Sail area calculations
Mainsail Area = P x E / 2 Headsail Area = (Luff x LP) / 2 (LP = shortest distance between clew and Luff) Genoa Area 150% = ( 1.5 x J x I ) / 2 Genoa Area 135% = ( 1.35 x J x I ) / 2 Fore-triangle 100% = ( I x J ) / 2 Spinnaker Area = 1.8 x J x I
Copyright � 2008 Sailboat Rig Dimensions All Rights Reserved.
The Worldwide Leader in Sailmaking
- Sail Care & Repair
- Sailing Gear
- Sail Finder
- Custom Sails
- One Design Sails
- Flying Sails
- New Sail Quote
- 3Di Technology
- Helix Technology
- Sail Design
- NPL RENEW Sustainable Sailcloth
- Sailcloth & Material Guide
- Polo Shirts
- Sweaters & Cardigans
- Sweatshirts & Hoodies
- Accessories
- Mid & Baselayers
- Deckwear & Footwear
- Luggage & Accessories
- Spring Summer '24
- Sailor Jackets
- NS x Slowear
- Sailor Jacket
- Sustainability
- North Sails Blog
- Sail Like A Girl
- Icon Sailor Jacket
- Our Locations
- North SUP Boards
- North Foils
- North Kiteboarding
- North Windsurfing
SAIL FINDER
SAILING GEAR
COLLECTIONS & COLLAB
COLLECTIONS
WE ARE NORTH SAILS
ACTION SPORTS
Popular Search Terms
Collections
Sorry, no results for ""

Sail Plan Dimensions
Sail plan dimensions, figure out your rig dimensions when it comes to your sails.

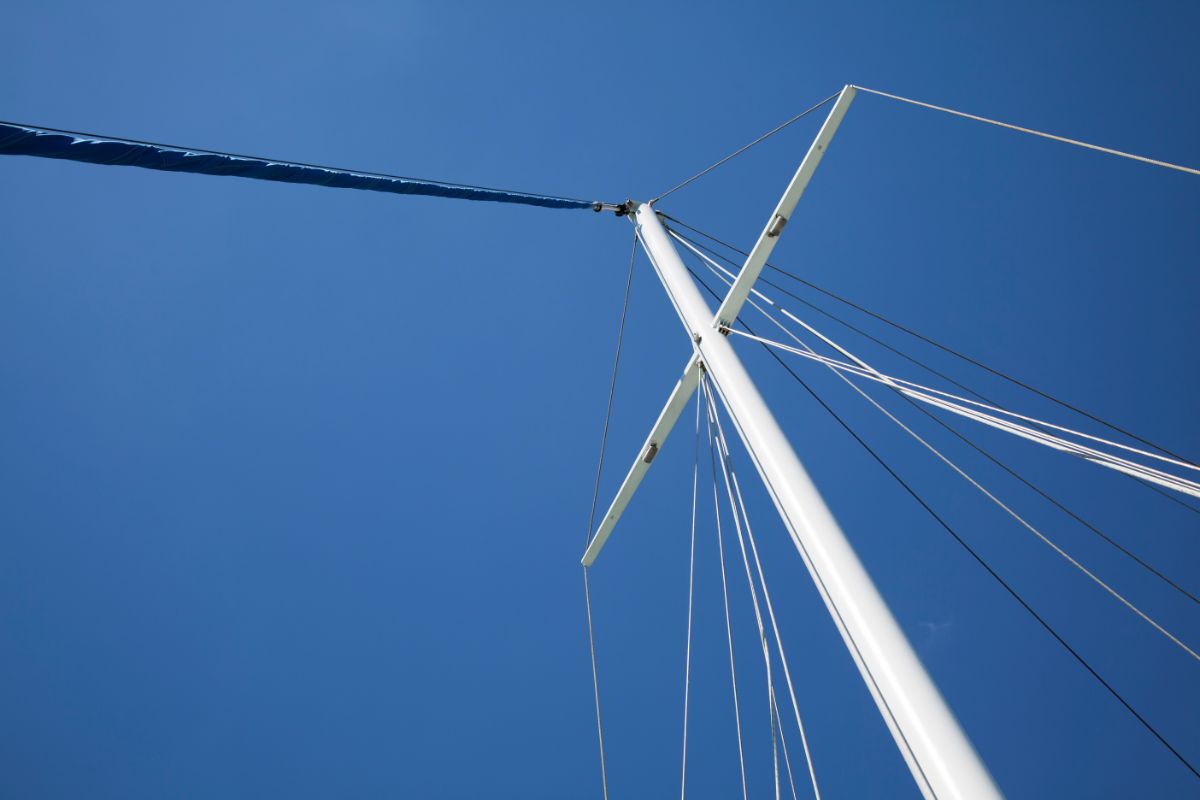
The basic rig dimension for a yacht are generally understood. However, there are some differences in how some sailors describe these dimensions. Here is how we define them at North Sails.
I – Height of Foretriangle Elevation of Forestay, measured down to elevation of main shrouds at sheer line.
J – Base of Foretriangle Horizontal distance measured from front face of mast at deck to position of headstay at sheer line.
P – Mainsail Hoist Elevation of upper mast band or maximum main halyard position, measured down to lower mast band or top of boom.
E- Mainsail Foot Horizontal distance measured from aft face of mast at top of boom to boom band or maximum outhaul position.
Is – Height of Inner Foretriangle Elevation of Forestay, measured down to elevation of main shrouds at sheer line.
Js – Base of Inner Foretriangle Horizontal distance measured from front face of mast at deck to position of inner headstay at sheer line.
Py – Mizzen Mainsail Hoist Elevation of upper mast band or maximum main halyard position, measured down to lower mast band or top of boom.
Ey – Mizzen Mainsail Foot Horizontal distance measured from aft face of mizzen mast at top of boom to boom band or maximum outhaul position.
ISP – Elevation of Spinnaker Halyard Measured down to elevation of main shrouds at sheer line.
SPL – Spinnaker Pole Length
STL – Spinnaker Tack Length Horizontal distance measured from front face of mast at deck, forward and horizontally to position of spinnaker tack attachment point.

