of thumb, larger boats tend to use genoas with larger overlapping areas, providing more driving force in lighter winds. On the other hand, smaller boats might benefit from self-tacking jibs that require less crew effort during maneuvers.
4. What are the advantages of having a single mast?
Having only one mast simplifies the overall design and maintenance of a sailboat while reducing costs associated with rigging hardware and maintenance tasks like checking multiple spreaders or stays. Additionally, it makes maneuvering under bridges or low clearance areas less complicated, ensuring that your sailing adventures are not confined solely to open waters .
5. Can I sail a sloop rig alone?
Yes, you can! Sloop rigged sailboats are renowned for their excellent single-handed capabilities. The balanced configuration of the sails allows for relatively easy trimming and handling, making it possible for a competent sailor to operate the boat without assistance. However, caution should always be exercised while sailing solo, especially in challenging weather conditions .
6. Are there any drawbacks to choosing a sloop rig?
While sloop rigs are versatile and beloved by many sailors, they do have some limitations. When encountering heavy weather or strong winds, sail changes may be required more frequently compared to other configurations like ketch or cutter rigs. Additionally, managing the headsail when sailing upwind can pose challenges due to its larger area relative to the mainsail.
In conclusion, sloop rigged sailboats offer a sought-after combination of versatility and ease of handling that has propelled them into popularity among sailors worldwide. The ability to adapt to various wind conditions and their single-handed capabilities make them appealing choices for both seasoned sailors and novices setting out on their nautical journeys. However, it’s crucial to consider the specific requirements of your sailing plans before committing to this rig configuration.
So set your sights on those open waters and hoist those sails high; with a sloop rigged sailboat beneath you, there is little stopping you from embarking on unforgettable sailing adventures!
Exploring the Advantages of a Sloop Rigging Design in Sailboats
Title: Unraveling the Hidden Gems: Exploring the Advantages of a Sloop Rigging Design in Sailboats
Introduction: When it comes to sailboat rigging designs, one design stands out among the rest – the sloop rigging. This elegant and versatile configuration has been favored by sailors for centuries. In this blog post, we embark on a captivating journey to unravel the numerous advantages of choosing a sloop rigging for your sailboat . Brace yourself as we navigate through its professional, witty, and clever intricacies!
1. Versatility at Its Finest: The sloop rigging design encapsulates versatility like no other. With its single mast and two sails – a mainsail and a headsail – sailboats equipped with sloop rigs can adapt effortlessly to varying weather conditions. Be it gentle zephyrs or gale-force winds; the adaptability of a sloop allows sailors to cruise comfortably across all conditions.
2. Superior Upwind Performance: While many rigs struggle against headwinds, the sloop rig shines bright as an epitome of upwind performance mastery. Thanks to its efficient aerodynamics, the powerful mainsail delivers excellent propulsion by capturing and funneling favorable air currents into forward momentum. Meanwhile, the smaller headsail optimizes balance while maintaining manageable helm control.
3. Ease of Handling: Sailing should be an enjoyable experience that doesn’t require constant battling with complicated rig configurations. The beauty of a sloop rig lies in its simplicity. The ability to hoist or reef sails quickly turns novice sailors into confident captains navigating effortlessly through unpredictable waters .
4. Enhanced Maneuverability: Picture this: you encounter an unexpected obstacle on your sailing adventure—a tight angle that demands nimble navigation skills and quick reaction times from your sailboat’s rigging setup! Fear not, for with a perfectly balanced sloop rig design, executing even challenging maneuvers becomes an exhilarating experience. Sailors can effortlessly tack, jibe, and alter their course without compromising stability or control.
5. Reduced Crew Requirements: When you embark on a solo sailing voyage, having a sailboat that complements self-reliance is essential. The sloop rig offers exactly this advantage by minimizing crew requirements. With the right combination of high-quality winches, cleats, and easily adjustable lines, managing the sails becomes a one-person job. Feel like taking your sailing escapade to new horizons? The sloop rig provides the freedom to do so independently!
6. Enhanced Performance in Light Winds: Navigating through calmer waters brings its own charm but often poses challenges for other rigging configurations . Enter the sloop rig’s lighter headsail! This smaller sail allows sailors to harness even the slightest breeze efficiently while enjoying serene moments at sea.
7. Wide Range of Combinations: From schooners to cutters, ketches to yawls – sloop rigs have served as an inspiration for various hybrid designs throughout history. Sailboat enthusiasts find immense pleasure in exploring different combinations within a sloop rig setup, tailoring their craft to match their unique preferences and sailing goals.
Conclusion: As sailors prepare to embark on exhilarating adventures across vast oceans or tranquil lakes alike, it becomes paramount to choose a sailboat equipped with the right rigging design – one that truly encapsulates versatility, maneuverability, ease of handling, and enhanced performance under diverse conditions. The timeless beauty of a sloop rigging design offers all these advantages and more! So set sail with confidence; may your journey be filled with professional expertise intertwined with wittiness and cleverness – all brought to life through your trusty sloop-rigged vessel!
Mastering the Art of Sailing: Tips and Tricks for Maneuvering a Sloop Rigged Sailboat
Sailing is not just a hobby; it is an art form that requires skill, finesse, and a deep understanding of the elements. For those who have chosen to embark on this exhilarating adventure, mastering the art of sailing is a lifelong pursuit. In this blog post, we will delve into the world of sloop rigged sailboats and provide you with some valuable tips and tricks to enhance your maneuvering abilities.
First things first – what exactly is a sloop rigged sailboat? A sloop rig consists of a single mast located towards the front of the boat , along with two sails – a mainsail attached to the mast and a foresail or jib at the front. This configuration offers simplicity in terms of handling and maneuverability, making it ideal for beginners as well as seasoned sailors .
To truly master the art of sailing in a sloop rigged sailboat, one must develop expert handling techniques. One important aspect to consider is trimming your sails correctly. The main sail controls your boat ‘s speed and direction while sailing upwind, whereas the jib helps with balance and stability. By adjusting these sails appropriately based on wind conditions, you can optimize your boat ‘s performance.
When tacking or turning through the wind in order to change direction, pay close attention to steering techniques. To execute successful tacks smoothly and efficiently, always plan ahead by assessing wind direction and anticipating any obstacles or other boats nearby. Maintain control of your helm throughout the tack by making small adjustments rather than abrupt maneuvers .
Another fundamental skill in sailing is knowing how to gybe – turning downwind while crossing through the wind. When gybing in a sloop rig setup, always be cautious as this maneuver can be quite powerful due to changes in wind pressure against both sails simultaneously. It is essential to properly control your mainsail during this maneuver by keeping tension on its sheets while giving careful attention to maintaining balance.
Successfully docking or mooring a sailboat is an additional critical aspect to master. The ability to approach a dock or mooring buoy confidently and skillfully will greatly enhance your sailing experience. To ensure a smooth docking, it is crucial to consider wind direction, current, and space limitations in relation to your boat’s maneuverability. Practice various docking techniques such as the ‘bow-in’ or ‘stern-in’ method to increase your versatility.
Now that we have covered some of the key techniques for maneuvering a sloop rigged sailboat, let’s discuss some tips and tricks to make your sailing experience even more enjoyable.
1. Stay aware of your surroundings: Always be mindful of other boats, navigational hazards, and changing weather conditions . Keep in touch with VHF radios or marine apps on smartphones for any necessary communication.
2. Practice makes perfect: Spend time on the water honing your skills by undertaking various maneuvers repeatedly. With practice comes confidence and fine-tuned abilities.
3. Communicate effectively with crew members: Clear communication is essential when working together to maneuver the sailboat smoothly . Develop efficient communication protocols that everyone can understand and follow.
4. Seek advice from experienced sailors: Attend sailing seminars, join sailing clubs, or connect with seasoned sailors who can offer invaluable insights based on their own experiences.
5. Embrace challenges: Sailing can be unpredictable at times; don’t shy away from challenging conditions or maneuvers. Instead, view them as opportunities for growth and improvement.
In conclusion, mastering the art of sailing a sloop rigged sailboat demands constant learning, practice, and attention to detail. By focusing on proper sail trimming techniques along with proficient steering methods like tacking and gybing, you can navigate through diverse wind conditions effortlessly. Additionally, mastering docking maneuvers while maintaining awareness of your surroundings will ensure safe adventures on the open water.
So hoist those sails high, keep an eye on the horizon ahead and embark upon this incredible journey of mastering the art of sailing a sloop rigged sailboat. Happy sailing!
Advancing Your Skills: Expert Advice on Upgrading and Maintaining a Sloop Rigged Sailboat
Welcome aboard, sailors! Today, we are thrilled to present you with expert advice on advancing your skills in upgrading and maintaining a sloop rigged sailboat. Whether you are an experienced sailor looking to take your sailing game to the next level or a novice just beginning your nautical journey, this blog post is for you.
The sloop rig is one of the most popular and versatile sailboat configurations out there. Consisting of a single mast and two sails, the main and jib, it offers simplicity and efficiency while providing enough power to tackle various weather conditions . However, like any vessel, a sloop rigged sailboat requires regular care and potential upgrades to keep it sailing smoothly.
1. Regular maintenance: The key to prolonging the life of your boat lies in its regular maintenance . From checking for any signs of wear and tear on your rigging to inspecting hull integrity and cleaning the bottom of your boat, consistency is crucial. By establishing a routine maintenance schedule that encompasses these tasks along with others like lubricating winches, checking light fixtures, and servicing the engine if applicable, you can ensure that your sloop rig remains in tip-top shape throughout its lifetime.
2. Upgrading your rig: As technology advances in the sailing world, it’s essential to stay updated with modern equipment that can enhance both performance and safety on board. If you’re considering upgrading certain aspects of your sloop rig setup, there are several areas worth exploring:
– Sails: Investing in high-quality sails specifically designed for optimal performance in different wind conditions can make a world of difference. Consider lightweight materials that increase speed or durable options for more rugged sailing environments.
– Rigging: Keeping up with advancements in rigging technology can greatly benefit your sailing experience. Upgrade options like low-stretch lines or high-performance blocks can improve maneuverability while reducing overall wear on your boat.
– Electronics: Equipping your sailboat with modern navigational and communication systems can enhance safety and convenience. From GPS chartplotters to AIS (Automatic Identification System) receivers, these upgrades provide valuable information on your vessel’s position and the surrounding maritime traffic.
3. Developing your sailing skills: An upgraded sailboat is only as good as the sailor operating it. In addition to investing in your boat, advancing your own sailing skills is paramount. Attend local sailing courses or workshops offered by experienced sailors or sailing clubs, allowing you to learn new techniques, strategies, and safety protocols specific to sloop rigged sailboats.
4. Joining a community: Engaging with fellow sailors who share your passion for sloop rigged sailboats is a valuable way to boost your knowledge and broaden your horizons. Participating in regattas, joining online forums like Sailnet or CruisersForum, or even connecting with local yacht clubs can expose you to a wealth of wisdom and provide opportunities for networking and collaboration.
Remember, upgrading and maintaining a sloop rig sailboat isn’t just about improving performance; it’s about ensuring the safety of yourself, your crew, and the vessel itself. By incorporating regular maintenance practices, exploring upgrade options that suit your needs, actively honing your sailing skills, and engaging with the vibrant sailing community around you, you will set yourself up for an extraordinary voyage filled with thrilling adventures on the high seas.
So grab that rigging manual, hoist those sails high, and set forth on an incredible journey of advancing your skills in upgrading and maintaining a sloop rigged sailboat!
Recent Posts
- Approaching a Mooring Buoy: Essential Tips for Safe Navigation
- Best Tiller Autopilot: Enhance Your Sailing Experience
- Nautical Navigator: Essential Tools and Techniques for Seamanship
- Sail Making Material: A Comprehensive Guide
- 2 Person Dinghy: The Ultimate Guide to Choosing the Perfect Boat
- Sailboat Gear and Equipment
- Sailboat Lifestyle
- Sailboat Maintenance
- Sailboat Racing
- Sailboat Tips and Tricks
- Sailboat Types
- Sailing Adventures
- Sailing Destinations
- Sailing Safety
- Sailing Techniques
BoatNews.com
How to recognize a sailboat, the sloop

If for you all sailing boats are the same, this is how to differentiate sloop from cutter. To help you classify the types of sailboats, here is a series called "Learn to recognize them". Today, here are the characteristics of a sloop.
The sloop - or sloup - is a type of rigging with a single mast and a single jib . It is the most widely used rig on our modern pleasure yachts . He gradually replaced the cutter ( at least two jibs to discover here ) with the advent of the winch and reel.
Indeed, with these manoeuvring aids, there is no need to split the sail area. As the sail changes have disappeared, there is no need to make them easier by using several small sails.

The sloop has only one mast. If he has 2, then we are in the presence of a ketch , a schooner or a yawl (which some call sloop to tape-cul).

The sloop rig is nowadays the most widely used in the production of modern sailboats. Indeed, with a mainsail that can easily be reduced with reefs, to which is added a jib (often called a genoa because the clew is further back than the mast) often rigged on a furling system, it is the easiest configuration to take to the sea.

Attention! A cutter that has rigged only one jib in strong winds, for example, is not a sloop . A cutter remains a cutter, regardless of its sail configuration.
Just as a sloop that rigs a gennaker (downwind sail ) over its jib is not a cutter despite the fact that it has 2 headsails. A sloop remains a sloop even if it changes sail configuration.


Home » Blog » Bluewater sailboats » The best bluewater sailboats (we analyzed 2,000 boats to find out)
The best bluewater sailboats (we analyzed 2,000 boats to find out)
By Author Fiona McGlynn
Posted on Last updated: May 16, 2023
We analyzed two-thousand bluewater sailboats to bring you a list of proven offshore designs

What are the best bluewater sailboats?
This was a question we asked a lot of experienced cruisers when we decided to sail across the Pacific. We needed a boat after all, and we wanted to buy the best bluewater sailboat we could afford.
We heard a lot of strong opinions.
Some sailors thought it was reckless to go offshore in any boat that didn’t have a full keel.
Others prioritized performance, and wouldn’t dream of going anywhere in a slow boat like the Westsail 32 (a.k.a. a “Wet Snail 32”).
Opinions like these left us feeling confused like we had to choose between safety and performance.
If we learned anything from these conversations, it’s that what makes a bluewater boat is a hotly debated topic!
However, there’s a way to cut through all the opinions and get to the bottom of it. The solution is….
We analyzed just under 2,000 boats embarking on ocean crossings (over a 12 year time period) and came up with a list of the ten best bluewater sailboats.
Where did we get our data?
The data for our best bluewater sailboats list comes from 12 years of entries in the Pacific Puddle Jump (PPJ), an annual cross-Pacific rally. We took part in 2017 and had a ball!
You can read about the methodology we used to analyze this data at the bottom of the post.
What do we mean by “best”?
We know, that word is overused on the internet!
Simply, based on our data set, these were the most common makes and models entered in the PPJ cross-Pacific rally. There were at least 10 PPJ rally entries for every make of boat on our top 10 list.
So, these boats are 100% good to go?
No! A bluewater boat isn’t necessarily a seaworthy boat. Almost every cruiser we know made substantial repairs and additions to get their offshore boat ready, adding watermakers , life rafts, solar panels, and more.
Also, you should always have a boat inspected by a professional and accredited marine surveyor before buying it or taking it offshore.
But my bluewater baby boat isn’t on this list!?
There are hundreds of excellent bluewater yachts that are not on this list. For instance, we sailed across the Pacific in a Dufour 35, which didn’t even come close to making our top 10 list.
Choosing the right boat is very much an individual journey.
Where can I find these bluewater boats for sale?
We recognize that a top 10 list won’t get you very far if you’re shopping for a bluewater boat (especially if you’re looking in the used market).
So, to help you find your perfect boat, we’re going to create a big list of bluewater boats that you can use to refine your search on Yachtworld, Craigslist, or any other places to buy a used boat .
Sign up for our newsletter to get our big list of bluewater boats list as soon as it comes out.
We’re also working on a series of posts by size class. For example, if you’re looking for a smaller boat, you can narrow it down to the best bluewater sailboats under 40 feet .
Takeaways from our analysis
There were no big surprises on an individual boat level. All of these makes are considered good cruisers, some of them are even best-selling designs! However, there were a few things that caught our eye.
“Go simple, go small, go now” still holds water
We were thrilled to see the smallest boat in our roundup at the very top of the list! Westsail 32 owners can take pride in their small but mighty yachts (and ignore all those snail-sayers).
While undoubtedly there’s been a trend towards bigger bluewater cruisers in recent years, small cruising sailboats seem to be holding their own. 60% of the monohulls on this list were under 40 feet (if you count the Valiant 40 which sneaks just under at 39.92 feet).
Cat got our tongue
So, we knew catamarans were a thing, but we didn’t fully appreciate HOW popular they’d become!
50% of our top 10 bluewater boat list consists of catamarans—a good fact to toss out the next time you’re trying to garner a happy hour invite on the party boat next door (which will undoubtedly be a catamaran).
Still got it!
We’ve got good news for all you good old boat lovers! 60% of the boats on our list were first built before 2000.
While these older models are less performance-oriented than modern designs, cruisers value these boats for their ability to stand up to rough seas and heavy weather. It just goes to show that solid bones and classic looks never go out of style.
Alright, without further ado, let’s dive into our list of the 10 best bluewater boats!
The 10 best bluewater boats
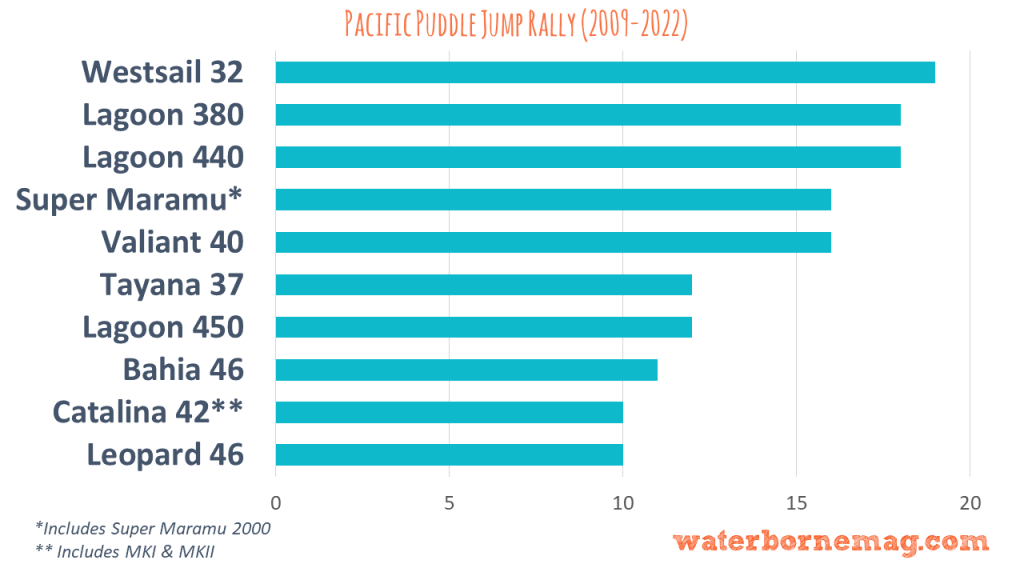
1. Westsail 32

The Westsail 32 is one of the most iconic bluewater cruisers and 19 have set out to cross the Pacific in the PPJ rally since 2009.
In 1973, this small cruising sailboat garnered a 4-page spread in Time magazine. The article inspired many Americans to set sail and the Westsail 32, with its double-ender design, set the standard for what a real bluewater cruiser should look like.
There were approximately 830 built between 1971 and 1980.
This small boat has taken sailors on ocean crossings and circumnavigations. Though considered “slow” by some, the heavily-built Westsail 32 has developed a loyal following for her other excellent offshore cruising characteristics.
If you’re interested in small bluewater sailboats, check out our post on the best small sailboats for sailing around the world .
2. Lagoon 380

The Lagoon 380 is a reliable, solidly built catamaran and considered roomy for its size. We counted 18 of them in our data set. With over 800 boats built , it may be one of the best-selling catamarans in the world. Like the other boats on this list, the Lagoon 380 has proven itself on long passages and ocean crossings, winning it many loyal fans.
3. Lagoon 440

18 Lagoon 440s have set out to cross the Pacific in the PPJ rally since 2009.
Why leave the comforts of home, when you can take them with you? The Lagoon 440 is a luxurious long-range cruiser, offering beautiful wood joinery, spacious accommodations, and a deluxe galley. Oh, and you have the option of an electric boat motor !
SAIL and Sailing Magazine have both done in-depth reviews of the Lagoon 440 if you want to learn more.
4. Amel Super Maramu (incl. SM 2000)

If you follow the adventures of SV Delos on YouTube, you probably know that the star of the show (SV Delos— in case the title didn’t give it away ) is an Amel Super Maramu. These classic bluewater sailboats can be found all over the world, proof they can go the distance.
We counted 16 Amel Super Maramus and Super Maramu 2000s in our list of PPJ entries.
Ready to join the cult of Amel? Read more about the iconic brand in Yachting World.
5. Valiant 40

When I interviewed legendary yacht designer, Bob Perry, for Good Old Boat in 2019, he told me that the Valiant 40 was one of the boats that most defined him and marked the real start of his career.
At the time, heavy displacement cruisers were considered sluggish and slow, especially in light winds.
Perry’s innovation with the Valiant 40 was to combine a classic double ender above the waterline, with an IOR racing hull shape below the waterline. The result was the first “performance cruiser”, a blockbuster hit, with over 200 boats built in the 1970s.
It’s no surprise we counted 16 Valiant 40s in our data set.
Cruising World magazine dubbed it “a fast, comfortable, and safe cruising yacht,” and there’s no doubt it’s covered some serious nautical miles.
It’s worth noting that there were blistering problems with hull numbers 120-249 (boats built between 1976 and 1981). Later models did not have this problem. Despite the blistering issues, the Valiant 40 remains one of the most highly thought of bluewater designs.
6. TAYANA 37

The Tayana 37 is another hugely popular Perry design. The first boat rolled off the production line in 1976 and since then, nearly 600 boats have been built. Beautiful classic lines and a proven track record have won the Tayana 37 a devoted following of offshore enthusiasts.
12 Tayana 37s have set out to cross the Pacific in the PPJ rally since 2009. Read more about the Tayana 37 in this Practical Sailor review .
7. Lagoon 450

If this list is starting to sound like a paid advertisement, I swear we’re not on Lagoon’s payroll! This is the third Lagoon on our list, but the data doesn’t lie. Lagoon is making some of the best cruising sailboats.
The 450 has been a hot seller for Lagoon, with over 800 built since its launch in 2014. While not a performance cat, the Lagoon 450 travels at a reasonable speed and is brimming with luxury amenities.
At least 12 owners in the PPJ rally chose the Lagoon 450 to take them across the Pacific. It’s no wonder SAIL had so many good things to say about it.
8. Fountaine Pajot Bahia 46

There were 11 Fountaine Pajot Bahia 46s in our data set.
Fountaine Pajot released the Bahia 46 in 1997, a sleek design for traveling long distances. Its generously-sized water and fuel tanks along with ample storage for cruising gear are a real plus for the self-sufficient sailor.
According to Cruising World , “Cruising-cat aficionados should put the Bahia 46 on their “must-see” list.”
9. Catalina 42 (MKI, MKII)

10 Catalina 42s (MKI and MKII) have set out to cross the Pacific in the PPJ rally since 2009.
The Catalina 42 was designed under the guidance of the legendary yacht designer and Catalina’s chief engineer, Gerry Douglas.
One of Catalina’s philosophies is to offer “as much boat for the money as possible,” and the Catalina 42 is no exception. According to Practical Sailor , Catalina aims to price its boats 15% to 20% below major production boats like Hunter and Beneteau.
Practical Sailor has a great in-depth review of the Catalina 42 .
10. Leopard 46

Since 2009, 10 Leopard 46s have embarked on Pacific crossings in the PPJ rally.
Leopards have won legions of fans for their high build quality, robust engineering, and excellent performance.
The Leopard 46 also boasts something of a racing pedigree. It was built in South Africa by Robertson and Caine and designed by Gino Morelli and Pete Melvin, who came up with the record-breaking catamaran Playstation / Cheyenne 125 .
Read more about the Leopard 46 in this Cruising World review .
Methodology
What the data is and isn’t.
The PPJ data was a real boon because it reflects a wide range of cruising boats: small, big, old, new, expensive, and affordable. We think this may be because the PPJ is a very financially accessible rally—the standard entry cost is $125 or $100 if you’re under 35 (age or boat length!).
We did look at data from other (pricier) rallies but found that the results skewed towards more expensive boats.
Needless to say, the data we used is just a sample of the bluewater boats that crossed the Pacific over the last 10+ years. Many cruisers cross oceans without participating in a rally!
Entries vs. completions
The data we used is a list of the PPJ entries, not necessarily the boats that completed the rally. In instances where we saw the same boat entered multiple years in a row, we assumed they’d postponed their crossing and deleted all but the latest entry to avoid double counting.
Boat make variations
The world of boat building and naming can get pretty complicated. Sometimes a manufacturer changes a boat’s name a year or two into production, other times the name remains the same but the boat undergoes a dramatic update.
For the most part, we’ve used SailboatData.com’s classification system (if they list the boats separately, then we have also), except where there are two separately listed models that have the same LOA, beam, and displacement.
Fiona McGlynn is an award-winning boating writer who created Waterborne as a place to learn about living aboard and traveling the world by sailboat. She has written for boating magazines including BoatUS, SAIL, Cruising World, and Good Old Boat. She’s also a contributing editor at Good Old Boat and BoatUS Magazine. In 2017, Fiona and her husband completed a 3-year, 13,000-mile voyage from Vancouver to Mexico to Australia on their 35-foot sailboat.
Terms and Conditions - Privacy Policy

Home Modern classic
Welcome to Leonardo Yachts. In close collaboration with the leading designers in the yachting world such as Hoek Design and Dykstra Naval Architects, we build daysailers that embody the true essence of a modern classic yacht. Our modern classic sailing yachts combine the timeless appeal of a classic yacht with the cutting edge technology of a modern cruiser. Enjoy the exceptional comfort and unrivaled performance or our Spirit of Tradition yachts, without making compromises on beauty and elegance. Our modern classic sailing yachts truly are the ideal combination of old and new…

Like a true modern classic yacht, our Eagles all have a classic look with the characteristic long overhangs, classic yacht lines and high gloss mahogany varnished exterior woodwork. The looks are completed by the Edson classic steering pedestal with Ritchie stainless steel compass and the stainless steel 7 spoke steering wheel with high gloss varnished mahogany rim. The interior of our modern classic sailboats can be made in different styles from matt varnished mahogany for a truly classic look or a classic styled white interior with mahogany or teak finish. But also light oak is possible or full teak wood, whatever your preference would be.
The classic lines and looks are integrated in a modern sailing yacht. The designs are made with the latest technology giving the yachts very good and easy to handle sailing characteristics. The modern keels in fin shape can be even upgraded for more performance to a bulb shaped deep draft keel making them fast and easily manouvrable. The modern technology can also be found in the electric package for the winches by which adjusting the sails becomes as easy as pushing a button. The sails from North Sails also hold the latest technology with the 3Di design, making the sails very shape stable to increase the sailing performance. To complete a race set-up, a carbon mast and boom can be added to get the most out of the speed. Standard, our modern classic yachts are delivered with Volvo Penta engines, but off course electric propulsion is available for all models.If you share our passion for modern classic sailing, we would be honoured to help fulfil your aspirations. Together we build the most beautiful Spirit of Tradition boats ever seen.
Get in touch and explore all our options.
No products in the cart.
Sailing Ellidah is supported by our readers. Buying through our links may earn us an affiliate commission at no extra cost to you.
The Standing Rigging On A Sailboat Explained
The standing rigging on a sailboat is a system of stainless steel wires that holds the mast upright and supports the spars.
In this guide, I’ll explain the basics of a sailboat’s hardware and rigging, how it works, and why it is a fundamental and vital part of the vessel. We’ll look at the different parts of the rig, where they are located, and their function.
We will also peek at a couple of different types of rigs and their variations to determine their differences. In the end, I will explain some additional terms and answer some practical questions I often get asked.
But first off, it is essential to understand what standing rigging is and its purpose on a sailboat.
The purpose of the standing rigging
Like I said in the beginning, the standing rigging on a sailboat is a system of stainless steel wires that holds the mast upright and supports the spars. When sailing, the rig helps transfer wind forces from the sails to the boat’s structure. This is critical for maintaining the stability and performance of the vessel.
The rig can also consist of other materials, such as synthetic lines or steel rods, yet its purpose is the same. But more on that later.
Since the rig supports the mast, you’ll need to ensure that it is always in appropriate condition before taking your boat out to sea. Let me give you an example from a recent experience.
Dismasting horrors
I had a company inspect the entire rig on my sailboat while preparing for an Atlantic crossing. The rigger didn’t find any issues, but I decided to replace the rig anyway because of its unknown age. I wanted to do the job myself so I could learn how it is done correctly.
Not long after, we left Gibraltar and sailed through rough weather for eight days before arriving in Las Palmas. We were safe and sound and didn’t experience any issues. Unfortunately, several other boats arriving before us had suffered rig failures. They lost their masts and sails—a sorrowful sight but also a reminder of how vital the rigging is on a sailboat.
The most common types of rigging on a sailboat
The most commonly used rig type on modern sailing boats is the fore-and-aft Bermuda Sloop rig with one mast and just one headsail. Closely follows the Cutter rig and the Ketch rig. They all have a relatively simple rigging layout. Still, there are several variations and differences in how they are set up.
A sloop has a single mast, and the Ketch has one main mast and an additional shorter mizzen mast further aft. A Cutter rig is similar to the Bermuda Sloop with an additional cutter forestay, allowing it to fly two overlapping headsails.
You can learn more about the differences and the different types of sails they use in this guide. For now, we’ll focus on the Bermuda rig.
The difference between standing rigging and running rigging
Sometimes things can get confusing as some of our nautical terms are used for multiple items depending on the context. Let me clarify just briefly:
The rig or rigging on a sailboat is a common term for two parts:
- The standing rigging consists of wires supporting the mast on a sailboat and reinforcing the spars from the force of the sails when sailing.
- The running rigging consists of the halyards, sheets, and lines we use to hoist, lower, operate, and control the sails on a sailboat.
Check out my guide on running rigging here !
The difference between a fractional and a masthead rig
A Bermuda rig is split into two groups. The Masthead rig and the Fractional rig.
The Masthead rig has a forestay running from the bow to the top of the mast, and the spreaders point 90 degrees to the sides. A boat with a masthead rig typically carries a bigger overlapping headsail ( Genoa) and a smaller mainsail. Very typical on the Sloop, Ketch, and Cutter rigs.
A Fractional rig has forestays running from the bow to 1/4 – 1/8 from the top of the mast, and the spreaders are swept backward. A boat with a fractional rig also has the mast farther forward than a masthead rig, a bigger mainsail, and a smaller headsail, usually a Jib. Very typical on more performance-oriented sailboats.
There are exceptions in regards to the type of headsail, though. Many performance cruisers use a Genoa instead of a Jib , making the difference smaller.
Some people also fit an inner forestay, or a babystay, to allow flying a smaller staysail.
Explaining the parts and hardware of the standing rigging
The rigging on a sailing vessel relies on stays and shrouds in addition to many hardware parts to secure the mast properly. And we also have nautical terms for each of them. Since a system relies on every aspect of it to be in equally good condition, we want to familiarize ourselves with each part and understand its function.
Forestay and Backstay
The forestay is a wire that runs from the bow to the top of the mast. Some boats, like the Cutter rig, can have several additional inner forestays in different configurations.
The backstay is the wire that runs from the back of the boat to the top of the mast. Backstays have a tensioner, often hydraulic, to increase the tension when sailing upwind. Some rigs, like the Cutter, have running backstays and sometimes checkstays or runners, to support the rig.
The primary purpose of the forestay and backstay is to prevent the mast from moving fore and aft. The tensioner on the backstay also allows us to trim and tune the rig to get a better shape of the sails.
The shrouds are the wires or lines used on modern sailboats and yachts to support the mast from sideways motion.
There are usually four shrouds on each side of the vessel. They are connected to the side of the mast and run down to turnbuckles attached through toggles to the chainplates bolted on the deck.
- Cap shrouds run from the top of the mast to the deck, passing through the tips of the upper spreaders.
- Intermediate shrouds run from the lower part of the mast to the deck, passing through the lower set of spreaders.
- Lower shrouds are connected to the mast under the first spreader and run down to the deck – one fore and one aft on each side of the boat.
This configuration is called continuous rigging. We won’t go into the discontinuous rigging used on bigger boats in this guide, but if you are interested, you can read more about it here .
Shroud materials
Shrouds are usually made of 1 x 19 stainless steel wire. These wires are strong and relatively easy to install but are prone to stretch and corrosion to a certain degree. Another option is using stainless steel rods.
Rod rigging
Rod rigging has a stretch coefficient lower than wire but is more expensive and can be intricate to install. Alternatively, synthetic rigging is becoming more popular as it weighs less than wire and rods.
Synthetic rigging
Fibers like Dyneema and other aramids are lightweight and provide ultra-high tensile strength. However, they are expensive and much more vulnerable to chafing and UV damage than other options. In my opinion, they are best suited for racing and regatta-oriented sailboats.
Wire rigging
I recommend sticking to the classic 316-graded stainless steel wire rigging for cruising sailboats. It is also the most reasonable of the options. If you find yourself in trouble far from home, you are more likely to find replacement wire than another complex rigging type.
Relevant terms on sailboat rigging and hardware
The spreaders are the fins or wings that space the shrouds away from the mast. Most sailboats have at least one set, but some also have two or three. Once a vessel has more than three pairs of spreaders, we are probably talking about a big sailing yacht.
A turnbuckle is the fitting that connects the shrouds to the toggle and chainplate on the deck. These are adjustable, allowing you to tension the rig.
A chainplate is a metal plate bolted to a strong point on the deck or side of the hull. It is usually reinforced with a backing plate underneath to withstand the tension from the shrouds.
The term mast head should be distinct from the term masthead rigging. Out of context, the mast head is the top of the mast.
A toggle is a hardware fitting to connect the turnbuckles on the shrouds and the chainplate.
How tight should the standing rigging be?
It is essential to periodically check the tension of the standing rigging and make adjustments to ensure it is appropriately set. If the rig is too loose, it allows the mast to sway excessively, making the boat perform poorly.
You also risk applying a snatch load during a tack or a gybe which can damage the rig. On the other hand, if the standing rigging is too tight, it can strain the rig and the hull and lead to structural failure.
The standing rigging should be tightened enough to prevent the mast from bending sideways under any point of sail. If you can move the mast by pulling the cap shrouds by hand, the rigging is too loose and should be tensioned. Once the cap shrouds are tightened, follow up with the intermediates and finish with the lower shrouds. It is critical to tension the rig evenly on both sides.
The next you want to do is to take the boat out for a trip. Ensure that the mast isn’t bending over to the leeward side when you are sailing. A little movement in the leeward shrouds is normal, but they shouldn’t swing around. If the mast bends to the leeward side under load, the windward shrouds need to be tightened. Check the shrouds while sailing on both starboard and port tack.
Once the mast is in a column at any point of sail, your rigging should be tight and ready for action.
If you feel uncomfortable adjusting your rig, get a professional rigger to inspect and reset it.
How often should the standing rigging be replaced on a sailboat?
I asked the rigger who produced my new rig for Ellidah about how long I could expect my new rig to last, and he replied with the following:
The standing rigging should be replaced after 10 – 15 years, depending on how hard and often the boat has sailed. If it is well maintained and the vessel has sailed conservatively, it will probably last more than 20 years. However, corrosion or cracked strands indicate that the rig or parts are due for replacement regardless of age.
If you plan on doing extended offshore sailing and don’t know the age of your rig, I recommend replacing it even if it looks fine. This can be done without removing the mast from the boat while it is still in the water.
How much does it cost to replace the standing rigging?
The cost of replacing the standing rigging will vary greatly depending on the size of your boat and the location you get the job done. For my 41 feet sloop, I did most of the installation myself and paid approximately $4700 for the entire rig replacement.
Can Dyneema be used for standing rigging?
Dyneema is a durable synthetic fiber that can be used for standing rigging. Its low weight, and high tensile strength makes it especially popular amongst racers. Many cruisers also carry Dyneema onboard as spare parts for failing rigging.
How long does dyneema standing rigging last?
Dyneema rigging can outlast wire rigging if it doesn’t chafe on anything sharp. There are reports of Dyneema rigging lasting as long as 15 years, but manufacturers like Colligo claim their PVC shrink-wrapped lines should last 8 to 10 years. You can read more here .
Final words
Congratulations! By now, you should have a much better understanding of standing rigging on a sailboat. We’ve covered its purpose and its importance for performance and safety. While many types of rigs and variations exist, the hardware and concepts are often similar. Now it’s time to put your newfound knowledge into practice and set sail!
Or, if you’re not ready just yet, I recommend heading over to my following guide to learn more about running rigging on a sailboat.
Sharing is caring!
Skipper, Electrician and ROV Pilot
Robin is the founder and owner of Sailing Ellidah and has been living on his sailboat since 2019. He is currently on a journey to sail around the world and is passionate about writing his story and helpful content to inspire others who share his interest in sailing.
Very well written. Common sense layout with just enough photos and sketches. I enjoyed reading this article.
Thank you for the kind words.

Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *

15 Surprising Facts About Modern Sailboat Design

February 28, 2024
Key Takeaways
- Modern sailboat design dramatically enhances performance and experience.
- Understanding these design changes adds depth to our appreciation of sailing.
- Innovations in design are influenced by changes in racing regulations.
Discover the surprising facts about modern boat design as we explore the leaps and bounds that modern sailboat design has made.
The surprising facts about modern boat design are the use of advanced materials, computer-aided designs, hydrodynamic hulls, wind tunnel testing, and articulated rudders. The modern boat design also incorporates wing sails, and twin rudders, among other innovative designs.
As a sailing enthusiast, I possess a deep understanding of the intricacies that shape the modern sailing world. My knowledge encompasses the latest advancements in hull design, rigging techniques, materials, and sustainability practices. As such, I’ll reveal surprising facts that shed light on the innovation and engineering excellence driving the evolution of sailboat design in the 21st century.
Table of contents
Surprising Facts About Modern Sailboat Design
Have you ever looked at a modern sailboat and wondered about the innovative marvels that distinguish these vessels from their ancestors? The world of sailing has transformed dramatically, thanks to cutting-edge technology and revolutionary design elements.
Let's dive into the surprising facts that make today's sailboats a tidal wave of innovation.
From materials that sound straight out of a sci-fi novel to rudders that think for themselves, these facts will give you a new perspective on sailboats.
1. Advanced Materials
Modern sailboat design has been revolutionized by the use of advanced materials like carbon fiber and Kevlar, which offer unparalleled strength-to-weight ratios.
These materials are not limited to the hull; they have also transformed masts and rigging, resulting in lighter, faster, and more durable vessels.
Sailboats can now harness the power of these cutting-edge materials to achieve remarkable performance while maintaining structural integrity.
2. Computer-Aided Design (CAD)
The introduction of Computer-Aided Design (CAD) technology has elevated sailboat design to new heights.
Engineers and designers can now meticulously craft and simulate sailboat designs before the first physical piece is ever built.
This precision-driven approach allows for the creation of sailboats tailored for optimum performance, ensuring that every element, from hull shape to sail configuration, is optimized to perfection.
3. Hydrodynamic Hulls
Modern sailboat hulls are meticulously designed with hydrodynamics in mind. These sleek, streamlined shapes minimize drag and maximize speed, marking a significant departure from the bulky hulls of the past.
Sailboats are now engineered to slice through the water with minimal resistance, enhancing their overall performance.
4. Wind Tunnel Testing
Wind tunnel testing, a practice well-known in many industries has also made its way into sailboat design.
Sailboats undergo rigorous wind tunnel testing to perfect sail shapes and rig setups, optimizing aerodynamic efficiency.
This meticulous approach ensures that every knot of speed is squeezed out, making sailboats faster and more competitive.
5. Hydrofoils
Hydrofoils are like the magic carpets of the sea, revolutionizing sailboat speed and performance.
As speed increases, these underwater wings lift the hull above the water's surface, drastically reducing drag. They also enable breakneck speeds that were once considered unattainable for sailboats.
6. Articulated Rudders
Articulated rudders represent a significant advancement in sailboat design , offering sailors a remarkable degree of maneuverability and precise control, particularly at high speeds.
Comparable to a race car driver fine-tuning their steering, skippers can now navigate sailboats with exceptional precision. These rudders respond swiftly to helm adjustments, enhancing safety and optimizing performance in various conditions.
Whether executing tight maneuvers or maintaining a steady course, articulated rudders empower sailors with unparalleled control, making them a game-changer in modern sailboat design.
7. Wing Sails
The adoption of wing sails in sailboat design marks a departure from traditional canvas sails and ushers in a new era of sailboat efficiency and adaptability.
Resembling the wings of an airplane, these sails offer sailboats increased power, precise control, and exceptional adjustability.
Sailors can harness the wind more efficiently, optimizing their sail configurations to suit changing conditions.
Wing sails respond rapidly to shifts in the wind, providing a level of adaptability that was once unimaginable. This innovation has transformed sailboats into highly responsive and versatile vessels, ensuring optimal performance on the open seas.
8. Sustainability Features
Sustainability is at the forefront of modern sailboat design, reflecting the growing commitment to eco-friendly practices within the sailing community.
Sailboats are now equipped with innovative features such as electric propulsion systems, solar panels, and advanced water purification systems.
These sustainable technologies reduce environmental impact, allowing sailors to cruise the open seas while minimizing their carbon footprint.
As sustainability takes precedence, the integration of these eco-friendly features not only aligns with environmental values but also enhances the overall cruising experience, making it more responsible and enjoyable.
9. Self-Tacking Jibs
The introduction of self-tacking jibs has streamlined sailboat maneuvering , particularly for solo sailors or small crews. These ingenious sails automatically adjust to the wind's direction, eliminating the need for manually grinding winches when changing course.
This innovation significantly enhances convenience and usability, making sailing more accessible to a broader range of enthusiasts.
Whether navigating through gusty winds or executing precise tacks, self-tacking jibs simplify the sailing experience, allowing sailors to focus on enjoying the journey without the hassle of constant sail adjustments.
10. Canting Keels
Canting keels represent a pivotal development in sailboat design, offering a solution to the age-old challenge of sailboat stability when heeled over. These keels can be shifted from side to side, counteracting the natural inclination of sailboats to capsize when tilted.
This innovation allows for a more aggressive sail plan, enabling sailboats to achieve higher speeds without compromising safety.
The canting keels' ability to maintain stability while heeled over has revolutionized sailboat racing and performance, pushing the boundaries of what sailboats can achieve on the water.
11. Twin Rudders
Two rudders mean better control, especially when heeling, and improved performance by maintaining steerage even in challenging conditions.
It's like having four-wheel steering in your car—a game-changer for sure.
12. Integrated Navigation Systems
Touchscreen displays, GPS, and autopilot systems are no longer just for luxury cars. They've found their way onto sailboats, providing sailors with all the navigational aids they need at their fingertips.
13. Resin-Infused Hulls
Resin-infused hulls represent a pivotal advancement in sailboat construction, delivering stronger, lighter, and more resilient vessels with a superior finish.
This innovative manufacturing process involves infusing resin into a precisely arranged fiber matrix, resulting in a structurally sound hull that is both lightweight and exceptionally durable.
The benefits are twofold: a faster sailboat due to reduced weight and increased resilience to the elements.
14. Sail-Material Innovations
Modern sailboats continue to push the boundaries of speed and performance, thanks in large part to sail-material innovations.
Sails are now crafted from laminated fabrics and exotic fibers that are not only capable of withstanding the punishment of the high seas but also offer enhanced performance.
These advanced materials provide superior durability and strength, allowing sails to maintain their shape and efficiency even in challenging conditions.
Sailors can confidently navigate rough waters, harnessing the full potential of the wind to achieve remarkable speeds.
These sail-material innovations are at the heart of modern sailboat design, enabling sailors to explore new horizons and set sail like never before.
15. Foil-Assisted Monohulls
Foil-assisted monohulls represent an exhilarating advancement in sailboat design, harnessing the power of underwater wings to provide additional lift.
This innovative feature effectively reduces drag and allows the sailboat to ride higher and quicker in the water.
The result is a thrilling sailing experience that combines speed, stability, and agility. Foil-assisted monohulls are a game-changer for sailors who seek the thrill of high-speed sailing while maintaining control and stability.
This technology has redefined what is possible in monohull sailboats, offering an exhilarating ride for sailors who crave speed and adventure on the open seas.
Impact of Racing Regulations and Rating Systems on Sailboat Design
The world of sailboats is more intricate than it seems, especially when you throw in racing regulations and rating systems.
Regulations and rating systems aren’t just red tape; they are the invisible architects of modern sailboat design. From tweaking hull shapes to adjusting ballasts, these rules stir the pot, leading to innovation in search of that extra knot of speed.
Here’s a simple breakdown highlighting how racing regulations and rating systems have dramatically influenced sailboat design:
Frequently Asked Questions
Here are the FAQs on modern sailboat designs.
Can you list some notable evolutions in sailboat design since their invention?
Absolutely! Over time, sailboats have shed some serious weight and bulk. Think less 'pirate galleons', and more 'sleek sea greyhounds'. The nifty evolution includes trimmed-down overhangs at the bow and stern, giving modern sailboats a longer waterline for a given length overall.
What are a few unexpected benefits of modern sailboat design on the efficiency and speed of sailing?
For starters, contemporary sailboats are shaping up to be the marathon runners of the sea – sleeker, lighter, and roomier. All that extra width isn't just for cocktail parties on deck; it's for stability.
How do modern sailboats incorporate sustainability and eco-friendliness into their designs?
Designers are harnessing materials and technologies that lower the environmental impact like inventive hull coatings to reduce drag and engines that sip rather than gulp fuel.
Jacob Collier
Born into a family of sailing enthusiasts, words like “ballast” and “jibing” were often a part of dinner conversations. These days Jacob sails a Hallberg-Rassy 44, having covered almost 6000 NM. While he’s made several voyages, his favorite one is the trip from California to Hawaii as it was his first fully independent voyage.
by this author
Trending Now

What Does "Sailing By The Lee" Mean?

Best Sailing Duffle Bags: Top Picks For Boat Travel

The Best Sailing Schools And Programs: Reviews & Ratings

Affordable Sailboats You Can Build at Home

Best Small Sailboat Ornaments

Best Small Sailboats With Standing Headroom

Discover the Magic of Hydrofoil Sailboats

Best Bluewater Sailboats Under $50K

Hunter Sailboats: Are They Built for Bluewater Cruising?

How To Buy A Cheap Sailboat

What Is A Furler On A Sailboat?

How To Choose The Right Sailing Instructor

What Is Sail Roach?

Best Blue Water Sailboats Under 40 Feet

What Is A DaySailer Sailboat?

Are Catalina Sailboats Bluewater Boats?

Best Sailing Racing Electronics

How To Sail From California To Tahiti

Best Sailing Destinations In BC

Best Sailing Charter Destinations

Which Sailboats Have Lead Keels?

Best 2 Person Sailboats

What Sailboats Are Made In The USA?

Best Sailing Racing Compasses

Which Sailboats Hold Their Value?

Can You Sail In Maine In October?

Most Reliable Sailboats

Common Issues With Amel Yacht Sailboats

Basics Of Sailboat Racing Explained

What Is The Steering Wheel On A Ship Called?

Everything You Can Pull Behind A Boat

How To Tow A Skier Behind A Boat

Most Popular One-Design Sailboats

How Long Is A Laser Sailboat?

What Sailboats Are Used In The Olympics?

Why Do Sailboats Lean?

Cost To Dock A Sailboat

Cost To Sail Around The World

How Often Do Sailboats Capsize & Sink?

Are Sailboats Bad For The Environment?

Best Marine Epoxy

Best Sailing Destinations Chesapeake Bay

Best Pontoon Boat Brands

Best Marine Refrigerators

Best LED Navigation Lights

Best Marine Air Conditioners

Best Boating Watches For The Avid Sailor

Are Sailboats Cheaper Than Powerboats?

How Much Does A Laser Sailboat Cost?

How Often Do Sailboats Get Struck By Lightning?

How Do Sailboats Float?

Best Marine Water Softeners

Best Sailing Shirts

Best First Aid Kits For Boat Safety

Why Do Catamarans Have Trampolines?

Best Ropes For Mooring Lines

Who Has To Wear A Life Jacket On A Boat?

How Old Do You Have To Be To Wear A Life Jacket On A Boat?

Where To Store Life Jackets On A Boat

Best Winter Pontoon Boat Covers

Bennington Pontoon Winter Cover Review

Best Pontoon Boat Cover Support Systems

How To Paint Pontoon Boat Fencing

What To Bring On Pontoon Boat

What To Wear On A Pontoon Boat

Pontoon Boat Winter Storage Ideas

Best Pontoon Boat Accessories

How Tall Is A Pontoon Boat On A Trailer?

Where To Attach Tow Ropes To Pontoon Boats

Best Trolling Motors For Pontoon Boats

Best Pontoon Boats For The Money

Best Pontoon Winter Storage Blocks

How To Launch A Pontoon Boat By Yourself

Best Pontoon Boats

How Much To Rent A Pontoon Boat? (Cost)

What To Avoid When Buying A Pontoon Boat

Best Grills For Pontoon Boats

How To Store A Pontoon Boat For Winter

SwellPro SplashDrone 4 Review (Is It Worth It?)

Best Anchors For Pontoon Boats

What Size Trolling Motor For 24ft Pontoon Boats?

How Many People Can Fit On A Pontoon Boat?

Best Small Pontoon Boats

How To Start A Pontoon Boat

How Fast Can Pontoon Boats Go?

What Size Motor For A 20ft Pontoon Boat?

Where To Put Numbers On A Pontoon Boat

How To Launch A Pontoon Boat

How Much Do Pontoon Boats Cost?

Best Fishing Pontoon Boats

How Wide Is A Pontoon Boat Trailer?

How To Store A Pontoon Boat Without A Trailer

Best Pontoon Boat Covers

Top 5 Pontoon Boats (Best Brands & Options)

How To Add Flags To Pontoon Boats

Who Makes Crest Pontoon Boats?

What Is Underpinning On A Pontoon Boat?

How To Drive A Pontoon Boat

How To Anchor A Pontoon Boat

How Wide Is A Pontoon Boat?
Get The Best Sailing Content
Top Rated Posts
Lifeofsailing.com is a participant in the Amazon Services LLC Associates Program, an affiliate advertising program designed to provide a means for sites to earn advertising fees by advertising and linking to Amazon. This site also participates in other affiliate programs and is compensated for referring traffic and business to these companies. (866) 342-SAIL
© 2024 Life of Sailing Email: [email protected] Address: 11816 Inwood Rd #3024 Dallas, TX 75244 Disclaimer Privacy Policy
Types of Sailboats: Essential Guide for Every Sailor
Sailboats have been an essential part of human history, contributing to exploration, trade, and leisure. With a myriad of designs and sizes, these versatile vessels cater to various purposes and preferences. The defining characteristics of sailboats come from their rigging, sails, and hull design.

The basics of sailboat design play a significant role in the classification and function of these vessels. Hull shapes, keel types, and construction materials contribute to the speed, stability, and maneuverability of sailboats. Additionally, rigging and sails come in various shapes and sizes, which influence sailing performance and handling.
Key Takeaways
- Sailboats are classified by hull design, rigging, and sails that serve specific purposes.
- Designs and materials have a direct impact on the performance and handling of sailboats.
- A wide range of sailboat types exists, which cater to different needs and preferences.
Basics of Sailboat Design
Sailboats come in various shapes and sizes, designed for different purposes and sailing conditions. One can classify sailboats based on hull types, keel types, and mast configurations. This section will briefly discuss these basic components of sailboat design.
There are mainly two types of hulls: monohull and multihull.
- Monohull : This is the traditional and most common type of sailboat hull. It consists of a single hull, providing stability through the use of a keel or centerboard. Monohulls come in various shapes and sizes, suitable for various sailing conditions.
- Catamaran : Catamarans have two parallel hulls of equal size, offering increased stability and speed compared to monohulls. They are commonly used for cruising and racing.
- Trimaran : Trimarans have three hulls, with a larger central hull and two smaller outrigger hulls. This design offers even more stability and speed than catamarans.
The keel is an essential component in sailboat design, helping with stability and performance. There are various keel types, including:
- Full keel : This traditional design features a long and wide keel that extends along the boat's bottom. It offers good tracking and stability but sacrifices speed and maneuverability.
- Fin keel : Fin keels are shorter and deeper than full keels, providing a better combination of stability and maneuverability. These are common in modern monohull sailboats.
- Bulb keel : A bulb keel features a fin keel with a heavy bulb at the bottom, which concentrates the boat's weight, increasing stability and performance in rough conditions.
- Swing keel or centerboard : Swing keels and centerboards can be raised or lowered, allowing the boat to adapt to different water depths and sailing conditions. They are common in smaller boats and racing sailboats.

Mast Configuration
The mast configuration affects the sail plan and overall performance of a sailboat. Some common mast configurations include:
- Sloop : This is the most popular mast configuration and features a single mast with a mainsail and a headsail. The simple design makes it easy to handle and suitable for various sailing conditions.
- Cutter : Similar to the sloop, the cutter also has a single mast but carries two headsails, providing more sail area and better performance in heavy weather.
- Ketch : A ketch configuration has two masts: a taller main mast and a shorter mizzen mast. This design offers more flexibility in sail combinations and better balance in different sailing conditions.
- Yawl : Similar to a ketch, a yawl also features two masts but the mizzen is located further aft and is smaller. This design provides better balance and control, particularly in downwind sailing scenarios.
In conclusion, the basics of sailboat design involve selecting the appropriate hull type, keel type, and mast configuration for the desired sailing performance and conditions. Understanding these concepts can help sailors make informed decisions when choosing a sailboat or planning their sailing adventures.
Rigging and Sails
When it comes to sailboats, the rigging and sails play a crucial role in the boat's overall performance and capabilities. This section will briefly cover popular rig types and sail types seen on different sailboats.
There are several types of rigs commonly found on sailboats:
- Sloop : Sloops are the most common type of rig found on modern sailboats. They have a single mast with a mainsail and a single headsail, typically a genoa or jib.
- Ketch : Ketches have two masts, with the main mast taller than the mizzen mast situated aft. They carry a mainsail on the main mast and a mizzen sail on the mizzen mast. Ketches benefit from easier handling and reduced sail area under strong winds.
- Yawl : Similar to ketches, yawls have two masts, but the mizzen mast is smaller and sits further aft, behind the rudder post. Yawls are often chosen for their graceful appearance and improved balance.
- Schooner : Schooners have two or more masts, with the aft mast(s) typically taller than the forward mast(s). Schooners can handle more sails, offering increased sail area for better performance, especially downwind.
- Catboat : Catboats are single-masted sailboats with a single, large mainsail and no headsails. They have a wide beam, which provides stability and ample space for passengers.
- Cutter : Cutters are similar to sloops but carry two headsails, usually a jib and staysail. Cutters may have multiple headsails for increased versatility in various wind conditions.
In addition to the types of rigs, there are also several types of sails used on sailboats, including:
- Mainsail : The primary sail attached to the back of the main mast. It is typically raised on a track or luff groove and managed by a combination of halyard, sheet, and boom vang.
- Genoa : A large triangular sail that overlaps the mainsail, typically used in light winds to provide additional surface area for better performance.
- Jib : A smaller, non-overlapping triangular sail attached to the forestay. Jibs are easier to manage than genoas and are used in a variety of wind conditions.
- Spinnaker : A large, lightweight sail used primarily for downwind sailing . Spinnakers are often brightly colored and shaped like a parachute to catch wind efficiently.
- Staysail : A smaller sail typically used in cutter rigs, positioned between the main mast and the forestay. Staysails provide additional sail area and versatility in varied wind conditions.
Understanding the relationship between sail and rigging can help sailors optimize the performance of their sailboats. With various options for rig types and sail types, each sailboat can be configured to meet the unique needs of its skipper and crew.