FEATURED STORIES
Npl renew faq, flying sails 101.
21 December
CAPE 31 TUNING GUIDE
- Refresh page

Average Sailboat Mast Height

Last Updated by
Daniel Wade
August 30, 2022
Sailboat masts are known to be quite tall, but how tall do they get? The answer varies on rig type, boat size, and design attributes.
Small sailboats, under 20 feet in length, rarely have masts taller than 20 ft or shorter than 8 ft. Sailboats between 20 and 30 feet have masts up to 30 feet tall, and large 40+ foot sailboats often have masts that exceed 50 feet in height.
In this article, we'll cover the average mast height of various sailboats based on length, and we'll also provide a typical height range. Additionally, we'll compare mast height by rig type. Finally, we'll cover the benefits and disadvantages of tall and short masts.
We sourced the information used in this article from sailboat design guides and the sailing community. Additionally, we analyzed several boats from each length category to determine average mast heights.
Table of contents
Why are Mast Heights Different?
If you spend enough time around marinas, you'll undoubtedly notice the numerous masts that tower high above seemingly minuscule boats. Some are tall and thin, some are short and fat—and many are somewhere in between. So why do sailboat mast heights differ so much?
There are a lot of factors that contribute to mast height, not the least of which is boat size. Obviously, boats need a sail plan proportionate to their length, beam, and displacement in order to be efficient. The type of sail plan varies based on what the boat is used for.
Different rigs use different mast heights, even if the boat underneath is exactly the same. Let's assume we have two identical 30-foot boats. One has a tall mast and a triangular Bermuda rig, while another has a shorter mast with a four-sided rig.
The four-sided sail has a much greater area per foot of height than the triangular sail, so the mast doesn't need to be quite as high. Additionally, shorter masts can be thicker and stay within the same weight limits as a taller mast, so they can be thicker and stronger.
Average Mast Height by Sailboat Length
Now, we'll look at the average mast heights of sailboats by their overall length. We're not considering rig type beyond the fact that the majority of modern sailboats are Bermuda-rigged sloops—we'll get into that later. Here are some averages based on popular sailboats.
As you can see, the average mast height is highly dependent on the length of a sailboat. Most vessels have triangular rigs, which require a taller mast. It also seems as though mast height isn't usually far from the overall length of the boat, at least on tall single-masted vessels.
Why do Racing Sailboats Have Tall Masts?
Racing sailboats are known for their crazy mast heights and long, thin sails. There's a very simple reason for this, and it has to do with efficiency and drag. A taller and thinner sail is much more efficient for speed than a shorter and fatter sail. The same goes with the dimensions of the hull, as fast boats tend to be long and slender.
The science behind sail design is ancient and fascinating. In the 21st century, where the boat market values speed and agility, tall masts with thin triangular rigs are becoming increasingly popular. Short-masted vessels, once a key component of working offshore, are more durable but less common.
Average Mast Height of Multi-Masted Sailboats
Having multiple masts has distinct advantages, especially for cruising. Multi-masted sailboats are some of the best offshore cruisers ever built, and they are also remarkably durable. One of the main benefits of having multiple masts is that it adds a level of redundancy and increases your ability to finely control the vessel.
Multi-masted sailboats almost always have shorter and thicker masts when compared to similar single-masted vessels. Sailboats with four-sided mainsails, such as many classical schooners, are a particularly extreme example of this.
Gaff-rigged schooner masts are significantly shorter than triangular rig masts, sometimes more than 10 to 20% shorter. It's often the case that these vessels have a topmast that can be raised or lowered to add a triangular topsail, further increasing the area of the large four-sided sail plan.
What Sailboat Rigs Have Tall Masts?
Bermuda rigged sailboats (also known as Marconi rigged sailboats) are the most common tall-masted boats. Triangular rigs are tall because their sail area decreases as it moves up the sail, so they make up for it by adding height.
Fully-rigged ships also have very tall masts. These are the traditional sailing ships that are quite literally called 'tall ships' in the sailing community. They have multiple sails on each mast when fully deployed, and they usually have three or more masts and multiple headsails.
What Sailboat Rigs Have Short Masts?
The gaff rig is a common and classic sailboat rig that uses traditionally shorter masts. The gaff rig uses a square mainsail, which has more lateral area than a triangular mainsail. These vessels often deploy a topsail with or without a mast extension called a topmast.
The lateen rig is also famously simple and short-masted. It uses a triangular sail with spars that fly at an angle to the mast. It is an ancient sailing rig that was extremely common in the early days of civilization, and it served workboats across the world for centuries.
Are Shorter Masts Stronger?
Short masts can be stronger, but they aren't always. It depends on the design of the craft and is more dependent on rig type than the size of the mast itself. The strongest masts are found on gaff-rigged vessels. They are usually short and thick and traditionally made of wood.
The strength of the mast isn't so important when everything is working properly. It begins to matter in the event of a failure, like a broken stay.
A gaff-rigged vessel with a typical mast has a good chance of surviving a snapped stay as the mast can support itself. A Bermuda-rigged vessel, more likely than not, could lose its mast immediately after the standing rigging goes down.
What are Masts Made Of?
Masts are made of many different materials. Traditionally, wood was the mast material of choice. It was strong and lasted a very long time if maintained. Through the production sailboat era, when boatbuilders switched from wood to fiberglass for hulls, sailboat masts were mostly made of aluminum.
Today's high-tech racing sailboats have many more options to choose from. Composite materials, such as carbon fiber, are increasingly common due to their astounding strength-to-weight ratio. Alloy masts are also fairly common. Steel masts exist, but their use is usually confined to small sailboats and dinghies.
Related Articles
I've personally had thousands of questions about sailing and sailboats over the years. As I learn and experience sailing, and the community, I share the answers that work and make sense to me, here on Life of Sailing.
by this author
Learn About Sailboats
Most Recent

What Does "Sailing By The Lee" Mean?
October 3, 2023

The Best Sailing Schools And Programs: Reviews & Ratings
September 26, 2023
Important Legal Info
Lifeofsailing.com is a participant in the Amazon Services LLC Associates Program, an affiliate advertising program designed to provide a means for sites to earn advertising fees by advertising and linking to Amazon. This site also participates in other affiliate programs and is compensated for referring traffic and business to these companies.
Similar Posts

Affordable Sailboats You Can Build at Home
September 13, 2023

Best Small Sailboat Ornaments
September 12, 2023

Discover the Magic of Hydrofoil Sailboats
December 11, 2023
Popular Posts

Best Liveaboard Catamaran Sailboats
December 28, 2023

Can a Novice Sail Around the World?
Elizabeth O'Malley
June 15, 2022

4 Best Electric Outboard Motors

How Long Did It Take The Vikings To Sail To England?