Classes and Types of Sailboats
Monohulls are the most common type of sailboats, consisting of a single hull that provides stability and balance. They come in various sizes and designs, depending on their intended use. Some popular monohull sailboats include the Optimist , Finn, and Sunfish, which are frequently used for racing and recreational sailing. Monohulls tend to have a deeper draft, requiring more water depth than their multi-hull counterparts.
Multihulls, also known as multi-hull sailboats, are a more modern innovation in sailing. They feature two or more hulls connected by a frame or bridgedeck. This design offers increased stability and speed over monohulls. Some common types of multihulls are catamarans (with two hulls) and trimarans (with three hulls). Due to their wider beam and shallower draft, multihulls are particularly suitable for cruising in shallow waters and provide more living space on board.
One-Design Sailboats
One-Design sailboats are a specific class of racing sailboats in which all boats are built to the same design specifications, ensuring that the competition focuses on the skill of the sailor rather than the design of the boat. These boats must adhere to strict rules and standards, with minimal variations allowed in terms of hull shape, sail area, and rigging. Some popular one-design sailboats include the Enterprise and the aforementioned Optimist and Finn sailboats.
Dinghies and Skiffs
Dinghies and skiffs are small, lightweight sailboats that are often used for sailing classes, short-distance racing, or as tenders to larger boats. Dinghies usually have a single mast with a mainsail and sometimes a small jib. Some popular types of sailing dinghies include the Optimist, which is specifically designed for children, and the versatile Sunfish sailboat. Skiffs, on the other hand, are high-performance sailboats primarily used for racing. They have a larger sail area relative to their size and typically include features such as trapezes and planing hulls, which allow for faster speeds and greater maneuverability.
In conclusion, there are various classes and types of sailboats, each with its own unique features and characteristics. From the simplicity of monohulls to the stability and speed of multihulls, and from the fair competition of one-design sailboats to the excitement of dinghies and skiffs, there is a sailboat to satisfy every sailor's preferences.
Sailboat Size and Use
When exploring the world of sailboats, it's important to understand their different sizes and purposes. Sailboats can be categorized into three main types, each with unique characteristics and uses: Day Sailers , Racing Sailboats, and Cruising Sailboats .
Day Sailers
Day Sailers are small sailboats typically ranging from 10 to 24 feet in length. These boats are perfect for short sailing trips and are easy to maneuver for beginners. They have limited accommodations on board, providing just enough seats for a small group of people. Some popular day sailer models include the Laser, Sunfish, and Flying Scot. Lightweight and agile, Day Sailers are often used for:
- Recreation: casual sailing or exploring nearby waters with family and friends
- Training: beginner sailing lessons or practicing sailing techniques
- Competition: local club races or interclub regattas
Racing Sailboats
Racing Sailboats are designed to provide maximum speed, maneuverability, and efficiency on the water. Sizes may vary greatly, from small dinghies to large yachts. Key features of racing sailboats include a sleek hull shape, high-performance sails, and minimalistic interiors to reduce weight.
Career racers and sailing enthusiasts alike participate in various types of racing events , such as:
- One-design racing: all boats have identical specifications, emphasizing crew skill
- Handicap racing: boats of different sizes and designs compete with time adjustments
- Offshore racing: long-distance racing from one point to another, often around islands or across oceans
Cruising Sailboats
Cruising Sailboats are designed for longer journeys and extended stays on the water. They typically range from 25 to 70 feet in length and provide comfortable accommodations such as sleeping cabins, a galley, and storage spaces for supplies and equipment. Sailing cruisers prioritize stability, comfort, and durability for their voyage.
Here are some common types of cruising sailboats:
- Cruiser-racers: These boats combine the speed of a racing sailboat with the comfort and amenities of a cruising sailboat. They are ideal for families or sailors who enjoy participating in racing events while still having the option for leisurely cruises.
- Bluewater cruisers: Designed for handling the world's most demanding ocean conditions, bluewater cruisers are built with a focus on sturdy, self-reliant sailboats that can withstand long-distance voyages and challenging weather conditions.
- Multihulls: Catamarans and trimarans are gaining popularity in the cruising world for their typically more spacious interiors and level sailing characteristics. With two or three hulls, multihulls offer high levels of stability and speed for a comfortable cruising experience.
Understanding the differences between various sailboat types will help potential sailors select the perfect vessel for their sailing goals, skills, and preferences. Day Sailers, Racing Sailboats, and Cruising Sailboats each have their unique features, catering to distinct uses and sailing experiences.
Advanced Sailboat Features
Sailboats have evolved over time, and many advanced features have been developed to enhance performance and safety. In this section, we will discuss some of the key advanced features in modern sailboats, focusing on performance enhancements and safety/navigation.
Performance Enhancements
One critical component that impacts a sailboat's performance is the type of keel it has, which affects stability, resistance, and maneuverability . There are several kinds of keels such as fin keel , wing keel , and bulb keel . Fin keels offer low drag and high efficiency, making them suitable for racing sailboats. On the other hand, wing keels provide better stability at low speeds, while bulb keels provide a lower center of gravity to enhance overall stability and comfort during long voyages.
Another feature that contributes to a sailboat's performance is its sails and rigging. The jib is a triangular sail at the front of the boat, which helps improve its upwind performance. More advanced sailboats use a combination of shrouds , which are the supporting cables running along the sides of the boat, and stays , the cables that help hold the mast in place, to create a stable and efficient rigging system.
A sailboat's performance can also be influenced by the presence of a centerboard or daggerboard , which can be adjusted to optimize stability, maneuverability, and speed. When racing or navigating in shallow waters, retractable centerboards and daggerboards are particularly useful as they provide better performance and versatility.
Safety and Navigation
Safety and navigation onboard a sailboat relies on a combination of advanced gear and equipment. A modern sailboat is usually equipped with:
- GPS and chartplotters to assist with navigation and planning routes
- VHF radios for communication with other vessels and authorities
- Radar to detect obstacles, weather systems, and other vessels
- AIS (Automatic Identification System) which helps monitor nearby vessel traffic
The design of a sailboat's hull, rigging, sails, and hardware also contribute to its safety. The boom , the horizontal pole that extends the sail, should be properly secured and designed to avoid accidents while sailing. The keel , whether it's a fin, wing, or bulb keel, plays a vital role in the overall stability and safety of the sailboat. The choice of keel should be based on the intended use of the sailboat and the prevailing sailing conditions.
In summary, advanced sailboat features significantly improve the performance, safety, and navigation capabilities of modern sailboats. Innovations in keel design, rigging systems, and onboard navigational equipment have undoubtedly contributed to the overall enjoyment and safety of sailing.
Sailboat Ownership
Buying Considerations
When considering buying a sailboat , it is important to understand the different types of sailboats available and the purpose each serves. Sailboats can be broadly categorized into three types:
- Racing sailboats: Designed for speed and performance, with minimalistic interiors and advanced sail systems.
- Cruising sailboats: Built for comfort and longer trips, featuring more spacious interiors and amenities.
- Daysailers: Smaller, easy-to-handle boats that are often used for short trips and recreational sailing.
Prospective boat owners should consider factors such as boat size, type, budget, and intended use (solo vs. family sailing, charter operations, etc.). It's also essential to evaluate the availability of necessary gear and the level of experience required to handle the chosen sailboat.
Maintenance and Upkeep
Sailboat ownership involves maintenance and upkeep to ensure the boat remains functional, safe, and holds its value. Some common maintenance tasks include:
- Hull cleaning and inspection: Regularly inspect the hull for damages and clean off any growth to maintain performance and fuel efficiency.
- Antifouling paint: Apply antifouling paint to prevent marine organisms from attaching to the hull, which can negatively impact the boat's performance.
- Engine maintenance: Check and replace engine oil, inspect cooling and fuel systems, and clean or replace air filters.
In addition to regular maintenance, sailboat owners should also be prepared to replace or repair critical systems and components, such as:
- Sails: Monitor the condition of your sails and replace them as needed to maintain performance and safety.
- Rigging: Regularly inspect and maintain the standing and running rigging, and replace worn or compromised parts.
- Electronics and instruments: Ensure navigation systems, radios, and other electronic equipment are functioning properly.
Taking proper care of a sailboat can be time-consuming, and some owners may choose to charter their boats when not in use as a way to offset ownership costs. Others may opt for hiring professionals to manage routine maintenance, particularly when sailing solo or with limited sailing experience.

Historical and Special Sailboats
Tall ships and gaffers.
Tall Ships are large, traditionally rigged sailing vessels with multiple masts, typically square-rigged on at least one of their masts. Some examples of these ships include the clipper, brig, and square-rigged vessels. The clipper is a fast sailing ship known for its sleek hull and large sail area, while the brig features two square-rigged masts. Square-rigged ships were known for their impressive sail area and could cover large distances quickly.
Gaffers are a subset of historical sailing vessels with a gaff mainsail as their primary sail type. This gaff-rig is characterized by a spar (pole) that extends the top edge of the mainsail, giving it a quadrilateral shape to optimize wind coverage. Gaff mainsails were commonly used in England and influenced the development of other sailing vessels.
Classic and Antique Sailboats
Classic and antique sailboats refer to older, traditionally designed sailing vessels that have been preserved or restored. They often feature wooden construction and showcase a variety of rigging types, including gaff rigs and square rigs. These historical sailboats have unique designs, materials, and techniques that have since evolved or become rare.
Here are some examples of antique and classic sailboats:
- Sloop : A single-masted sailboat with a Bermuda rig and foresail
- Cutter : A single-masted vessel with a similar rig to the sloop, but with additional headsails for increased maneuverability
- Ketch : A two-masted sailboat with a smaller mizzen mast aft of the main mast
In summary, historical and special sailboats encompass a wide range of vessel types, from large, multi-masted tall ships to smaller, single-masted gaffers and classic sailboats. These vessels reflect the rich maritime history and the evolution of sailing techniques and designs over time.
Sailboat Culture and Lifestyle
Sailboat culture and lifestyle encompass a variety of aspects including racing events, leisurely cruising, and exploring new destinations. The main types of sailboats include racing yachts, cruising sailboats, and motorsailers, each offering a unique experience for sailors.
Regattas and Racing Circuits
A popular aspect of sailboat culture involves participating in regattas and racing circuits . These events create a competitive atmosphere and develop camaraderie among sailors. Racing sailboats are specifically designed for speed and agility , and sailors often team up to compete in prestigious races such as the Rolex Sydney Hobart Yacht Race or the America's Cup. Yacht clubs play an essential role in cultivating this competitive sailing environment.
Sailboat Charter and Tourism
Another facet of sailing culture is the sailboat charter and tourism industry, which allows people to experience the cruising lifestyle without owning a sailboat. Charters are offered for various types of sailboats, from family-sized cruising vessels to luxurious superyachts . Yacht sailing provides tourists with a unique travel experience, as they can explore diverse destinations, immerse themselves in local cultures, or simply relax on the open water.
Cruising sailboats are designed to provide comfortable living spaces and amenities, making them perfect for longer journeys or exploring remote destinations. Motorsailers, on the other hand, are equipped with both sails and engines, offering versatility and convenience for sailors.
Some popular sailing destinations include the Caribbean, Mediterranean Sea, and the South Pacific. These regions offer beautiful scenery, rich cultural experiences, and ideal sailing conditions.
The sailboat culture and lifestyle attract individuals who enjoy adventure, exploration, and camaraderie. From competitive racing events to leisurely cruising vacations, sailing offers diverse experiences that cater to a wide range of interests.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the distinguishing features of different sailboat classes?
There are various sailboat classes, each with its own distinguishing features. Monohulls, for example, are the most common type of sailboat and have a single hull. Multihulls, such as catamarans and trimarans, have two or three hulls, respectively. These differences in hull design often affect the boat's stability, speed, and maneuverability.
Which sailboat types are best for novice sailors?
Novice sailors often benefit from starting with smaller, more manageable boats. Sailing dinghies and daysailers are popular choices due to their simple rigging and ease of handling. These boats typically have a single mast and a limited number of sails, making them ideal for beginners to learn sailing basics.
What are common types of small sailboats ideal for day sailing?
For day sailing, small sailboats such as sailing dinghies, day sailers, and pocket cruisers are ideal options. These boats usually range between 12 and 25 feet in length and offer simplicity, ease of handling, and portability. Examples of common day sailing boats include the Sunfish, Laser, and O'Day Mariner.
How do the purposes of various sailboat types vary?
Sailboats serve different purposes based on their design, size, and features. Daysailers and dinghies are ideal for short trips, sailing lessons, and casual outings. Racing sailboats, with their lighter weight and streamlined design, are built for speed and competition. Cruising sailboats, on the other hand, are designed for longer voyages and often include living quarters and additional amenities for comfortable onboard living.
What is considered the most popular class of sailboat for recreational use?
The most popular class of sailboat for recreational use often varies depending on individual preferences and local conditions. However, monohulls are commonly preferred due to their widespread availability, versatility, and affordability. Within the monohull class, boats like the Sunfish, Laser, and Catalina 22 are popular choices for their ease of use and adaptability to various sailing conditions.
Could you describe a sailing dinghy designed for two people?
A two-person sailing dinghy typically has a simple rig with a single mast and one or more sails, making it easy to handle for both experienced and novice sailors. The RS Venture , for example, is a popular choice for two-person sailing. It features a spacious cockpit, durable construction, and simplicity in its rigging and control systems. These characteristics make it an excellent option for recreational sailing, training, and even racing.
Related Articles

India's Navy Soon to Be Stealthier: Advanced Technologies Enhancing Maritime Security
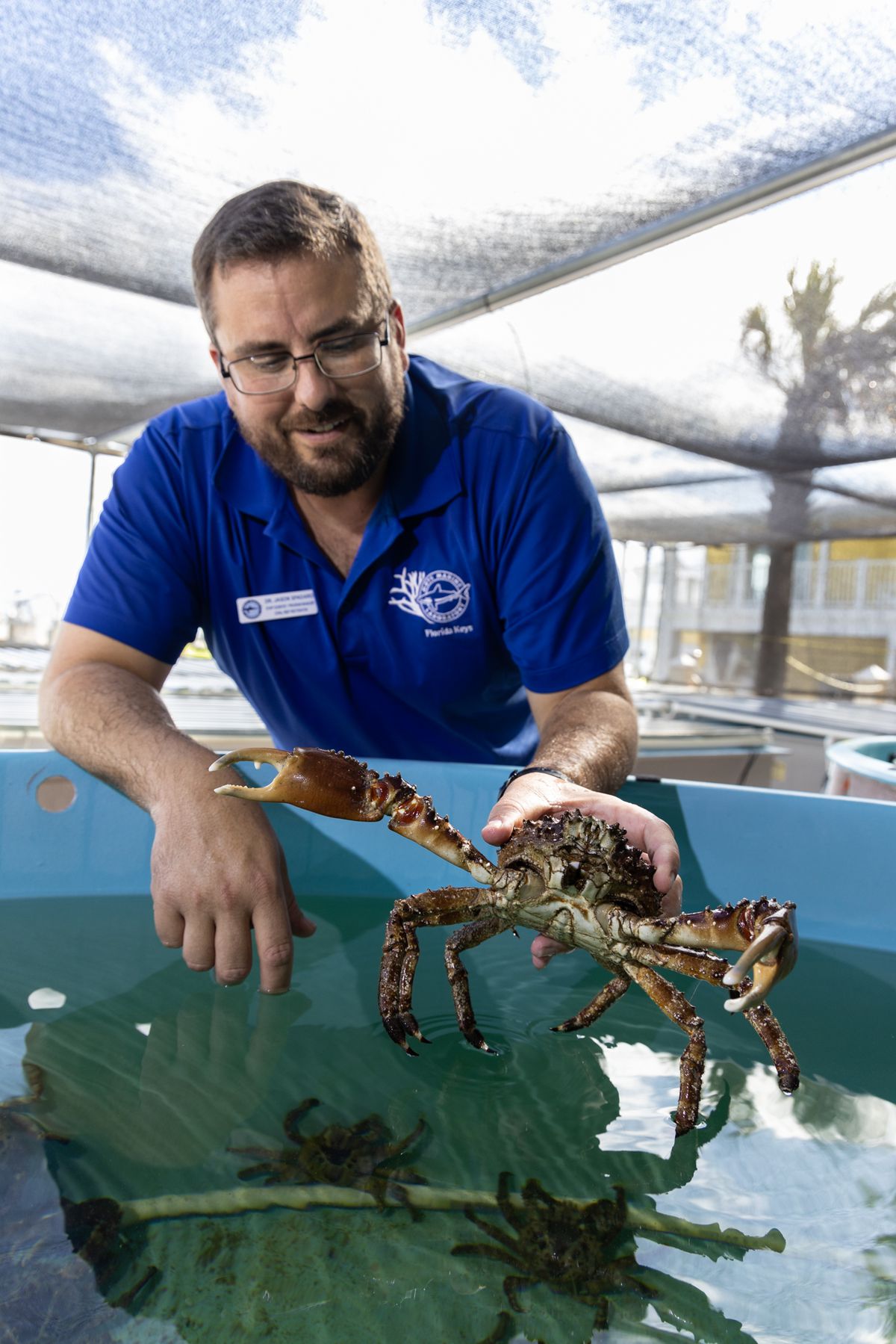