10 Best Sailboat Brands (And Why)
December 20, 2023

7 Best Places To Liveaboard A Sailboat
Get the best sailing content.
Top Rated Posts
Lifeofsailing.com is a participant in the Amazon Services LLC Associates Program, an affiliate advertising program designed to provide a means for sites to earn advertising fees by advertising and linking to Amazon. This site also participates in other affiliate programs and is compensated for referring traffic and business to these companies. (866) 342-SAIL
© 2024 Life of Sailing Email: [email protected] Address: 11816 Inwood Rd #3024 Dallas, TX 75244 Disclaimer Privacy Policy

How Tall Are Sailboat Masts? 9 Examples
The mast height of a sailboat varies with every model.
So what determines the height of a mast?
Here’s How Tall Sailboat Masts Are:
As a general rule of thumb, the height of a boat’s mast will be somewhere between 1.25 to 1.35 times the boat’s length, for an average of about 1.3 times the length overall (LOA) of the boat. An aspect of 2.5 or lower will be a low-aspect rig; above that is considered a high-aspect ratio.
Table of Contents

Understanding a Sailboat’s Mast and Rig
Sailboats are driven through the water by the power generated by their sails.
This is done using sail area. Sail area is calculated using the height of the mast and the length of the boom.
The battens, long strips of wood inserts in the sail, allow more sail area as they extend beyond a straight line from the head of the mast to the back of the boom, thus allowing more cloth to be carried.
Keep in mind that the mast height does not equal the luff length of the main; there is a distance between the deck and the top of the boom.
Most mains do not go all the way to the top of the boom mast.
Wind Gradient:
Designers are also aware of the wind gradient, meaning that as the wind blows over the water, the surface causes drag.
So the breeze is stronger the higher you get off of the surface.
Taller masts allow you to reach these stronger winds.
Mast Height:
While mast height is a prime determinant in the area, it is also possible to make a mast too tall so that the boat is always in danger of taking a knockdown.
Note there are some performance boats designed with masts that are too tall for the craft’s weight, assuming that the weight of the crew will balance out the sail area.
One thing to bear in mind here is a rig’s aspect ratio: this is determined by dividing the designed sail’s luff length by the length of the foot. An aspect of 2.5 or lower will be a low-aspect rig; above that is considered a high-aspect ratio.
Higher aspect boats perform better upwind; lower aspect ratios generally are more powerful in other wind conditions and are usually easier to control.
What’s the Average Height of Sailboat Masts?
Sailboats can range from 6 feet to a hundred or more feet in length if you throw out the multi-masted sailing ships of old.
The mast height for every single one is different.
The height of a mast is usually carefully calculated by figuring the amount of power needed to move a certain hull shape and weight through the water. In many cases, in the 1960s through the 1980s, some designers went by feel.
A few boatbuilders would use the same mast across several of their models to save money in some cases.
As a general rule of thumb, the height of a boat’s mast will be somewhere between 1.25 to 1.35 times the boat’s length, for an average of about 1.3 times the length overall (LOA) of the boat.
So, if you were going to average the mast heights of all 20-foot boats, you’d have about a 26-foot high mast and about 39 feet on 30-foot boats.
Boats built solely for cruising, particularly in offshore winds, will have shorter masts, and performance boats will have taller masts.
How do you Determine the Height of a Sailboat Mast?
Several factors determine a sailboat’s mast height.
A performance boat will have a higher aspect ratio for its sails and thus have a taller mast. Cruising boats will generally have smaller masts for the same length of the boat.
A wider and heavier boat than another boat will need more power to move it, so it will usually have a taller mast. If this heavy boat is a low-aspect-ratio rig designed for offshore work, it will probably have a comparably shorter mast for ease of handling in higher winds.
Conversely, a racing boat will be lighter but still have a taller mast to generate maximum power upwind.
Boats built for maximum performance will have very tall masts for their length and be very difficult to handle for an inexperienced crew – and sometimes for a trained, experienced crew as well, as the difficulties some of America’s Cup boats encounter demonstrate.
- The Melges 24 is a performance racer with a mast height of 31.4 feet for a head-to-head comparison. Her mainsail’s luff length is 28.92 feet, and the foot is 12.45 feet; she is a high-aspect-ratio boat.
- The Islander 24 has a mast height of 28.82, so it is 2 and 1/2 feet shorter than our Melges. The main’s luff length is 25.75 feet, and the foot is 11.52, for a low aspect ratio and much smaller main.
- The Islander 24 weighs 4,200 pounds, while the Melges 24 weighs less than 1,800 pounds.
How Tall is the Mast on a 40 ft Sailboat?
If a yawl or other rig with multiple masts, it will have shorter masts than a sloop.
If the boat is a fractional rig with a small foretriangle, like a modern high-aspect-ratio Hunter, the mast will be taller than another sloop of the same length:
- The old Tartan 40, an all-around great Sparkman & Stevens design from 1984, has a 51-foot mast. This is a classic racer/cruiser.
- The Nordic 40, designed around the same time, has a 52-foot mast.
- The Canadian-built C&C Crusader, designed in 1968, has a mast of 48 feet, but their later Mark 2 designs have masts of 53 to 55 feet in height.
These are all sloops. Ketch and yawl rigs will have masts shorter than this, as the smaller mizzens provide power (and helm balance).
So, this shows us that mast heights will fall into a range for any given length of the boat, again depending on other factors such as its function (primarily racing or cruising).
What is the Optimal Height of a Sailboat Mast?
As specified earlier, the designed height of a mast for any given sailboat generally falls between 1.25 and 1.35 times its length overall (as opposed to its waterline length).
The optimal height will be based on the designer’s calculations of the sail area and aspect ratio needed for the boat’s intended purpose. Beyond the simple racing/cruising divide, there are inshore and offshore cruisers and casual and serious racers.
Inshore cruising boats will generally be designed for maximum safety, and the mast height may be less than 1.25 times the length. Offshore cruisers may also be divided into casual and serious distance cruisers; a boat designed for better offshore cruising performance will have a taller mast.
It is unusual to find many cruising boats with a higher ratio than 1.3, however.
Racing boats will usually have a 1.35 ratio, though it can be as high as 1.5 or even higher at the extremes of the sport.
The mast height for America’s Cup AC50, a 50-foot catamaran, is 77 feet.
How Tall is the Tallest Sailboat Mast?
Two boats are currently competing for the title of having the world’s tallest mast.
Mirabella 5, now named M5 and launched in 2003, is the largest single-masted yacht ever built at 294 feet long.
Her mast is over 290 feet high.
The boom is nearly 90 feet in length. The mainsail has an area of 16,000 square feet! Her reacher (a large, light-weight genoa with some characteristics of a spinnaker), at 20,600 square feet, is the world’s largest sail.
The White Pearl, the world’s largest sailing yacht at nearly 350 feet, was launched in 2014. She has three carbon-fiber wing-style masts that are a little more than 90 meters high.
This puts the masts for the two yachts within a few feet of each other, though White Pearl gets the nod.
References:
Masts – Wikipedia
Sloops – Sailboat Cruising
World’s Tallest Carbon Fiber Masts
Click to share...
- Navigating the High Seas: A Comprehensive Guide to Sailboat Masts
Sailboat masts are the unsung heroes of the sailing world, silently supporting the sails and ensuring a smooth journey across the open waters. Whether you're a seasoned sailor or a novice, understanding the intricacies of sailboat masts is essential for a safe and enjoyable voyage. In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the world of sailboat masts, discussing their types, maintenance, and everything in between.
Types of Sailboat Masts
Sailboat masts come in various configurations, each with its advantages and drawbacks. The two primary types are keel-stepped and deck-stepped masts.
Keel-Stepped Masts
Keel-stepped masts are the most common type, extending through the deck and resting on the boat's keel. They provide excellent stability and are suitable for larger sailboats. However, they require careful maintenance to prevent water intrusion into the boat's cabin.
Deck-Stepped Masts
Deck-stepped masts rest on the deck of the boat, making them easier to install and remove. They are commonly found on smaller sailboats and are more forgiving in terms of maintenance. However, they may offer slightly less stability than keel-stepped masts.
Components of a Sailboat Mast
To understand mast maintenance better, it's essential to know the various components of a sailboat mast. The key parts include the masthead, spreaders, shrouds, and halyard sheaves.
The masthead is the topmost section of the mast, where the halyards are attached to raise and lower the sails. It also often houses instruments such as wind indicators and lights.
Spreaders and Shrouds
Spreaders are horizontal supports attached to the mast to help maintain the proper angle of the shrouds (cables or rods that provide lateral support to the mast). Properly adjusted spreaders and shrouds are crucial for mast stability and sail performance.
Mast Materials: Choosing the Right One
Sailboat masts are typically constructed from three primary materials: aluminum, wood, and carbon fiber. Each material has its unique characteristics and is suited to different sailing preferences.
Aluminum Masts
Aluminum masts are lightweight, durable, and relatively easy to maintain. They are commonly used in modern sailboats due to their cost-effectiveness and longevity.
Wooden Masts
Wooden masts, while classic and beautiful, require more maintenance than other materials. They are best suited for traditional or vintage sailboats, where aesthetics outweigh convenience.
Carbon Fiber Masts
Carbon fiber masts are the pinnacle of mast technology. They are incredibly lightweight and strong, enhancing a sailboat's performance. However, they come at a premium price.
Mast Maintenance
Proper mast maintenance is essential for safety and longevity. Regular cleaning, inspection, and addressing minor issues promptly can prevent costly repairs down the line.
Cleaning and Inspection
Regularly clean your mast to remove salt, dirt, and grime. Inspect it for signs of corrosion, wear, or damage, paying close attention to the masthead, spreaders, and shrouds.
Common Repairs and Their Costs
Common mast repairs include fixing corroded areas, replacing damaged spreaders, or repairing shrouds. The cost of repairs can vary widely, depending on the extent of the damage and the materials used.
Extending the Lifespan of Your Mast
Taking steps to prevent damage is essential. Avoid over-tightening halyards, protect your mast from UV radiation, and keep an eye on corrosion-prone areas.
Read our top notch articles on topics such as sailing , sailing tips and destinations in our Magazine .
Stepping and Unstepping a Mast
Stepping and unstepping a mast is a crucial skill for any sailboat owner. This process involves removing or installing the mast on your boat. Here's a step-by-step guide for safe mast handling.
Step-by-Step Guide for Safe Mast Handling
- Gather the necessary tools and equipment.
- Disconnect all electrical and rigging connections.
- Use a crane or mast-stepping system to safely lower or raise the mast.
- Secure the mast in its proper place.
- Reconnect all electrical and rigging connections.
When and Why to Unstep a Mast
You may need to unstep your mast for various reasons, such as transporting your sailboat or performing extensive maintenance. It's crucial to follow the manufacturer's recommendations and ensure a safe unstepping process.
Sailboat Mast Boot: Protecting Your Mast
A mast boot is a simple yet effective way to protect your mast from water intrusion and damage caused by the elements. Here's what you need to know.
The Purpose of a Mast Boot
A mast boot is a flexible material that wraps around the mast at the deck level. It prevents water from entering the cabin through the mast opening, keeping your boat dry and comfortable.
Installing and Maintaining a Mast Boot
Installing a mast boot is a straightforward DIY task. Regularly inspect and replace it if you notice any signs of wear or damage.
Replacing a Sailboat Mast
Despite your best efforts in maintenance, there may come a time when you need to replace your sailboat mast. Here's what you should consider.
Signs That Your Mast Needs Replacement
Common signs include severe corrosion, structural damage, or fatigue cracks. If your mast is beyond repair, it's essential to invest in a replacement promptly.
The Cost of Mast Replacement
The cost of mast replacement can vary significantly depending on the type of mast, materials, and additional rigging needed. It's advisable to obtain multiple quotes from reputable marine professionals.
Yacht Masts: Sailing in Style
For those looking to take their sailing experience to the next level, upgrading to a yacht mast can be a game-changer.
Differences Between Sailboat and Yacht Masts
Yacht masts are typically taller and offer enhanced sail performance. They are often equipped with advanced rigging systems and technology for a more luxurious sailing experience.
Upgrading to a Yacht Mast
Consult with a marine professional to determine if upgrading to a yacht mast is feasible for your sailboat. It can be a significant investment but can transform your sailing adventures.
Sailboat Mast Steps: Climbing to the Top
Mast steps are handy additions to your mast, allowing easier access to perform maintenance or enjoy panoramic views. Here's how to use them safely.
Using Mast Steps Safely
Always use proper safety equipment when climbing mast steps. Make sure they are securely attached to the mast and regularly inspect them for wear or damage.
The Advantages of Mast Steps
Mast steps provide convenience and accessibility, making sailboat maintenance tasks more manageable. They also offer an elevated vantage point for breathtaking views while at anchor.
Mast Maintenance Tips for Beginners
If you're new to sailboat ownership, these mast maintenance tips will help you get started on the right foot.
Essential Care for First-Time Sailboat Owners
- Establish a regular maintenance schedule.
- Seek advice from experienced sailors.
- Invest in quality cleaning and maintenance products.
Preventing Common Mistakes
Avoid common pitfalls, such as neglecting inspections or using harsh cleaning agents that can damage your mast's finish.
Sailing with a Mast in Top Condition
A well-maintained mast contributes to a safer and more enjoyable sailing experience. It enhances your boat's performance and ensures you can rely on it in various weather conditions.
How a Well-Maintained Mast Improves Performance
A properly maintained mast helps maintain sail shape, reducing drag and improving speed. It also ensures that your rigging remains strong and secure.
Safety Considerations
Never compromise on safety. Regularly inspect your mast, rigging, and all associated components to prevent accidents while at sea.
Sailboat masts are the backbone of any sailing adventure, and understanding their intricacies is crucial for a successful voyage. From choosing the right mast material to proper maintenance and upgrading options, this guide has covered it all. By following these guidelines, you can sail the high seas with confidence, knowing that your mast is in top condition.
So what are you waiting for ? Take a look at our range of charter boats and head to some of our favourite sailing destinations .

By Product Categories
Small Boat Blocks
Big Boat Blocks
Complementary Hardware
Travelers & Genoa Leads
Mainsail Handling
Headsail Handling
Mooring Solutions
Spare Parts
Accessories
Harken Canvas
Fly Soft-Attach Blocks
Carbo Air Blocks
Small Boat Classic
Flip-Flop Small Boat
GP Catamaran Ceramic Mainsheet Systems
Protexit™ Exit Blocks
Through-Deck
Wire High-Strength
Dinghy Vang
Small Boat Deck Organizers
Midrange Classic
Midrange Deck Organizers
Zircon Blocks
Element Blocks
Black Magic Air Blocks
Cruising ESP Blocks
Megayacht Blocks
Stainless Steel Blocks
Black Magic Air Runners
FlatWinder Powered Blocks
Mastbase Blocks
Over-the-Top
Crossover Blocks
Big Boat Deck Organizers
Cam Cleats & Kits
Cam Cleat Accessories
Cam Cleat Bases
Stand-Up Bases
Deck Organizers
Spinnaker Pole Cars
Soft Attachments
Fixed Padeyes
Removable Padeyes
Bolt-Down Fairleads
Grand Prix Jib Leads
Halyard Tensioners
Tiller Extensions
Peter's Desk Drawer
Dinghy Jib Leads
Crossbow Pivoting Self-Tacking Jib Traveler
13 mm Micro
22 mm Small Boat
27 mm Midrange
32 mm Big Boat
Windward Sheeting
42 mm Mini-Maxi
T-Track Genoa Lead
Access Rail System
13 mm AA Battcar System
22 mm A Battcar System
27 mm B Battcar System
32 mm C Battcar System
18 mm Switch Battcar System
26 mm Switch Battcar System
26 mm Trysail Switch
32 mm Switch Battcar System
32 mm Trysail Switch
40 mm Switch Battcar System
40 mm Trysail Switch System
Furling Mainsail Outhaul Systems
Single Line Reefing
Harken Vang-Master
Carbo Racing Foil
Small Boat Furling
Small Boat Underdeck
Reflex Furling
MKIV Jib Reefing & Furling
MKIV Underdeck Jib Reefing & Furling
Furling Accessories
Powered Furling
MKIV Ocean Furling
SnubbAir (Not a Winch)
Grand Prix Winches
Air Winches
Circuit Breakers
Analog Switches
Digital System Switch
Aluminum, Chrome & Bronze Winch Handles
Carbo OneTouch Locking Winch Handle
Service Kits
CLR Mooring Winches
Electric Captive Reel Winches
Hydraulic Captive Reel Winches
UniPower Radial
Single-Acting Integral Backstay Adjuster
Single-Acting Cylinders
Locking Cylinders
Double-Pull Cylinders
Grand Prix Cylinders
Hydraulic Cylinder Rod End Blocks
Hydraulic Cylinder End Fittings
Control Valves
Control Manifolds
Control Panels
Compact Control Panel
Rotary Pumps
Hydraulic Pump Handles
Power Systems
Repair Kits
Ball Bearings
Block Spare Parts
Traveler Cars
Furling Spare Parts
Winch Spare Parts
Winch Service Kits
Blockheads Gear
Promo & Gifts
Marine Grip
harkengear.com
Jeep/Truck tops
Garage storage
One-design Covers
Boat accessories
Canvas bags
By Type of Sailing
Dinghy / One-Design
Offshore Racing
Coastal / Day Cruising
Bluewater Cruising
Megayachts / Custom
Service Guide
Tech/Service
deck layouts
Data Sheets (SDS)
How to choose
System diagrams
Calculators
Reeving diagrams
Traveler Purchase Selection Guide
How to Choose
Testimonials
Hoister Videos
Request a Quote
Request Samples
Fabric details
Cover Styles
Canvas Videos
Contract Services
Materials and Components
Our Equipment
Contract Cut-and-Sew Project Spotlight
- Harken at the front
- Safety & Rescue
Support / Tech/Service Articles
Rig Dimensions
The following abbreviations are often used to describe various measurements on a sailboat. Precise technical definitions exist for each abbreviation, but the following is a list of simple descriptions.
If you would like to link to or reprint this article please contact [email protected] .