Mote Marine Restoring Coral: Caribbean King Crabs to the Rescue
Charting Unchartered Waters with Sea Magazine's Sea-farer's Guide

Canoe Paddles: Choosing the Best Type for Your Adventure

Cigarette Boat: A High-Speed Marvel on Water

Sarasota Boat Races 2023: A Thrilling Preview of Upcoming Events
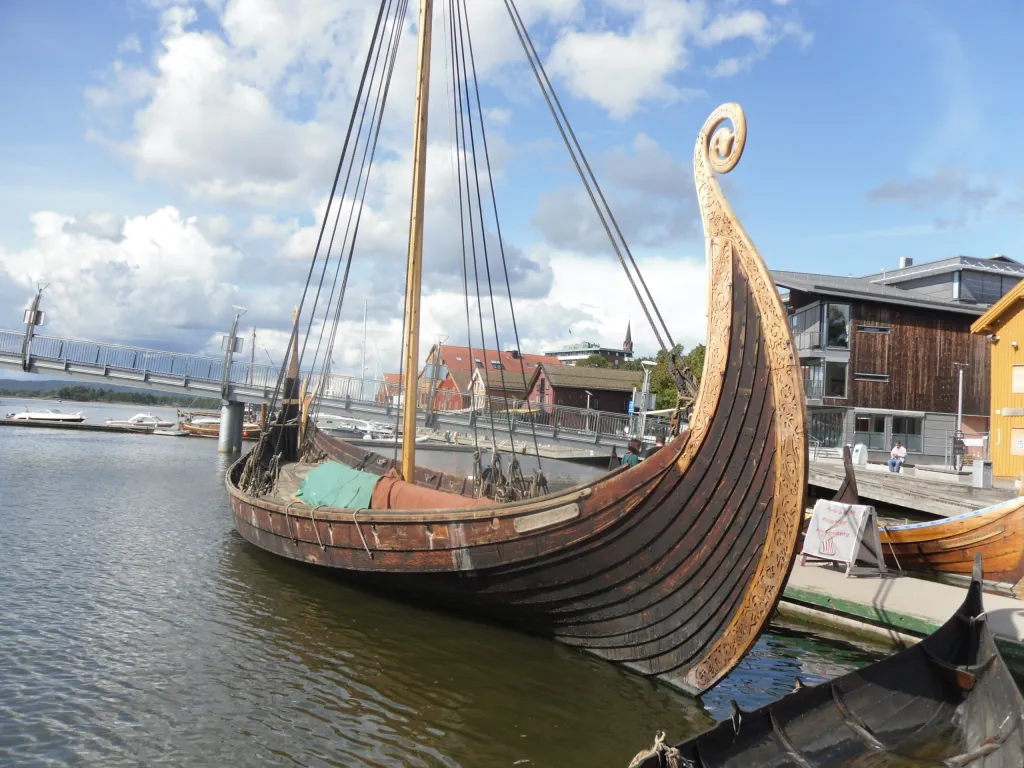

Oseberg Viking Ship: Unveiling the Splendor of Norse Maritime Heritage

What is a Gale Warning: Essential Facts and Safety Tips
Weather Forecast
2:00 pm, 06/12: -11°C - Partly Cloudy
2:00 am, 07/12: -4°C - Clear
2:00 pm, 07/12: -7°C - Partly Cloudy
2:00 am, 08/12: -3°C - Overcast
- Cruising Compass
- Multihulls Today
- Advertising & Rates
- Author Guidelines

Introducing the New Twin-Keel, Deck Saloon Sirius 40DS

New 2024 Bavaria C50 Tour with Yacht Broker Ian Van Tuyl

Dufour 41: European Family Cruising Boat of the Year
Annapolis Sailboat Show 2023: 19 New Multihulls Previewed

2023 Newport International Boat Show Starts Today

Notes From the Annapolis Sailboat Show 2022

Energy Afloat: Lithium, Solar and Wind Are the Perfect Combination

Anatomy of a Tragedy at Sea

What if a Sailboat Hits a Whale?!?

Update on the Bitter End Yacht Club, Virgin Gorda, BVI

Charter in Puerto Rico. Enjoy Amazing Food, Music and Culture

With Charter Season Ahead, What’s Up in the BVI?
AIS Mystery: Ships Displaced and Strangely Circling

Holiday Sales. Garmin Marine Stuff up to 20% Off

The ocean is your parking lot (published July 2012)
For centuries, heaving-to has been the most reliable trick in a sailor’s arsenal for “parking” a sailboat at sea. Throughout that time, sailing vessels have changed and sailors have changed with them, but one fact remains—heaving-to is an important and necessary skill every sailor should master.
On ships of yesteryear, heaving-to was somewhat complex due to sail size and vessel maneuverability. In contrast, heaving-to in a modern sloop is quite easily done with minimal effort. By using a headsail, mainsail and rudder, we have the ability to heave-to for hours or days if required.
WHAT, WHY, WHEN? Simply put, heaving-to is a maneuver used to slow a sailboat’s progress and calm its motion while at sea. When successfully “hove-to,” a sailboat will gently drift to leeward at a greatly reduced speed. The reasons for heaving-to are numerous and often situational. When teaching students the maneuver, I impart the three Rs of heaving-to: Rest, Repairs and Reefing.
When sailing in rough seas (especially shorthanded), there will come a time when you need rest. Resting could mean sleeping, eating, or simply completing tasks that might be difficult or dangerous while underway. Making coffee or a warm meal, using the head, waiting for daybreak outside a harbor and navigation fall into this category. So too does one of the main reasons sailors heave-to—waiting out rough weather. Heaving-to is a completely acceptable storm tactic during the passage of a moderate squall or large front, especially when compared to riding out a storm with bare poles in a heavy sea.
Your need for calm could also come in the form of repairs to your vessel. Working over a diesel engine is far easier when hove-to than when beating into a punishing sea. Also, if a shroud were to break, heaving-to opposite the broken rigging will allow you to assess the damage and possibly make a repair.
When reefing, it may be necessary to send a crewmember forward to use lines near the mast or to attach a luff cringle on the reefing hook. Heaving-to makes this considerably safer and much easier for crew to move forward and work on deck.
HOW TO HEAVE-TO? One of the best ways to heave-to in a modern sloop is to use the tacking method. Start off close-hauled or on a close reach. Turn the bow of the boat through the wind slower than you would during a normal tack and DO NOT release the jib. The goal here is to let the jib backwind and stall the boat’s momentum.
When the bow has passed through the eye of the wind, the jib will be backed to windward. As pressure on the backwinded jib forces the bow to leeward, ease the main and feather the boat into the wind. If you have too much momentum, the bow will want to tack back through the wind, so go slow. Eventually your speed will diminish to a point where the rudder will lose steerage and stall. At the same time the rudder stalls, the bow will blow down. When this happens, turn the helm hard to windward and lock it in place. If you are on a tiller steered boat, push the tiller to leeward and lash it down.
Another acceptable method for heaving-to is to sail close-hauled and tension the windward jibsheet while easing the leeward jibsheet. Once the jib is backed to weather, ease the main and start feathering into the wind to reduce speed and stall the rudder. When the bow blows down, turn the helm hard to windward and lock it. This option is more physically demanding in heavy weather and can be difficult when sailing short-handed.
When hove-to, the sails are essentially canceling themselves out. The rudder and main are trying to drive the bow into the wind, while pressure on the backed jib keeps the bow pinned down. The boat will settle in and drift slightly forward and to leeward. Look down at the water over the windward side of the boat and you will notice turbulence being created by the keel and rudder. This turbulent water is helping to break the oncoming sea as it gets to your boat, thus making your ride more comfortable.
The ideal way to lay hove-to, especially in heavy seas, is at a 45° angle to oncoming waves. Laying abeam can be dangerous and unpleasant. To ensure you are not laying broadside to the swell, trim in the mainsail. Tensioning the main will bring your bow into the swell at an angle and make the boat’s motion more comfortable and safe. It will also keep the main from flogging noisily and causing unnecessary wear to the sail.
When you are ready to get underway again, there are a few good options for getting out of being hove-to. If your intended course is the one you were on prior to heaving–to, unlock the helm and turn it hard to leeward. This will turn you downwind and eventually to a gybe. Once you have safely gybed, you can easily continue to any point of sail on your original tack.
If your desired tack is the one you hove-to on, bring the rudder amidships, release the windward jibsheet—allowing the jib to blow through—and tension the leeward jibsheet. From here, you can steer and trim for your intended course.
THINGS TO REMEMBER Just because you are successfully hove-to and comfortably making a sandwich down below does not mean you can jettison good seamanship. Always keep the following in mind when heaving-to. Every sailboat responds differently when hove-to. Try different sail configurations and reef the sails as necessary for a given wind strength. Also, vessels with a full keel will have a more comfortable motion and will drift slower when hove-to. Fin keel and bulb-keeled boats tend to skitter across the water faster due to the lack of lateral resistance below the waterline. If you plan to stay hove-to for a while, be sure to note how fast and in what direction you are moving.
Make sure you maintain a good watch and always consider how much sea room you have before heaving-to. In the middle of the Atlantic you could lay hove-to for days, but in Narragansett Bay you could be on a collision coarse with another vessel or on the rocks in minutes. In areas congested with other sailboats, try heaving-to on a starboard tack and you will maintain right of way over those on port tack.
If you plan on being hove-to for a while, inspect the rig for places where lines and sails may be chaffing. On boats with an overlapping genoa, the sail will lay against the shrouds and spreaders. To relieve this, reef the sail or ease it slightly to move the clew off the shrouds.

Andrew Cross, a USCG licensed captain and US Sailing certified sailing and navigation instructor, is also the editor of www.cruisingcompass.com. After putting thousands of miles under his keel on the East Coast and in the Caribbean, he and his wife Jill now reside in Seattle and are looking forward to cruising the Great Northwest and beyond.
Author: Andy Cross
17 Sailboat Types Explained: How To Recognize Them
Ever wondered what type of sailboat you're looking at? Identifying sailboats isn't hard, you just have to know what to look for. In this article, I'll help you.
Every time I'm around a large number of sailboats, I look around in awe (especially with the bigger ones). I recognize some, but with most of them, I'll have to ask the owner. When they answer, I try to hide my ignorance. The words don't make any sense!
So here's a complete list with pictures of the most common sailboat types today. For each of them, I'll explain exactly where the name comes from, and how you can recognize it easily.

So here's my list of popular sailboat types, explained:
Bermuda sloop, sailing hydrofoil, dutch barge, chinese junk, square-rigged tall ship, in conclusion, how to recognize any sailboat.
Before we get started, I wanted to quickly explain what you should look for when you try to identify a sailboat.
The type of sailboat is always determined by one of these four things:
- The type of hull
- The type of keel
- The number of masts
- And the type of sails and rig
The hull is the boat's body. There are basically three hull types: monohull, catamaran, and trimaran. Simply said: do I see one hull, two hulls (catamaran) or three hulls (trimaran)? Most sailboats are monohulls.
Next, there is the keel type. The keel is the underwater part of the hull. Mostly, you won't be able to see that, because it's underwater. So we'll leave that for now.
The sail plan
The last factor is the number of masts and the sail plan. The sail plan, simply put, is the number of sails, the type of sails, and how the sails are mounted to the masts (also called rigging ).
Sailboat are mostly named after the sail plan, but occasionally, a sail type is thrown in there as well.
So now we know what to pay attention to, let's go and check out some sailboats!

Dinghies are the smallest and most simple sailboats around.
They are your typical training sailboats. Small boats with an open hull, with just one mast and one sail. Perfect for learning the ways of the wind.
On average, they are between 6 and 20 ft long. Mostly sailed single-handed (solo). There's no special rigging, just the mainsail. The mainsail is commonly a Bermuda (triangular) mainsail. Dinghies have a simple rudder stick and no special equipment or rigging.
Dinghies are great for learning how to sail. The smaller the boat, the better you feel the impact of your trim and actions.
How to recognize a sailing dinghy:
- short (8ft)
- one Bermuda sail
- open hull design
- rudder stick
Common places to spot them: lakes, near docks

If you'd ask a kid to draw a sailboat, she'll most probably draw this one. The Bermuda Sloop is the most popular and most common sailboat type today. You'll definitely recognize this one.
How to recognize a Bermuda Sloop:
- triangular mainsail (called a Bermuda sail)
- a foresail (also called the jib)
- fore-and-aft rigged
- medium-sized (12 - 50 ft)
Fore-and-aft rigged just means "from front to back". This type of rigging helps to sail upwind.
Any sailboat with one mast and two sails could still be a sloop. Even if the sails are another shape or rigged in another way. For example, here's a gaff-rigged sloop (more on the gaff rig later):

If you want to learn all about sail rigs, check out my full Guide to Understanding Sail Rig Types here. It has good infographics and explains it in more detail
The Bermuda sloop has a lot of advantages over other sailboat types (which is why it's so popular):
- the Bermuda rig is very maneuverable and pretty fast in almost all conditions
- it's really versatile
- you can sail it by yourself without any problems
- it's a simple setup
Common places to spot a sloop: everywhere. Smaller sloops are more common for inland waters, rivers, and lakes. Medium-sized and large sloops are very popular cruising boats.

Cutters have one mast but three or more sails. Most cutters are Bermuda rigged, which means they look a lot like sloops.
How to recognize a cutter:
- looks like a sloop
- two or more headsails instead of one
- commonly one mast
- sometimes an extra mast with mainsail
Cutters have more sail area, which makes them faster, but also harder to sail single-handed. There's also more strain on the mast and rigging.
Common places to spot a cutter: everywhere. Cutters are very popular for cruising.
They mostly have a Bermuda rig, which means triangular sails. But there are also gaff cutters and naval cutters, and some have two masts.
Here's an example of a two-masted naval cutter with an extra gaff mainsail and top gaff:

The Hydrofoil is a pretty new sailboat design. It's a racing sailboat with thin wing foils under the hull. These lift up the hull, out of the water, reducing the displacement to nearly zero. The foils create downforce and keep it from lifting off entirely.
This makes the hydrofoil extremely fast and also impressive.
The hydrofoil refers to the keel type. There are both monohull and multihull hydrofoils.
How to recognize a hydrofoil:
- it flies above the waterline and has small fins
Common places to spot a hydrofoil: at racing events

Famous catamaran: La Vagabonde from Sailing La Vagabonde
A catamaran is a type of cruising and racing multihull sailboat with two hulls. The hulls are always the same size.
Most catamarans have a standard Bermuda rig. The catamaran refers to the hull, so it can have any number of masts, sails, sail types and rig type.
How to recognize a catamaran:
- any boat with two hulls is called a catamaran
Common places to spot catamarans: coastal waters, The Caribbean, shallow reefs
The advantages of a catamaran: Catamarans heel less than monohulls and are more buoyant. Because of the double hull, they don't need as deep a keel to be stable. They have a smaller displacement, making them faster. They also have a very shallow draft. That's why catamarans are so popular in the Caribbean, where there's lots of shallow water.
Catamarans are nearly impossible to capsize:
"Compared with a monohull, a cruising catamaran sailboat has a high initial resistance to heeling and capsize—a fifty-footer requires four times the force to initiate a capsize than an equivalent monohull." Source: Wikipedia

How to recognize a trimaran:
- any boat with three hulls is called a trimaran
Trimarans have three hulls, so it's a multi-hull design. It's mostly a regular monohull with two smaller hulls or floaters on the sides. Some trimarans can be trailered by winching in the auxiliary hulls, like this:

This makes them very suitable for long-term cruising, but also for regular docking. This is great for crowded areas and small berths, like in the Mediterranean. It sure is more cost-effective than the catamaran (but you also don't have the extra storage and living space!).
Common places to spot Trimarans: mostly popular for long-term cruising, you'll find the trimaran in coastal areas.

Gaffer refers to gaff-rigged, which is the way the sails are rigged. A gaff rig is a rectangular sail with a top pole, or 'spar', which attaches it to the mast. This pole is called the 'gaff'. To hoist the mainsail, you hoist this top spar with a separate halyard. Most gaffers carry additional gaff topsails as well.
Gaff rigs are a bit less versatile than sloops. Because of the gaff, they can have a larger sail area. So they will perform better with downwind points of sail. Upwind, however, they handle less well.
How to recognize a gaffer:
- sail is rectangular
- mainsail has a top pole (or spar)
Since a gaffer refers to the rig type, and not the mast configuration or keel type, all sailboats with this kind of rigging can be called 'gaffers'.
Common places to spot a gaffer: Gaffers are popular inland sailboats. It's a more traditional rig, being used recreationally.

Schooners used to be extremely popular before sloops took over. Schooners are easy to sail but slower than sloops. They handle better than sloops in all comfortable (cruising) points of sail, except for upwind.
How to recognize a schooner:
- mostly two masts
- smaller mast in front
- taller mast in the back
- fore-and-aft rigged sails
- gaff-rigged mainsails (spar on top of the sail)
Common places to spot a schooner: coastal marinas, bays

How to recognize a ketch:
- medium-sized (30 ft and up)
- smaller mast in back
- taller mast in front
- both masts have a mainsail
The ketch refers to the sail plan (mast configuration and type of rig). Ketches actually handle really well. The back mast (mizzenmast) powers the hull, giving the skipper more control. Because of the extra mainsail, the ketch has shorter masts. This means less stress on masts and rigging, and less heel.
Common places to spot a ketch: larger marinas, coastal regions

How to recognize a yawl:
- main mast in front
- much smaller mast in the back
- back mast doesn't carry a mainsail
The aft mast is called a mizzenmast. Most ketches are gaff-rigged, so they have a spar at the top of the sail. They sometimes carry gaff topsails. They are harder to sail than sloops.
The yawl refers to the sail plan (mast configuration and type of rig).
Common places to spot a yawl: they are not as popular as sloops, and most yawls are vintage sailboat models. You'll find most being used as daysailers on lakes and in bays.

Dutch Barges are very traditional cargo ships for inland waters. My hometown is literally littered with a very well-known type of barge, the Skutsje. This is a Frisian design with leeboards.
Skutsjes don't have a keel but use leeboards for stability instead, which are the 'swords' or boards on the side of the hull.
How to recognize a Dutch Barge:
- most barges have one or two masts
- large, wooden masts
- leeboards (wooden wings on the side of the hull)
- mostly gaff-rigged sails (pole on top of the sail, attached to mast)
- a ducktail transom

The clipper is one of the latest sailboat designs before steam-powered vessels took over. The cutter has a large cargo area for transporting cargo. But they also needed to be fast to compete with steam vessels. It's a large, yet surprisingly fast sailboat model, and is known for its good handling.
This made them good for trade, especially transporting valuable goods like tea or spices.
How to recognize a Clipper:
- mostly three masts
- square-rigged sails
- narrow but long, steel hull
Common places to spot a clipper: inland waters, used as houseboats, but coastal waters as well. There are a lot of clippers on the Frisian Lakes and Waddenzee in The Netherlands (where I live).

This particular junk is Satu, from the Chesapeake Bay Area.
The Chinese Junk is an ancient type of sailboat. Junks were used to sail to Indonesia and India from the start of the Middle Ages onward (500 AD). The word junk supposedly comes from the Chinese word 'jung', meaning 'floating house'.
How to recognize a Chinese junk:
- medium-sized (30 - 50 ft)
- large, flat sails with full-length battens
- stern (back of the hull) opens up in a high deck
- mostly two masts (sometimes one)
- with two mainsails, sails are traditionally maroon
- lug-rigged sails
The junk has a large sail area. The full-length battens make sure the sails stay flat. It's one of the flattest sails around, which makes it good for downwind courses. This also comes at a cost: the junk doesn't sail as well upwind.

The cat rig is a sail plan with most commonly just one mast and one sail, the mainsail.
Most sailing dinghies are cats, but there are also larger boats with this type of sail plan. The picture above is a great example.
How to recognize a cat rig:
- smaller boats
- mostly one mast
- one sail per mast
- no standing rigging
Cat-rigged refers to the rigging, not the mast configuration or sail type. So you can have cats with a Bermuda sail (called a Bermuda Cat) or gaff-rigged sail (called a Gaff Cat), and so on. There are also Cat Ketches and Cat Schooners, for example. These have two masts.
The important thing to know is: cats have one sail per mast and no standing rigging .
Most typical place to spot Cats: lakes and inland waters

Famous brig: HMS Beagle (Charles Darwin's ship)
A brig was a very popular type of small warship of the U.S. navy during the 19th century. They were used in the American Revolution and other wars with the United Kingdom. They carry 10-18 guns and are relatively fast and maneuverable. They required less crew than a square-rigged ship.
How to recognize a brig:
- square-rigged foremast
- mainmast square-rigged or square-rigged and gaff-rigged

How to recognize a tall ship:
- three or four masts
- square sails with a pole across the top
- multiple square sails on each mast
- a lot of lines and rigging
Square-rigged ships, or tall ships, are what we think of when we think of pirate ships. Now, most pirate ships weren't actually tall ships, but they come from around the same period. They used to be built from wood, but more modern tall ships are nearly always steel.
Tall ships have three or four masts and square sails which are square-rigged. That means they are attached to the masts with yards.
We have the tall ship races every four years, where dozens of tall ships meet and race just offshore.
Most common place to spot Tall Ships: Museums, special events, open ocean

This is a bonus type since it is not very common anymore. As far as I know, there's only one left.
The Trabaccolo is a small cargo ship used in the Adriatic Sea. It has lug sails. A lug rig is a rectangular sail, but on a long pole or yard that runs fore-and-aft. It was a popular Venetian sailboat used for trade.
The name comes from the Italian word trabacca , which means tent, referring to the sails.
How to recognize a Trabaccolo:
- wide and short hull
- sails look like a tent
Most common place to spot Trabaccolo's: the Marine Museum of Cesenatico has a fully restored Trabaccolo.
So, there you have it. Now you know what to look for, and how to recognize the most common sailboat types easily. Next time you encounter a magnificent sailboat, you'll know what it's called - or where to find out quickly.

I loved this article. I had no idea there were so many kinds of sailboats.
i have a large sailing boat about 28ft. that im having a difficult time identifying. it was my fathers & unfortunately hes passed away now. any helpful information would be appreciated.
Jorge Eusali Castro Archbold
I find a saleboat boat but i can find the módem…os registré out off bru’x, and the saleboat name is TADCOZ, can you tell me who to go about this matter in getting info.thank con voz your time…
Leave a comment
You may also like, guide to understanding sail rig types (with pictures).
There are a lot of different sail rig types and it can be difficult to remember what's what. So I've come up with a system. Let me explain it in this article.

How Much Sailboats Cost On Average (380+ Prices Compared)
Own your first boat within a year on any budget.
A sailboat doesn't have to be expensive if you know what you're doing. If you want to learn how to make your sailing dream reality within a year, leave your email and I'll send you free updates . I don't like spam - I will only send helpful content.
Ready to Own Your First Boat?
Just tell us the best email address to send your tips to:

My Cruiser Life Magazine
Basics of Sailboat Hull Design – EXPLAINED For Owners
There are a lot of different sailboats in the world. In fact, they’ve been making sailboats for thousands of years. And over that time, mankind and naval architects (okay, mostly the naval architects!) have learned a thing or two.
If you’re wondering what makes one sailboat different from another, consider this article a primer. It certainly doesn’t contain everything you’d need to know to build a sailboat, but it gives the novice boater some ideas of what goes on behind the curtain. It will also provide some tips to help you compare different boats on the water, and hopefully, it will guide you towards the sort of boat you could call home one day.
Table of Contents
Displacement hulls, semi displacement hulls, planing hulls, history of sailboat hull design, greater waterline length, distinctive hull shape and fin keel designs, ratios in hull design, the hull truth and nothing but the truth, sail boat hull design faqs.

Basics of Hull Design
When you think about a sailboat hull and how it is built, you might start thinking about the shape of a keel. This has certainly spurred a lot of different designs over the years, but the hull of a sailboat today is designed almost independently of the keel.
In fact, if you look at a particular make and model of sailboat, you’ll notice that the makers often offer it with a variety of keel options. For example, this new Jeanneau Sun Odyssey comes with either a full fin bulb keel, shallow draft bulb fin, or very shallow draft swing keel. Where older long keel designs had the keel included in the hull mold, today’s bolt-on fin keel designs allow the manufacturers more leeway in customizing a yacht to your specifications.
What you’re left with is a hull, and boat hulls take three basic forms.
- Displacement hull
- Semi-displacement hulls
- Planing hulls
Most times, the hull of a sailboat will be a displacement hull. To float, a boat must displace a volume of water equal in weight to that of the yacht. This is Archimedes Principle , and it’s how displacement hulled boats get their name.
The displacement hull sailboat has dominated the Maritimes for thousands of years. It has only been in the last century that other designs have caught on, thanks to advances in engine technologies. In short, sailboats and sail-powered ships are nearly always displacement cruisers because they lack the power to do anything else.
A displacement hull rides low in the water and continuously displaces its weight in water. That means that all of that water must be pushed out of the vessel’s way, and this creates some operating limitations. As it pushes the water, water is built up ahead of the boat in a bow wave. This wave creates a trough along the side of the boat, and the wave goes up again at the stern. The distance between the two waves is a limiting factor because the wave trough between them creates a suction.
This suction pulls the boat down and creates drag as the vessel moves through the water. So in effect, no matter how much power is applied to a displacement hulled vessel, it cannot go faster than a certain speed. That speed is referred to as the hull speed, and it’s a factor of a boat’s length and width.
For an average 38 foot sailboat, the hull speed is around 8.3 knots. This is why shipping companies competed to have the fastest ship for many years by building larger and larger ships.
While they might sound old-school and boring, displacement hulls are very efficient because they require very little power—and therefore very little fuel—to get them up to hull speed. This is one reason enormous container ships operate so efficiently.

Of course, living in the 21st century, you undoubtedly have seen boats go faster than their hull speed. Going faster is simply a matter of defeating the bow wave in one way or another.
One way is to build the boat so that it can step up onto and ride the bow wave like a surfer. This is basically what a semi-displacement hull does. With enough power, this type of boat can surf its bow wave, break the suction it creates and beat its displacement hull speed.
With even more power, a boat can leave its bow wave in the dust and zoom past it. This requires the boat’s bottom to channel water away and sit on the surface. Once it is out of the water, any speed is achievable with enough power.
But it takes enormous amounts of power to get a boat on plane, so planing hulls are hardly efficient. But they are fast. Speedboats are planing hulls, so if you require speed, go ahead and research the cost of a speedboat .
The most stable and forgiving planing hull designs have a deep v hull. A very shallow draft, flat bottomed boat can plane too, but it provides an unforgiving and rough ride in any sort of chop.

If you compare the shapes of the sailboats of today with the cruising boat designs of the 1960s and 70s, you’ll notice that quite a lot has changed in the last 50-plus years. Of course, the old designs are still popular among sailors, but it’s not easy to find a boat like that being built today.
Today’s boats are sleeker. They have wide transoms and flat bottoms. They’re more likely to support fin keels and spade rudders. Rigs have also changed, with the fractional sloop being the preferred setup for most modern production boats.
Why have boats changed so much? And why did boats look so different back then?
One reason was the racing standards of the day. Boats in the 1960s were built to the IOR (International Offshore Rule). Since many owners raced their boats, the IOR handicaps standardized things to make fair play between different makes and models on the racecourse.
The IOR rule book was dense and complicated. But as manufacturers started building yachts, or as they looked at the competition and tried to do better, they all took a basic form. The IOR rule wasn’t the only one around . There were also the Universal Rule, International Rule, Yacht Racing Association Rul, Bermuda Rule, and a slew of others.
Part of this similarity was the rule, and part of it was simply the collective knowledge and tradition of yacht building. But at that time, there was much less distance between the yachts you could buy from the manufacturers and those setting off on long-distance races.
Today, those wishing to compete in serious racing a building boat’s purpose-built for the task. As a result, one-design racing is now more popular. And similarly, pleasure boats designed for leisurely coastal and offshore hops are likewise built for the task at hand. No longer are the lines blurred between the two, and no longer are one set of sailors “making do” with the requirements set by the other set.
Modern Features of Sailboat Hull Design
So, what exactly sets today’s cruising and liveaboard boats apart from those built-in decades past?
Today’s designs usually feature plumb bows and the maximum beam carried to the aft end. The broad transom allows for a walk-through swim platform and sometimes even storage for the dinghy in a “garage.”
The other significant advantage of this layout is that it maximizes waterline length, which makes a faster boat. Unfortunately, while the boats of yesteryear might have had lovely graceful overhangs, their waterline lengths are generally no match for newer boats.
The wide beam carried aft also provides an enormous amount of living space. The surface area of modern cockpits is nothing short of astounding when it comes to living and entertaining.
If you look at the hull lines or can catch a glimpse of these boats out of the water, you’ll notice their underwater profiles are radically different too. It’s hard to find a full keel design boat today. Instead, fin keels dominate, along with high aspect ratio spade rudders.
The flat bottom boats of today mean a more stable boat that rides flatter. These boats can really move without heeling over like past designs. Additionally, their designs make it possible in some cases for these boats to surf their bow waves, meaning that with enough power, they can easily achieve and sometimes exceed—at least for short bursts—their hull speeds. Many of these features have been found on race boats for decades.
There are downsides to these designs, of course. The flat bottom boats often tend to pound when sailing upwind , but most sailors like the extra speed when heading downwind.

How Do You Make a Stable Hull
Ultimately, the job of a sailboat hull is to keep the boat afloat and create stability. These are the fundamentals of a seaworthy vessel.
There are two types of stability that a design addresses . The first is the initial stability, which is how resistant to heeling the design is. For example, compare a classic, narrow-beamed monohull and a wide catamaran for a moment. The monohull has very little initial stability because it heels over in even light winds. That doesn’t mean it tips over, but it is relatively easy to make heel.
A catamaran, on the other hand, has very high initial stability. It resists the heel and remains level. Designers call this type of stability form stability.
There is also secondary stability, or ultimate stability. This is how resistant the boat is to a total capsize. Monohull sailboats have an immense amount of ballast low in their keels, which means they have very high ultimate stability. A narrow monohull has low form stability but very high ultimate stability. A sailor would likely describe this boat as “tender,” but they would never doubt its ability to right itself after a knock-down or capsize.
On the other hand, the catamaran has extremely high form stability, but once the boat heels, it has little ultimate stability. In other words, beyond a certain point, there is nothing to prevent it from capsizing.
Both catamarans and modern monohulls’ hull shapes use their beams to reduce the amount of ballast and weight . A lighter boat can sail fast, but to make it more stable, naval architects increase the beam to increase the form stability.
If you’d like to know more about how stable a hull is, you’ll want to learn about the Gz Curve , which is the mathematical calculation you can make based on a hull’s form and ultimate stabilities.
How does a lowly sailor make heads or tails out of this? You don’t have to be a naval architect when comparing different designs to understand the basics. Two ratios can help you predict how stable a design will be .
The first is the displacement to length ratio . The formula to calculate it is D / (0.01L)^3 , where D is displacement in tons and L is waterline length in feet. But most sailboat specifications, like those found on sailboatdata.com , list the D/L Ratio.
This ratio helps understand how heavy a boat is for its length. Heavier boats must move more water to make way, so a heavy boat is more likely to be slower. But, for the ocean-going cruiser, a heavy boat means a stable boat that requires much force to jostle or toss about. A light displacement boat might pound in a seaway, and a heavy one is likely to provide a softer ride.
The second ratio of interest is the sail area to displacement ratio. To calculate, take SA / (D)^0.67 , where SA is the sail area in square feet and D is displacement in cubic feet. Again, many online sites provide the ratio calculated for specific makes and models.
This ratio tells you how much power a boat has. A lower ratio means that the boat doesn’t have much power to move its weight, while a bigger number means it has more “get up and go.” Of course, if you really want to sail fast, you’d want the boat to have a low displacement/length and a high sail area/displacement.
Multihull Sailboat Hulls
Multihull sailboats are more popular than ever before. While many people quote catamaran speed as their primary interest, the fact is that multihulls have a lot to offer cruising and traveling boaters. These vessels are not limited to coastal cruising, as was once believed. Most sizable cats and trimarans are ocean certified.
Both catamarans and trimaran hull designs allow for fast sailing. Their wide beam allows them to sail flat while having extreme form stability.

Catamarans have two hulls connected by a large bridge deck. The best part for cruisers is that their big surface area is full of living space. The bridge deck usually features large, open cockpits with connecting salons. Wrap around windows let in tons of light and fresh air.
Trimarans are basically monohulls with an outrigger hull on each side. Their designs are generally less spacious than catamarans, but they sail even faster. In addition, the outer hulls eliminate the need for heavy ballast, significantly reducing the wetted area of the hulls.
Boaters and cruising sailors don’t need to be experts in yacht design, but having a rough understanding of the basics can help you pick the right boat. Boat design is a series of compromises, and knowing the ones that designers and builders take will help you understand what the boat is for and how it should be used.
What is the most efficient boat hull design?
The most efficient hull design is the displacement hull. This type of boat sits low in the water and pushes the water out of its way. It is limited to its designed hull speed, a factor of its length. But cruising at hull speed or less requires very little energy and can be done very efficiently.
By way of example, most sailboats have very small engines. A typical 40-foot sailboat has a 50 horsepower motor that burns around one gallon of diesel every hour. In contrast, a 40-foot planing speedboat may have 1,000 horsepower (or more). Its multiple motors would likely be consuming more than 100 gallons per hour (or more). Using these rough numbers, the sailboat achieves about 8 miles per gallon, while the speedboat gets around 2 mpg.
What are sail boat hulls made of?
Nearly all modern sailboats are made of fiberglass.
Traditionally, boats were made of wood, and many traditional vessels still are today. There are also metal boats made of steel or aluminum, but these designs are less common. Metal boats are more common in expedition yachts or those used in high-latitude sailing.
Matt has been boating around Florida for over 25 years in everything from small powerboats to large cruising catamarans. He currently lives aboard a 38-foot Cabo Rico sailboat with his wife Lucy and adventure dog Chelsea. Together, they cruise between winters in The Bahamas and summers in the Chesapeake Bay.
- Bahasa Indonesia
- Slovenščina
- Science & Tech
- Russian Kitchen
Check out Moscow’s NEW electric river trams (PHOTOS)

Water transportation has become another sector for the eco-friendly improvements the Moscow government is implementing. And it means business. On July 15, 2021, on the dock of Moscow’s ‘Zaryadye’ park, mayor Sergey Sobyanin was shown the first model of the upcoming river cruise boat.

The model of the electrical boat with panoramic windows measures 22 meters in length. The river tram - as Muscovites call them - has a passenger capacity of 42, including two disabled seats. The trams will also get cutting edge info panels, USB docking stations, Wi-Fi, spaces for scooters and bicycles, as well as chairs and desks for working on the go. The boats will be available all year round, according to ‘Mosgortrans’, the regional transport agency.

Passengers will be able to pay with their ‘Troika’ public transport card, credit cards or bank cards.
The main clientele targeted are people living in Moscow’s river districts - the upcoming trams will shorten their travel time in comparison to buses and other transportation by five times, Mosgortrans stated.

As the river trams are being rolled out, Moscow docks will also see mini-stations, some of which will also be outfitted with charging docks for speed-charging the boats.

Moscow is set to announce the start of the tender for construction and supply in September 2021. The first trams are scheduled to launch in June 2022 on two routes - from Kievskaya Station, through Moscow City, into Fili; and from ZIL to Pechatniki.

“Two full-scale routes will be created in 2022-2023, serviced by 20 river trams and a number of river stations. We’ll continue to develop them further if they prove to be popular with the citizens,” the Moscow mayor said .
If using any of Russia Beyond's content, partly or in full, always provide an active hyperlink to the original material.
to our newsletter!
Get the week's best stories straight to your inbox
- Face it: Moscow Metro to introduce FACIAL payment technology
- What does Moscow smell like?
- Riding Moscow’s train of tomorrow (PHOTOS)
This website uses cookies. Click here to find out more.
Download Thrillophilia App
Book Tour and Activities on the Go!