Product Categories
- United States
- New Zealand
- United Kingdom

Sailboat Mast: Everything You Need To Know
Anyone who loves sails and boating needs to know their sailing boat from the inside out. If you are new to the sport, then you are probably wondering about things like a sailboat mast and everything around it.
In this article, we have everything you need to know about a sailboat mast, like what it is, its different types, as well as the material it is made of.
All you have to do is keep reading below to find it all out!
What Is A Sailboat Mast?
A sailboat mast is a tall pole that is attached to the deck. It helps secure the sail’s length to the boat and upholds the sail’s structure.
A sailboat mast is the most defining characteristic of a sailboat, helping keep the sail in place. What’s amazing about it is that it can even be taller than the vessel’s length!
Although conventional sailboats use wood, the majority of the newer sailboat masts are constructed of aluminum. The kind of sailboat mast a vessel has depends on the kind of sail plan supported.
What Are The Parts Of A Sailboat Mast?
The sailing mast is essentially a pole that cannot operate effectively without certain critical components.
Moving from the deck to the rest of the sailboat, we can first see the mast boot, which prevents the water from draining down the mast and flooding the cabin.
The stays are the long cords hooked up on each side of the mast, and they hold the mast up off the ground under massive force.
A gooseneck pipe fitting joins the boom to the mast. The sail is raised and lowered using halyard lines that go to the mast’s highest point.
Types Of Sailboat Masts
Rigs with one mast.
Many people that are not aware of the modern sailboat design envision single-mast sailboats.
The reason why this type of sailboat is so widely known is that these masts are low-cost to construct and fairly simple to operate alone.
Sloops, cutters, and catboats are among the most popular rigs with only one mast.
Sloop Masts
Nowadays, sloop rig vessels are the most popular type of sailing boat. Sloops typically have only one mast positioned somewhere on the front third or the middle of the deck, even though some boat models might vary a bit.
A sloop mast is equipped with a big mainsail and a jib sail (see also ‘ Why Are Sails Made In A Triangular Shape? ‘). A Bermuda-rigged sloop has only one towering mast and a triangle-shaped sail. Other not-so-popular gaff-rigged sloops have a significantly smaller mast and bigger 4-point mainsails.
Catboat Masts
Catboats are distinctive New England boats that have a forward-mounted standard mast and a long boom. A catboat, unlike a sloop-rigged boat, is only equipped with one sail.
It is also typically mounted (more or less) right in front of the boat, and it is commonly short and relatively thick.
Catboats are frequently gaff-rigged. In a single-mast design, gaff-rigged sail designs (see also ‘ The Definition And History Of The Lateen (Triangular) Sail ‘) succeed in making the most out of short masts and are relatively simple to maneuver.
The mast of gaff-rigged catboats is shorter than that of a Bermuda-rigged boat of comparable size, but it is typically taller than that of comparable gaff-rigged crafts.
Cutter Mast
A cutter-rigged sailboat has only one towering mast and several headsails, which is why it can be mistaken for sloops when seen from afar.
However, because cutters use numerous headsails rather than one standard jib (see also ‘ Everything You Need To Know About Sailboat Jibs ‘), their masts are typically taller than those of comparable-sized sloops.
In several places, a gaff-rigged cutter is far more usual than a gaff-rigged sloop. Even at times when its sails are folded, a cutter can be distinguished from a sloop.
This is due to the fact that cutters frequently have a protracted bowsprit and two front stays; the forestay and the jib stay.
Rigs With Multiple Masts
Multi-mast sailboats (see also ‘ Small Sailboats: What Are They Called? ‘) are not as popular as single-mast sailboats. That is why the design and structure of a multi-mast boat usually make it classier and more navigable.
A multi-mast boat provides more than simply great looks. It also provides speed and efficient control for skilled seamen.
Most of these boats have two masts, which seem to be frequently smaller than the masts on comparable-sized single-mast crafts. Yawl, ketch, as well as schooner rigs, are among the most popular types.
Yawls are sturdy multi-mast boats whose length ranges from 20 to more than 50 ft. A yawl has a lengthy forward main mast and a small mizzen mast at the back of the vessel. This type is also frequently gaff-rigged and was previously used as a utility boat.
A yawl-rigged boat can also self-steer by using the mizzen mast and sail. The yawl can be distinguished from many other double-mast vessels by its short mizzen mast, which is frequently half the size of the main mast.
Furthermore, the mizzen mast is located toward the back of the rudder post.
Ketch Masts
Ketch masts can be mistaken for yawls with a quick look. However, ketch masts are equipped with two masts of comparable size and a significantly bigger mizzen mast. A ketch boat’s mizzen mast is located at the front of the rudder post.
Ketch-rigged vessels are frequently gaff-rigged, with topsails on each one of their masts. Triangle-shaped sailplanes on some ketch-rigged vessels prevent the necessity for a topsail.
Ketch masts, much like the yawl ones, have a headsail, a mainsail, and a mizzen sail that are similar in size to the mainsail. Finally, a ketch-rigged vessel can sail while handling more than one rear sail.
Schooner Masts
Schooners are some of the most beautiful multi-mast sailboats. They are clearly more similar to ketches than yawls. However, if you closely look at a schooner, you will see that it will feature a smaller foremast and a longer (or nearly equal-sized) mast behind it.
Schooner masts are large and heavy, but they are generally shorter than single-mast vessels of comparable size.
This is due to the fact that double-masted vessels share the sail plan over 2 masts and do not require the additional length to compensate for the reduced sail space.
Finally, they are typically gaff-rigged, with topsails and topmasts that expand the mast’s length.
Masts Of Tall Ships
Tall ships are those traditional large cruising ships that ruled the seas well before age of steam. Renowned ships with this massive and intricate rig setup include the U.S.S Constitution as well as the H.M.S. Victory.
Tall ships have 3 or more massive masts that are frequently constructed using big tree trunks. Tall ships with 5 or more masts are quite common too.
Tall ships typically are as long as 100 feet or more, since the size and sophistication of these square-rigged vessels render them only useful at scale.
Tall ships have main masts, foremasts, mizzen masts, and gaff-rigged jigger masts at the back of their mizzen masts.