- Things to do
- Moscow Boat Tour, Book Now @ Flat 14% Off
- Moscow Boat Tour
Moscow Boat Tour Includes
Moscow boat tour overview.
Want to explore the iconic Moscow city from a different perspective? Go for this thrilling Moscow sightseeing river cruise and enjoy an unforgettable experience on a modern and comfortable yacht. Sail across the stunning Moskva River, and have a pleasurable time with your loved ones through savoring delicious food, appreciating historical views of the city, and relaxing in a cozy ambiance on board.
What To Expect from Moscow boat tour
Enjoy a relaxing cruise through the pristine Moskva River Join this exciting Moscow boat tour and spend a pleasurable time onboard a luxury yacht with your loved ones while enjoying a relaxing sail and appreciating the panoramic views of the city's skyline and landmarks.
Be amazed by the panoramic views of the city The Moscow River boat tours offer the best ways to witness the elegance of the city from the waters either in daylight or in the evening time when the city dazzles with the illuminated LED lights. You can see the stunning views of the city's skyline from either the observation decks or from the huge glass windows.
Witness main landmarks from the water During the boat trip Moscow River you will pass through the city’s main architectural sites like Vorobyovy Hills, Kremlin, the Cathedral of Christ the Saviour, Peter the Great Statue, the Saint Basil's Cathedral, the Vodootvodny Canal and many more.
Join us for premium services Join this exciting Moscow sightseeing river cruise through us to have a memorable sail experience onboard a modern yacht along with excellent service, delightful cuisine, pleasant ambiance, and unforgettable views.
Know Before You Go
Ticket Variants: Depart from Gorky Park Pier Depart from Pier Hotel Radisson Royal Hotel
Meeting Point : Hotel Radisson Royal Hotel Pier or Gorky Park Pier Meeting Time: Please be at the meeting point 20 minutes before the scheduled departure time
Cruise Departure Time : 1:00 pm, 3:00 pm, 5:00 pm, 7:00 pm, and 9:00 pm
Address: Hotel Radisson Royal Hotel Pier, 2/1 Kutuzovskiy Avenue Bld. 1, Moscow, Russia-121248 Gorky Park Pier, Krymsky Val, 9, Moscow, Russia-119049 Getting There: Both locations are easily accessible through metro, taxi, or car
Itineraries of the Moskva River Cruise:
Depart from Pier Hotel Radisson Royal Hotel Pier Hotel Radisson Royal Hotel House of Government Moscow Mayor`s office Kievsky railway station Novodevichy Convent Moscow State University Luzhniki Stadium Vorobyevy (Sparrow) Hills Nyeskuchniy Garden Gorky Central Park of Culture and Leisure Krymsky Bridge (Crimean Bridge) Cathedral of Christ the Saviour Moscow Kremlin St. Basil’s Cathedral Skyscraper on Kotelnicheskaya Embankment Pier Hotel Radisson Royal Hotel
Depart from Gorky Park Pier Gorky Park Pier Krymsky Bridge (Crimean Bridge) Peter the Great monument Cathedral of Christ the Saviour Moscow Kremlin St. Basil’s Cathedral – Ustinsky Bridge Skyscraper on Kotelnicheskaya Embankment Krasnokholmsky bridge Gorky Central Park of Culture and Leisure Vorobyevy (Sparrow) Hills Kievsky railway station Ukraina Hotel Gorky Park Pier
Child Age is between the age 6 to 12 years old
Insider Tips: You can have more alcoholic drinks at your own expense The enclosed area is a no-smoking zone, whereas, you can smoke in the open area of observation decks The tour is wheelchair and stroller accessible Children under 5 years may join the tour for free with a paying adult
Other Inclusions
- 2-hour cruise along the Moscow River
Things To Carry
- Thrillophilia Voucher
- Valid ID Proof
- Please carry your passport or a valid ID proof for verification
- Dress code is smart casual and closed-toe shoes
- This is a group tour
Moscow Boat Tour: Cancellation Policy
- Free cancellation up to 24 hours before activity starts
Moscow Boat Tour: Refund Policy
- The applicable refund amount will be processed within 15 business days
- All applicable refunds will be done in traveller's thrillophilia wallet as Thrillcash
Moscow Boat Tour: Booking Confirmation Policy
- The customer receives a confirmation voucher via email within 24 hours of successful booking
- In case the preferred slots are unavailable, an alternate schedule of the customer’s preference will be arranged and a new confirmation voucher will be sent via email.
- Alternatively, the customer may choose to cancel their booking before confirmation and a full refund will be processed.
Write Your Story
Why Thrillophilia
Verified Reviews
25000+ Pictures and Reviews on the platform.
Best Price Guarantee
We have a best price guarantee. If you get the same product anywhere else at a cheaper price and you inform us about the same on the same day of your booking, we will refund the difference of cost to you.
10000+ Tours and Activities
We have activities across 17 countries, across every category so that you never miss best things to do anywhere.
Customer Delight
We are always able to support you so that you have a hassle free experience.

Message Supplier
Recommended Tours

6 Days / 5 Nights Moscow Tour, Russia
d 6 Days n 5 Nights

Women Only Tour to Russia, 2023
107065
d 8 Days n 7 Nights
More Things to do in Moscow
- Tours in Moscow
Superb Choice!
We assure the privacy of your contact data. This data will only be used by our team to contact you and no other purposes.

Thrillophilia
Experience 2500+ Tours
And Activities from 1200+ Suppliers
Subscribe To Newsletter
Subscribe our newsletter to recieve Latest deals, Offers and Packages in your inbox

Sign up with Your Facebook Account
Or use your Email
Exclusive Offers
Deals, Based on your interests
Hassle free Cancellation
Dont you have an Account?
Make sure you share the following:
- Tell Supplier name a little about yourself
- Include your prefered date
- Approximate no of travelers
Please specify the Travel date & Number of Travelers
Do you have an account?

- Thrillophilia Reviews
- Terms and Conditions
- Privacy Policy
- Copyright Policies
- We are Hiring
- Gift an Experience
Recent Blog Posts
- 60 Places You Need To Visit In India With Your Best Friend
- 50 Best Honeymoon Destinations In India
- 51 Places To Visit In India Before You Turn 30
- 50 Countries Where Getting A Visa Is Easier Than Ordering A Pizza
- GoPro Passport Program
- List Your Activities
- Advertise with us
Travel Agents
- Signup as Agent
- Agent Login
© 2024 Thrillophilia.com All rights reserved
Home News Highlights Best of the Week Alert reporting reveals a new European migration tactic — packed luxury sailboats landing in Italy
Best of the Week
Alert reporting reveals a new European migration tactic — packed luxury sailboats landing in Italy
Sailboats used by smugglers to transport migrants are beached on Le Cannelle beach at Isola Capo Rizzuto in the Calabria region of southern Italy, Nov. 13, 2021. Thousands of refugees have arrived in Italy this fall by a lesser-known Calabrian route from Turkey, paying heftier smuggling fees to travel below deck on crammed luxury sailboats that can be less conspicuous than the inflatable boats used in the Central Mediterranean. (AP Photo / Alessandra Tarantino)

By Patricia Thomas and Alessandra Tarantino
Rome producer Trisha Thomas, who has covered migration in Italy for more than two decades, spotted reports about an unusual increase of arrivals in Calabria, a southern region that had not previously been a main destination point for smugglers bringing people into Europe by boat from Africa or Turkey.
Thomas called the mayor and the head of the local Red Cross, who spoke of being overwhelmed by the influx. Then came a curious detail in Italian Coast Guard handout video: Instead of flimsy rubber rafts or wooden boats, Thomas spotted clips of sleek sailboats. Aid workers call these “1st class” crossings but there is nothing elite about them; 100 people may be packed below deck with meager food and water.
When Thomas called around,she found multiple examples of sailboats smuggling migrants all the way from Turkey,leading to a four-fold surge in sea arrivals at Calabria. She traveled to the southern region with photographer Alessandra Tarantino to learn more. There,they delivered all-formats spot coverage of two arrivals,then kept reporting on this new method of crossing the Mediterranean. Among the discoveries was the economics: A single trip on a stolen sailboat netted smugglers nearly a million dollars.
Speaking to new arrivals in local shelters,Thomas obtained user-generated video of migrants arriving on a Calabrian beach aboard a sailboat. She combined that footage with interviews of migrants, coast guard video and Tarantino’s drone shots of stranded sailboats to build a powerful video story used by more than 160 channels.

The text and photos also drew widespread play, including on major European news portal Euronews . A UK reporter told Thomas he was asked by his editors to match the AP story,but decided against sending a photographer because they couldn’t improve upon Tarantino’s images.
Dozens of reporters across Europe cover migration exclusively,but it took Thomas’ years of experience and Tarantino’s matchless visuals to score the beat in all formats.
For alert,resourceful coverage that reveals a new aspect of European migration and the startling economics behind it, Thomas and Tarantino receive AP’s Best of the Week — Second Winner award.
Visit AP.org to request a trial subscription to AP’s video,photo and text services. For breaking news, visit apnews.com

Submission Links
By The Associated Press
Dec. 3, 2021
Explore related services
Access the worlds stories at your fingertips
Related articles

A leaked trove of documents opens a rare window into Chinese hacking practices
Mar. 1, 2024

Cole captures Olympics’ impact on island life in Tahiti in stunning visuals

Persistence leads to riveting story on missing and murdered Indigenous people
- Breaking news
- Business and finance
- Entertainment
- Religion and faith
- AP Newsroom
- AP Stylebook
- AP StoryShare
- Live & location
- AP Productions
- Branded content and advertising
- Workflow Solutions
- AP’s local news AI initiative
- Metadata services
- AP Daybooks
- How AP counts the vote
- How we declare winners
- AP VoteCast: how we survey the electorate
- By industry
- Awards and recognition
- Media center
- News values
- Supporting AP
- Corporate Archives
- AP Customer Zone
- Join Newsletter & Get 10% Off Your First Order