Mast Materials For Sailboats
The masts of sailboats (see also ‘ Two-Mast Sailboat Types ‘) are typically constructed of aluminum or other specific types of wood. Until the 1950s, almost all sailboat masts were constructed of wood.
That began changing around the time that fiberglass vessels rose to fame, with aluminum being now the most used mast material.
Aluminum Masts For Sailboats
Aluminum has become the most popular modern mast material. Aluminum masts are lighter in weight, hollow, and simple to produce. Such reasonably priced masts efficiently withstand seawater. These masts are also heavy for their size.
If there is one drawback to this type of mast that would be galvanic corrosion, which happens extremely quickly once seawater is in contact with aluminum and another metal, like steel and copper.
So, in types like the Bermuda-rigged sloop which are frequently made with aluminum, that is an issue.
Wooden Masts For Sailboats
The typical material for sailboat masts is wood, which is still employed for many specially designed boats nowadays.
Wood masts are big and bulky, yet very sturdy, and proper maintenance can guarantee their lengthy (over 100 years!) lifespan. They are also prevalent on gaff-rigged vessels because wood is best suited for short masts.
The Fir family provides the most popular mast wood. Although Douglas Fir is widely used, regional models (such as British, Columbian, and Yellow Fir) are also ideal.
Several sailboats, especially the tall ships, have masts made of pine and sometimes redwood. Other cedar species like the Port Orford or the Oregon cedar, can also be used for masts and spars.

Carbon Fiber Masts For Sailboats
Carbon fiber masts are a relatively new addition to the boatbuilding industry, and they have a few perks over the wood and aluminum ones.
First of all, carbon fiber is both strong and light, making it perfect for sailboats designed for races and which typically have tall masts. The best top-quality carbon fiber masts in the business are used by ships competing in America’s Cup races.
Maintenance Of Masts
It is critical to maintaining the sailboat masts and all of their associated hardware. Masts’ stays, lines, and halyards must be regularly checked, modified, and replaced on a regular basis. Masts made of wood must be lacquered and inspected for rot.
Masts made of aluminum do not typically require regular checks and maintenance, but any indications of a corrosive environment should be acted upon right away.
Build a clear maintenance schedule with your regional boat repairman or boating specialist. Keep in mind that preventative maintenance is always less expensive and simpler than repair work.
Choosing The Right Mast
For those who own a production boat, the options will be determined by the model and manufacturer.
The important factors to keep in mind for one-off boats without a designer sail plan are:
- the masts step’s features
- the length and displacement of the boat
- the addition of backstays and running backstays
- the quantity and placement of chainplates
If the mast is on a step on deck rather than on the structural beam, an image of the step may be useful to the mast maker.
For those who frequently take part in races, a carbon mast will save them from the extra weight and enhance their performance.
The Bottom Line
We hope that this article was helpful in learning more about a sailboat mast, the different types of mast you can see on vessels, as well as the materials they are made of, and their maintenance requirements.
Masts play a vital role in holding the boats in place, allowing people to keep on sailing to their dream destination, and they are also an eye-catching element of sailboats thanks to their vertical form and their length that often surpasses that of the sailboat itself.
Depending on the use of the boat, you will get a different type of mast, and the material it will be made of, its size, height, and weight, will guarantee the best sailing experience!
Related Posts:


- Measurements
On this page
Rig measurements are following the WS Equipment Rules of Sailing (ERS) with only a couple of modifications specific for offshore boats:
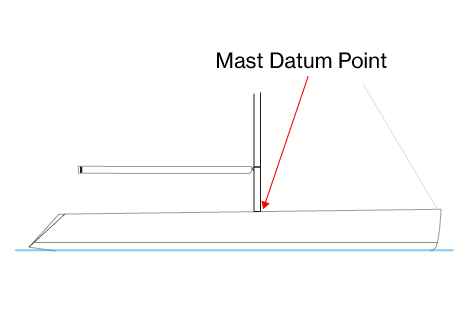
- Mast datum point is at the top point of the section at the foreside of the mast
- Rigging point is attachment of the forestay to the mast, or the intersection of the extended forestay with the mast structure.
Mast datum point and Foretriangle base
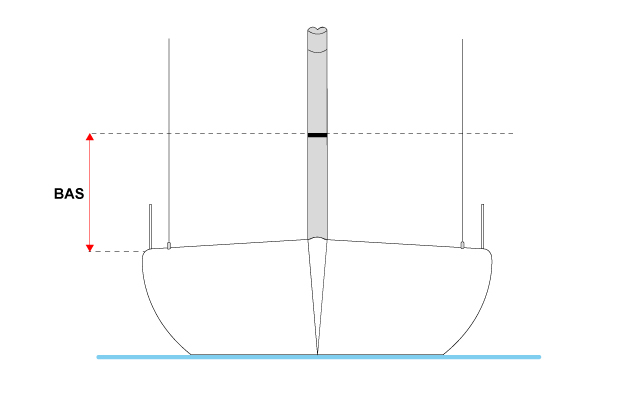
BAS and J with SFJ measurements are defining vertical and longitudinal position of the mast and sail plan relative to the hull. BAS is the height from the mast datum point to the boom or lower black band on the mast. It is used also as a reference point for the halyards hoist measurements on the mast. J is probably the best-known measurement on boat, since it is used to define the size of headsails. It is defined as the horizontal distance between the front side of the mast and the intersection of the forestay with the deck. SFJ then determines the distance of the forward point of J to the actual foremost point on the hull.
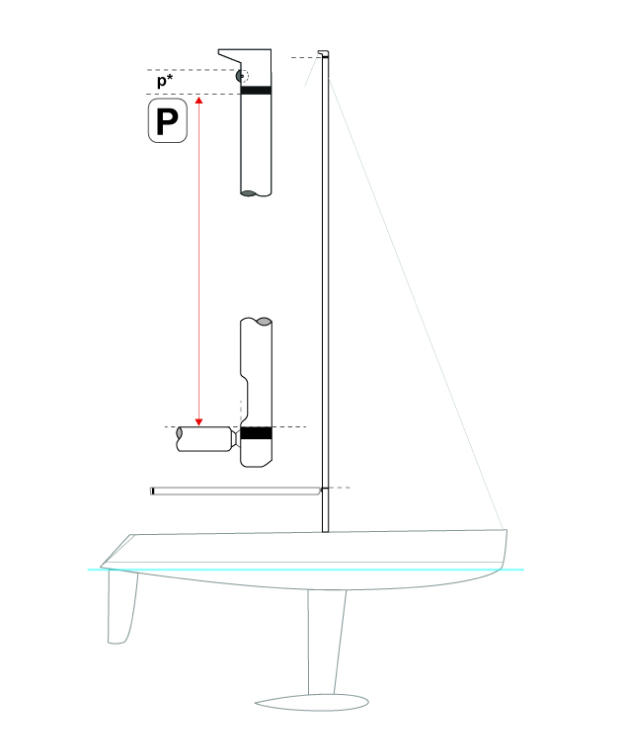
P is distance between the black bands and the mast that are limiting the position of the mainsail luff - while racing the mainsail luff must be between these bands. In the absence of the upper black band, P is measured to the upper part of the main halyard sheave. IG is defined as the height of the foretriangle and is the vertical distance from the mast datum point (at the sheerline at the mast) to the forestay attachment to the mast. Similar to IG , ISP is the spinnaker halyard height and is the maximum height that the head of the spinnaker or headsail set flying can be hoisted.
Mast profiles are measured for maximum dimensions above 0.5 * P transversely (MDT1) and longitudinally (MDL1) as well as for the minimum dimensions transversely (MDT2) and longitudinally (MDTL2) . Taper length TL is the vertical distance from the upper black band to the point where maximum mast profile dimensions occurs. Thus, TL is 0 if mast is not tapered.
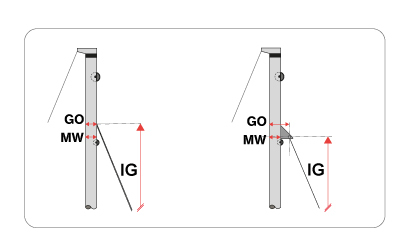