Join / Login
Model ship clubs of the usa.
- Updated on: 24th January 2021
- Written by Gary Renshaw
Model Ship building is a craft that has been around since water transport first began. Every boat ever built has a unique story to tell. The model ship clubs of the United States have an important part to play in continuing the skills and tradition of the art of model ship building. Here we have compiled a list of the model ships clubs that are situated across the United States.
California Model Ship Clubs
Ship modelers association.
The Ship Modelers Association (SMA) is the largest ship modeling club in California, and one of the largest in the nation. They seek to foster research and interest in the nautical heritage of the United States by researching and building scale ship models.
Sacramento Mo del Shipwrights
The Sacramento Model Shipwrights, are a club of radio-control model ship enthusiasts, who sail at the lake in Elk Grove Regional Park in Elk Grove, California. They are known for building civilian and military models, which are powered by electric motors, steam engines, or sail.
South Bay Model Shipwrights
The South Bay Model Shipwrights is a club to learn and share info on shipbuilding techniques using a variety of materials. Member’s projects include model ships from plastic and wood from commercial kits and scratch built vessels in resin and wood.
Club members have built ships ranging from 3’ to 56” in Over All length. Members have built vessels from all timeframes in human history. This includes rafts, Viking Ships, Galleons, Clipper Ships, Japanese and Chinese Sailing ships, Steam Ferry Boats, and modern era combat ships.
At club meetings they discuss maritime construction, current events, history, and archaeology.
Channel Islands Maritime Museum Ship Model Guild
The Channel Islands Maritime Museum sponsors a Ship Model Guild, an active club of local model builders, who meet once a month at the Museum. The public is welcome to the monthly meetings, third Tuesday of the month at 6:30 PM and all are welcome to join the Guild.
Learn Maritime history by building models of ships that made history. Techniques for wood, plastic or metal construction are addressed at the meetings. Every meeting is different as members discuss their progress during the “show and tell” sessions. Interesting bits of information are exchanged about the ships of adventure on the high seas.
Inland Nautical Society
Inland Nautical Society is a club for Radio Controlled Model Boaters. The club have beginners who have never built a model before, to the experienced modelers who have built museum quality models. The club has a reputation of friendly and knowledgeable members who are eager to share a wealth of their knowledge and expertise of radio controlled modeling.
San Diego Ship Modeler’s Guild
The San Diego Ship Modeler’s Guild welcomes people of all ages with an interest in preserving maritime history through the art of ship modeling. Membership ranges from new ship modelers to experienced master modelers. Ship model projects include period sailing ships through to contemporary steel navy.
Hyde Street Pier Model Shipwrights
The Hyde Street Pier Model Shipwrights are associated with the San Francisco Maritime National Historical Park, a unit of the National Park Service, and have a model shop aboard the historic ferryboat Eureka berthed at the Hyde Street Pier.
Anyone interested in model shipbuilding is welcome to attend their meetings. Members can offer advice and support on all stages of model shipbuilding, from selecting a kit for your first model to advanced layout and scratch building.
San Francisco Model Yacht Club
Colorado model ship clubs, rocky mountain shipwrights.
The Rocky Mountain Shipwrights group of model ship builders in Colorado dedicated to promoting, developing, and furthering scale model shipbuilding. With about 50 members, building many types and sizes of model ships – from Egyptian barges to WWII destroyers, ships in bottles to all-paper models, miniature liners to four-foot men of war. Several members and their creations have won national and regional awards, and some have built models now on display at maritime museums nationwide.
But they are not all expert modelers. Some members are working on their first models. They get advice and encouragement from those who are more experienced, and the goal is for everyone to enjoy the hobby of building model ships and to get the satisfaction of completing and displaying their work.
Connecticut Model Ship Clubs
Connecticut marine model society.
Connecticut Marine Model Society are a group of enthusiastic ship model builders from Connecticut. They meet on the second Saturday of the month from September to June in West Haven, Ct. They build models from scratch or from kits; both wood and plastic. The subjects range from wooden sailing ship to present day ships of steel.
Florida Model Ship Clubs
Southwest florida shipmodeler’s guild.
The Southwest Florida Shipmodeler’s Guild purpose is to provide and promote a forum from which its members can share their model ship building knowledge, skills and techniques, personal experiences, nautical history and any other related maritime interests that might benefit its membership. Their goal is to learn and grow in competence in pursuing the construction of ship models in an atmosphere of constructive fellowship, assistance, and active participation.
Their members come from all walks of life and represent all levels of ship modeling skill from novice to expert. Meeting in a friendly and informal environment at the beautiful Fort Myers Riverside Community Center.
Tampa Bay Ship Model Society
The Tampa Bay Ship Model Society brings together model ship builders, both newcomers and veteran builders, for the mutual benefit of expanding their knowledge of ships, research, techniques, and further develop their abilities in all areas relevant to ship model building and maritime history.
Members model in all materials; wood, metal, paper and polymers, from plans only, or commercial kits, vessels from every era and purpose; Exploration, Steel Navy, Submarines, Yachts, Tugs, Commercial, Fishing, Liners, Working Small Craft, Coast Guard, River/Paddle Wheel, Racing Power and Sail.
Georgia Model Ship Clubs
Atlanta model shipwrights.
Atlanta Model Shipwrights aim to educate and promote model shipbuilding through fellowship mentoring and instruction in a non-competitive environment. Meetings are held the second Saturday of each month from 10:00 AM to 12:00 PM.
Illinois Model Ship Clubs
The north shore deadeyes.
The North Shore Deadeyes primarily focused on static scale ship models with an emphasis on the Great Age of Sail, but builders of models from all eras and at all levels of skill welcome.
Midwest Model Shipwrights
The Midwest Model Shipwrights was formed in 1982 by individuals who had a common interest in model ship building and maritime history. Goals of the club are to discuss and share modeling ideas and concepts while making new friends.
Vessels built by the Shipwrights represent a variety of types and eras. Sizes range from miniatures a few inches in length to radio control warships over five feet long, and from basic to amazingly complex. Their membership includes beginning through to advanced modelers, some of whose works can be found in museums, galleries and private collections.
In spite of all these accomplishments, the organization’s primary focus remains the interaction between expert, intermediate and novice.
Indiana Model Ship Clubs
Admirals of indianapolis.
Admirals of Indianapolis club’s members build and operate scale merchant ships, pleasure craft, work boats, military ships, sailboats, and just about anything that floats or submerges (in the case of submarine models). Many boats are built from kits and some are scratch-built from plans and photographs. The models are powered by electric motors, steam engines, or wind power in the case of sailboats.
Kansas Model Ship Clubs
Kansas city square riggers modeling association.
The Kansas City Square Riggers Club are a model ship-building enthusiasts club based out of the greater Kansas City area. They welcome builders of all skill levels and interests. If you are into naval research and model building they would love to hear from you.
Massachusetts Model Ship Clubs
Uss constitution model shipwright guild.
The USS Constitution Model Shipwright Guild is the largest model ship association on the East Coast. Meetings overlooking Old Ironsides at the USS Constitution Museum are well attended. In addition to monthly meetings, the Guild takes part in the annual meeting of model clubs from Connecticut, Massachusetts, New York, New Jersey, and Pennsylvania. They also attend the annual Salem Maritime Festival and the Antique & Classic Boat Festival, as well as the biennial Woods Hole Model Boat Show.
Novices and experienced model builders alike can have fun developing resources, experiences, and skills by joining us. SS Constitution Model Shipwright Guild
U.S. Vintage Model Yacht Group
The US Vintage Model Yacht Group is a Special Interest Group of the American Model Yachting Association. Their organizational goals are the preservation, building, and sailing of older model yacht designs and the study of the history of the sport of model yachting.
“Vintage” primarily means any older model sailboats no longer sailed (or never raced) in serious competition. These encompass free-sailing model yachts, older designs converted to R/C and pre-1970s R/C sailing models. This includes class racing yachts, non-class sailing models, and commercially-built toys of the past. There are also replica models built to the older designs and new designs recreating older sailboat styles.
The group also support those who sail traditional sailing craft models, such as Schooners, Skipjacks, and other scale models. The hulls are generally made of wood, with some fiberglass models, and range in length from 1 to 6 ft. The rigs are usually constructed from wood or aluminum, with cotton or dacron sails.
Marine Modelers Club of New England
The Marine Modelers Club of New England have about 50 members, based in the greater Boston area. They meet monthly, usually pond-side, when the weather allows it. Meetings are rather informal, with little time spent on business, and lots of time talking about RC boats.
Their members are a creative bunch, and there is usually an interesting array of models at gatherings. Their modelers are a creative bunch and there is usually an interesting array of models at their gatherings. Their interests include tugboats, warships, pleasure craft, sailboats (both scale and racing) and pond sailors.
Merrimack Valley Ship Model Club
The Merrimack Valley Ship Model Club are an enthusiastic and friendly group of model ship makers who share a particular interest in the naval history of Newburyport, and the Merrimack River Valley area.
Maryland Model Ship Clubs
CBMM’s volunteer Maritime Model Guild supports the curatorial needs of CBMM with exhibition models and building kits that are available for purchase online and at the Museum Store. In addition, the Guild offers classes for building scratch models, and the annual Maritime Model Expo featuring “live” steamboat models, skipjacks with working sails, speedboats, tugs, and other radio-controlled miniatures.
The group also hosts children’s model-making activities at CBMM’s signature events and other outreach and educational programs throughout the year.
Washington Ship Model Society
The Washington Ship Model Society (WSMS) was founded in 1929 and is the oldest continuously active ship model club in the United States. The organization is composed of active ship model enthusiasts from the Greater Washington, DC, Metropolitan Area. Its purpose is to provide a socially enjoyable means for serious ship modelers to meet, share, and expand upon their common avocation through the exchange of ideas and knowledge.
The society draws its members from all walks of life and many different occupations. The modelers’ skills range from absolute beginners to professionals who have constructed models for maritime exhibits in the Smithsonian Institution and other museums throughout the United States and Europe. Over the years, members have written numerous articles for nautical research and ship model publications. Society membership has included such notables as President Franklin D. Roosevelt, then Major (and later General) George Patton, Howard I. Chappelle, and Paul E. Garber.
The interests of the modelers are as varied as their occupations, ranging from 17th-century sailing vessels to radio-controlled models of modern powered craft. All types of ship models have been constructed, in static display and operating versions, and in wood, brass, plastic, and card media.
The society conducts monthly meetings, alternating between Virginia and Maryland locations. The meeting format consists of brief society business, informal discussions of members’ model projects and a program or presentation relating to a nautical or ship modeling topic. Society members also form subgroups to focus on common modeling interests, such as steel (modern) ship modeling or plank-on-frame modeling. Subgroups are open to all members and meet on a periodic basis, generally in members’ homes. The club’s newsletter, the Lynx , is published monthly.
Maine Model Ship Clubs
Down east ship modelers guild.
The Down East Ship Modelers Guild is an active group of static and R/C modelers, ranging from novice to experienced. They meet on the second Thursday of each month from 1 pm – 3 pm at the Legion Hall in Bath, Maine. The group has a long history of association with the Maine Maritime Museum , also in Bath, ME.
Michigan Model Ship Clubs
Great lakes nautical society.
The Great Lakes Nautical Society is a club consisting of model shipbuilders, who are interested in persevering Great Lakes history through model ship building, the model ship shows and educational seminars put on by the club members. The club is open to anyone with an interest in model shipbuilding and the Great Lakes.
Minnesota Model Ship Clubs
The state of Minnesota currently has no model ship clubs listed.
Missouri Model Ship Clubs
St. louis admirals model boat club.
The St. Louis Admirals R/C Model Boat Club is a group of hobbyists dedicated to sharing the knowledge and fun of the R/C model boat hobby. The depth and breadth of experience the club offers, combined with its laid-back atmosphere, attract the beginner modeler and master builders alike.
Nevada Model Ship Clubs
The state of Nevada currently has no model ship clubs listed.
New Hampshire Model Ship Clubs
Their members are a creative bunch, and there is usually an interesting array of models at gatherings. Their modelers are a creative bunch and there is usually an interesting array of model at their gatherings. Their interests include tugboats, warships, pleasure craft, sailboats (both scale and racing) and pond sailors.
New Jersey Model Ship Clubs
The ship model society of new jersey.
The Ship Model Society of New Jersey is dedicated to the pursuit and enjoyment of ship model building in all its forms. They welcome those who enjoy or would like to learn more about this fascinating hobby. Membership spans all skill levels, from novice or highly accomplished and from gadget guru to historical recreator. Meetings aim to share collective wisdom and resources, and provide the opportunity to enjoy the company of other modelers.
South Orange Seaport Society
South Orange Seaport Society is a group of folks of all ages who like model boating. They have boats from kits and scratch builds, electric and steam-driven, quite a few fun electric race boats, and some eccentric things. A group of people from all walks of life who like RC boating.
New Mexico Model Ship Clubs
The state of New Mexico currently has no model ship clubs listed.
New York Model Ship Clubs
Buffalo model boat club.
Radio Controlled model boating is a fascinating hobby that can be as simple or as complex as one wants and can be enjoyed by all age groups. There are as many types of model boats as there are full sizes: enough to satisfy all tastes and interests. Those who enjoy the excitement of speed will find plenty of thrills and competition in the fast electric field. Sailing enthusiasts will find that the racing of radio-controlled sailboats offers all the challenge and exhilaration of the full-sized yachts. Builders of exact scale models get the added satisfaction of operating their craft under full radio control.
The Model Shipwright Guild of Western New York
Upon a chance introduction at the Military History Society of Rochester New York in 2015 several like-minded individuals, working through the Nautical Research Guild, were able to form our group. They quickly realized they were an enthusiastic collection of ship modelers and researchers interested in the history and preservation of our maritime legacy in the age of sail and more.
The Model Shipwright Guild of Western New York brings together members from near and far; Rochester NY, Syracuse NY, Buffalo NY and even Lisbon Portugal. From all walks of life, experience, endeavours with varied nautical interests making for a very dynamic group.
They draw in subject matter experts to enlighten the club meetings on the historical nature of the naval and maritime craft, and their accurate modeling.
Empire State Model Mariners
The Empire State Model Mariners club was founded in 1988, by a group of model boat enthusiasts. The club is a non-profit organization aimed at recreational RC boating and building, with emphasis placed on helping each other and welcoming new members.
We welcome all classes of modelers, from beginners to experts. Boats can be ready to runs, semi kits, kits and scratch built. Whatever your passion is, pleasure crafts, speedboats, workboats, fishing vessels or military replicas.
North Carolina Model Ship Clubs
Carolina maritime society.
The Carolina Maritime Model Society exists to promote the production of high-quality ship models and encourage members and the public to participate in this craft that is as old as shipbuilding itself.
The society is the only such organization in the entire state and has become a major vehicle for widening public interest in North Carolina’s maritime history and culture.
Ohio Model Ship Clubs
Shipwrights of ohio.
The Shipwrights of Ohio is a club dedicated to model shipbuilding. All types of ships and boats: sailing to steel navy, wood, resin, plastic, kits to scratch built, static to radio control. for all ages – young to retirees, and all skill levels – beginner to expert. Members share their skills, ideas and expertise.
The Shipwrights of Ohio were founded in 2004. Its purpose is to provide a socially enjoyable means for serious and not-so-serious ship modelers to meet, share, and expand their common avocation through the exchange of ideas and skill knowledge. Skills range from beginners to those who build museum quality models.
Oklahoma Model Ship Clubs
The state of Oklahoma currently has no model ship clubs listed.
Oregon Model Ship Clubs
The state of Oregon currently has no model ship clubs listed.
Pennsylvania Model Ship Clubs
Philadelphia ship model society.
The Ship Model Shack is the home of the Philadelphia Ship Model Society , the oldest ship modeling society in America. The Museum is home to over 50 ship models, but this is the only place to see them being created right before your eyes. Have a seat, and watch a model come together while talking with the modelers.
Rhode Island Model Ship Clubs
Tennessee model ship clubs.
The state of Tennessee currently has no model ship clubs listed.
Texas Model Ship Clubs
Gulf coast ship modelers society.
The Gulf Coast Ship Model Society is a welcoming group of amateur and professional ship modelers who enjoy sharing their work and discussing tips and tricks of the trade.
Meetings are held on the second Saturday every odd month from 10:00am – 1:00pm at the Houston Maritime Museum. Members are encouraged to bring models they are working on for a ‘show & tell’ discussion.
Utah Model Ship Clubs
Utah State currently has no model ship clubs listed.
Virginia Model Ship Clubs
The Washington Ship Model Society (WSMS) was founded in 1929 and is the oldest continuously active ship model club in the United States. The organization is composed of active ship model enthusiasts from the Greater Washington, DC, Metropolitan Area. Its purpose is to provide a socially enjoyable means for serious shipmodelers to meet, share, and expand upon their common avocation through the exchange of ideas and knowledge.
The society draws its membership from all walks of life and many different occupations. The modelers’ skills range from absolute beginners to professionals who have constructed models for maritime exhibits in the Smithsonian Institution and other museums throughout the United States and Europe. Over the years, members have written numerous articles for nautical research and ship model publications. Society membership has included such notables as President Franklin D. Roosevelt, then Major (and later General) George Patton, Howard I. Chappelle, and Paul E. Garber.
The interests of the modelers are as varied as their occupations, ranging from 17th century sailing vessels to radio-controlled models of modern powered craft. All types of ship models have been constructed, in static display and operating versions, and in wood, brass, plastic, and card media.
The society conducts monthly meetings, alternating between Virginia and Maryland locations. The meeting format consists of brief society business, informal discussions of members’ model projects and a program or presentation relating to a nautical or ship modeling topic. Society members also form subgroups to focus on common modeling interests, such as steel (modern) ship modeling or plank-on-frame modeling. Subgroups are open to all members and meet on a periodic basis, generally in members’ homes. The club’s newsletter, the Lynx , is published monthly.
Hampton Roads Ship Model Society
The Hampton Roads Ship Model Society, founded in 1967, is an association of individuals who are interested in pursuing the art of ship model building and the exploration of maritime history. The primary purpose of the society is to bring together persons interested in building quality ship models so that they may have the opportunity to exchange views and improve their skills. Members are people representing a wide range of ages who come from many varied occupations and backgrounds. Members come from as far north as the Northern Neck, as far west as western suburbs of Richmond and as far south as the border of North Carolina. Honorary members hail from such dispersed locations as Annapolis, Maryland and Toronto, Canada.
The interests of our members runs full spectrum, from the historical (photos and records), artistic (painting), decorative (pond yachts/half hulls), radio-controlled (RC) models, to highly detailed and historically accurate scale reproductions of all ship types. The skill level of members runs the full gamut from complete novices to highly skilled experts who have won top awards in highly regarded competitions both in the United States and abroad. Models built by past and present members of the Society can be found in many of our nation’s premier museums. Model builders of all skill levels are always welcome. The Society is dedicated to helping ship model builders new to the craft learn new skills while giving experienced builders the opportunity to perfect their abilities. Even the most highly-skilled members are always seeking to improve their techniques with the help and advice of other Society members.
Washington Model Ship Clubs
The state of Washington currently has no model ship clubs listed.
Wisconsin Model Ship Clubs
Wisconsin scale boating association.
The Wisconsin Scale Boating Association is about promoting and enjoying the model shipbuilding hobby.
They are a “scale” model club. Models are representative of an actual boat or type of boat, either static or operational. Radio-Controlled models attempt to recreate authentic operation and look like a full size boat.
The club participates in several events throughout the year. Membership is open to anyone who has an interest in the model boating hobby.
KNOW A MODEL SHIP CLUB NOT ON THIS LIST?
If you know of a model ship club that is not on this list of United States Model Ship Clubs please let us know here

Learn The Art Of Building A Model Ship
Get started in wooden model ship building today
Join 18,543 other modelers to hear about specials, new products and modeling tips
- Become a Member
- Modeling Hub
- Model Ship Building
- Maritime History
- Affiliate Program
Information
- Terms & Conditions
- Privacy Policy
Copyright © 2023 Modelers Central. ABN: 31 114 830 732
- Claim 10% Off First Order
- Get 5% off ALL orders with a Membership
- Gift Vouchers
- Help & Advice
Modelers Central. 2023, All rights reserved.

- Claim 10% Off Your First Order
- Get 5% Off All Orders With A Membership

Get 10% off
Your first order.
10% off applies only to full-price items. By providing your email address, you agree to our Terms & Privacy Policy

10% off applies only to full-price items. By providing your email address & mobile number, you agree to our Terms & Privacy Policy and consent to receive marketing messages from Modelers Central at the addresses provided. You can unsubscribe at any time by replying STOP.

IMAGES
COMMENTS
Modern sloops are generally made from carbon fiber, although traditionally this craft was built from wood like many other sailboats in the early 17 th and 18 th centuries. ... Sloop sailing vessels for sale on YachtWorld are listed for a swath of prices from $6,510 on the relatively moderate end all the way up to $3,948,518 for the most ...
A lively sailboat with a good turn of speed, the thoroughly modern sloop employed a Hall spar and rod-rigging, and was available with a fixed, 6' 4" fin keel or a keel-centerboard that drew 4' 2" with the board up and a deep 7' 8" with the board down. stock photo
To highlight how these boat design principles play out, Practical Sailor looks at classic sailboats such as the Bill Shaw-designed Pearson 32, Ericson 41, Valiant 40, and Peterson 44, and compares their keel/sail ratios and lead values to more modern sailboat designs such as the Catalina, Hunter, Tartan, and Beneteau. In the course of taking ...
For almost 20 years, we've called this awards program SAIL Best Boats, but this year, we're refining and renaming this program to better and more fairly represent the boats we've selected. Restricting boats to categories and labels—such as Best Cruising Monohull 30-40 feet and Best Performance Monohull 40-50 feet—doesn't bring our readers the full picture.
The mission of this modern classic sloop is to provide easy day-sailing to have fun with friends and family. ... a 65′ cold-molded modern classic sailboat, and resulted in a better final product. Part 6: Launching Anna. After two years of design, technology, and craftsmanship, Lyman-Morse launched the 65′ sloop Anna on brisk April afternoon
The 192-foot sailing superyacht 'Kokomo' is a massive charter sloop, ... This Boatmaker Builds 1960s-Inspired Cruisers With a Modern Twist. Here's How.
The sloop rig is commonly found in modern recreational sailboats due to its versatility, enabling sailors to enjoy cruising, racing, or day sailing with ease. Its streamlined design and sleek appearance on the water make it both aesthetically pleasing and efficient, capturing the essence of the sailing experience.
Hallberg-Rassy, Lagoon, Hanse, X-Yachts. > Most popular brands in the Caribbean 1500, 2008-2012: Jeanneau, Hallberg-Rassy, Hylas, Tayana, Beneteau, Island Packet, J/Boats, Amel, Lagoon, Catalina. Armchair admirals and chat-room bores may warn dolorously of lightweight structures failing in big seas and rigs crumpling at the merest hint of a ...
A sloop rigged sailboat refers to a popular type of sailing vessel with one mast and two sails - a mainsail located at the rear (aft) of the mast and a headsail at the front (forward). This configuration allows for efficient wind capture and provides great maneuverability in different wind conditions. 2) The Main Components:
Know-how: Modern Rigs 101. Peter Nielsen. Mar 5, 2020. This classic Sabre carries the kind of masthead rig typical of its era; note how the large genoa sheets outside the shrouds (left); This X-Yachts performance-cruiser provides an excellent example of a modern fractional rig; note the narrow headsail (right).
The sloop - or sloup - is a type of rigging with a single mast and a single jib . It is the most widely used rig on our modern pleasure yachts. He gradually replaced the cutter ( at least two jibs to discover here ) with the advent of the winch and reel. Indeed, with these manoeuvring aids, there is no need to split the sail area.
The 10 best bluewater boats. 1. Westsail 32. Photo credit: SailboatData.com. The Westsail 32 is one of the most iconic bluewater cruisers and 19 have set out to cross the Pacific in the PPJ rally since 2009. In 1973, this small cruising sailboat garnered a 4-page spread in Time magazine.
The interior of our modern classic sailboats can be made in different styles from matt varnished mahogany for a truly classic look or a classic styled white interior with mahogany or teak finish. But also light oak is possible or full teak wood, whatever your preference would be. ... The classic lines and looks are integrated in a modern ...
The most commonly used rig type on modern sailing boats is the fore-and-aft Bermuda Sloop rig with one mast and just one headsail. Closely follows the Cutter rig and the Ketch rig. They all have a relatively simple rigging layout. Still, there are several variations and differences in how they are set up.
14. Sail-Material Innovations. Modern sailboats continue to push the boundaries of speed and performance, thanks in large part to sail-material innovations. Sails are now crafted from laminated fabrics and exotic fibers that are not only capable of withstanding the punishment of the high seas but also offer enhanced performance.
Sloop: Sloops are the most common type of rig found on modern sailboats. They have a single mast with a mainsail and a single headsail, typically a genoa or jib. ... For day sailing, small sailboats such as sailing dinghies, day sailers, and pocket cruisers are ideal options. These boats usually range between 12 and 25 feet in length and offer ...
In contrast, heaving-to in a modern sloop is quite easily done with minimal effort. By using a headsail, mainsail and rudder, we have the ability to heave-to for hours or days if required. WHAT, WHY, WHEN? Simply put, heaving-to is a maneuver used to slow a sailboat's progress and calm its motion while at sea.
one mast. triangular mainsail (called a Bermuda sail) a foresail (also called the jib) fore-and-aft rigged. medium-sized (12 - 50 ft) Fore-and-aft rigged just means "from front to back". This type of rigging helps to sail upwind. Any sailboat with one mast and two sails could still be a sloop.
9. Creature Comforts. Water makers were once dubbed the least-reliable piece of equipment aboard, but no longer. Refrigeration, electric heads, advanced stereos with satellite radio, and air conditioning have also evolved to become reliable and commonplace on modern sailboats.
The displacement hull sailboat has dominated the Maritimes for thousands of years. It has only been in the last century that other designs have caught on, thanks to advances in engine technologies. In short, sailboats and sail-powered ships are nearly always displacement cruisers because they lack the power to do anything else.
Surprisingly, the luxurious boats are priced rather modestly, and a single ticket goes for $17-$32 (1,100-2,000 rubles); also expect a reasonable restaurant bill on top.
On July 15, 2021, on the dock of Moscow's 'Zaryadye' park, mayor Sergey Sobyanin was shown the first model of the upcoming river cruise boat. The model of the electrical boat with panoramic ...
Moscow Boat Tour. N N N N N 29 ratings 4.5. h 2 Hours l Moscow. Enjoy a relaxing cruise through the pristine Moskva River. Be amazed by the panoramic views of the city. Witness main landmarks from the water. Join us for premium services. Starting From 14% OFF. O1,420 O1,220 per adult.
Speaking to new arrivals in local shelters,Thomas obtained user-generated video of migrants arriving on a Calabrian beach aboard a sailboat. She combined that footage with interviews of migrants, coast guard video and Tarantino's drone shots of stranded sailboats to build a powerful video story used by more than 160 channels.
"Vintage" primarily means any older model sailboats no longer sailed (or never raced) in serious competition. These encompass free-sailing model yachts, older designs converted to R/C and pre-1970s R/C sailing models. This includes class racing yachts, non-class sailing models, and commercially-built toys of the past.