If there is a structure element of forestay attachment to the mast, then its distance from the aft side of the mast is measured as GO . Mast width MW at that height provides elements for the calculation of the actual intersection of the forestay with the front side of the mast.
Mast weight (MWT) and mast centre of gravity (MCG) are important factor determining a boat's stability. It can be measured by weighing the mast at a single point and finding the actual centre of gravity, or by two separate weight measurements at the same points from which total weight and centre of gravity position are calculated.
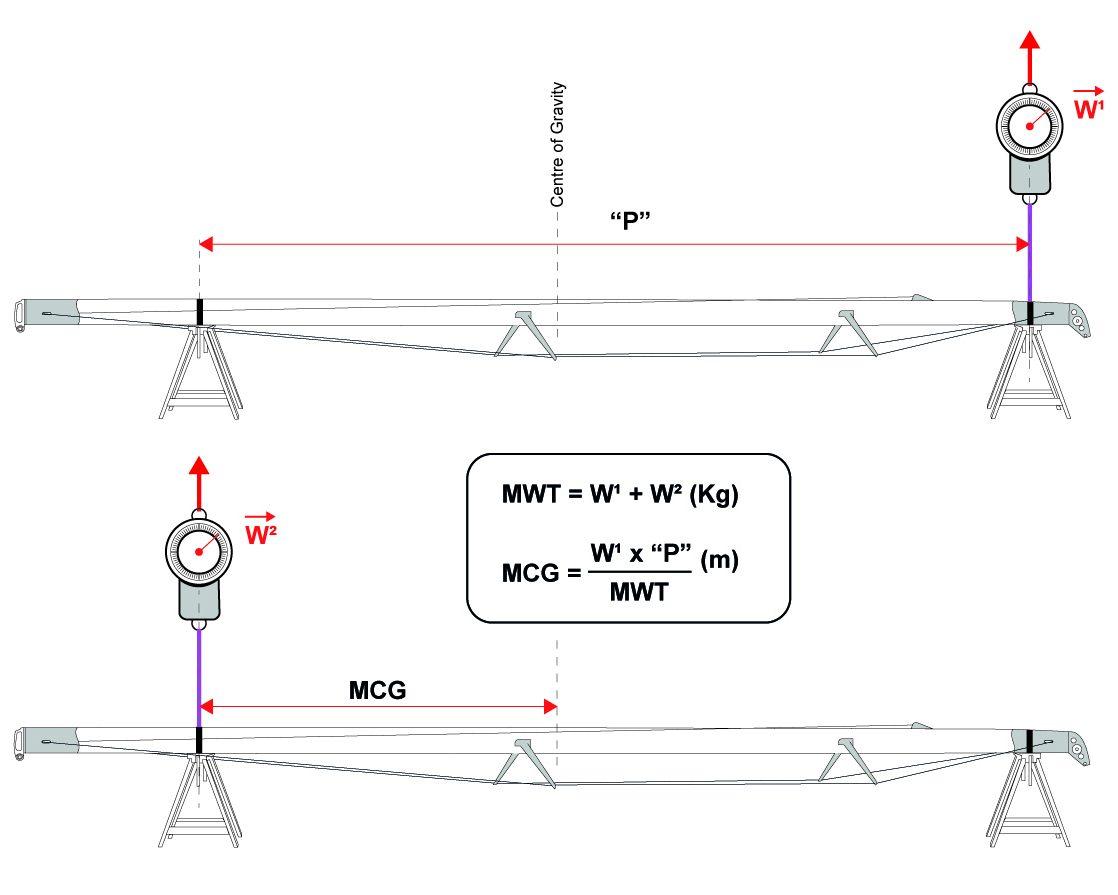
The mast is weighed with: forestay, backstay, spreaders, jumpers, shrouds, chain plates, runners, lights, antennae, wiring and other permanently fitted components all slack stretched down and secured with light material at the bottom of the mast. Excluded are: checkstays, halyards, boom vang and reefing lines.
If the mast is not weighed, then lightweight defaults for aluminium or carbon mast are used. Actual mast weight measurements will therefore always give a more favorable rating.
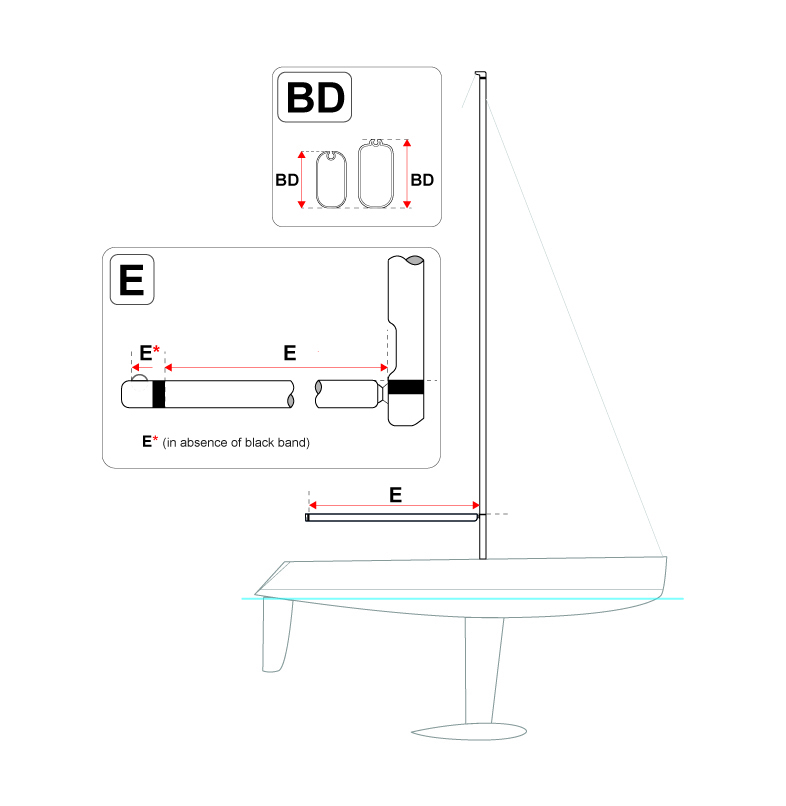
E is the measured distance from the aft side of the mast to the black band on the boom that limits the position to which mainsail foot may be extended. In the absence of the black band, it shall be measured to the point on the boom as aft as the mainsail clew can reach.
Boom diameter BD is measured as a vertical cross section.
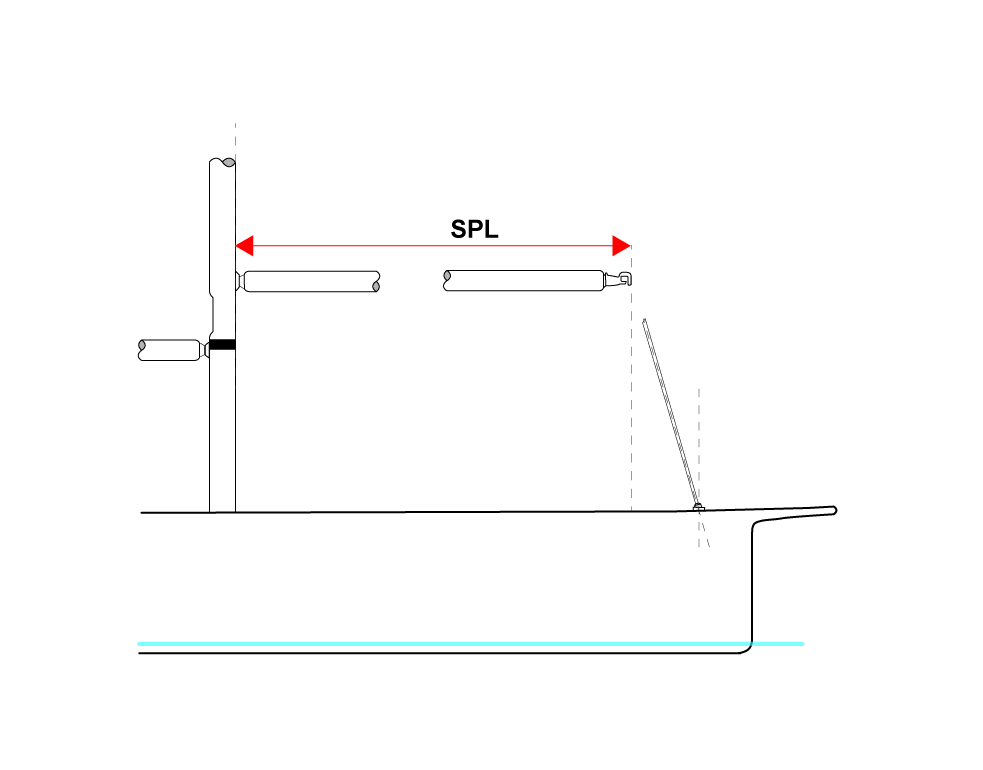
Spinnaker pole and bowsprit
Spinnaker pole length ( SPL ) the horizontal distance from the forward face of the mast spar, ignoring any fittings and tracks, measured on or near the centerline of the boat, to the extremity of the spinnaker pole. . The tack point of spinnaker ( TPS ) when it is tacked on the boat's centerline is the distance from the foreside of the mast to the foremost point on which the asymmetric spinnaker or any headsail set flying can be tacked. If the bowsprit is retractable TPS shall be measured with it in its fully-extended position.
Other rig details
In addition to the measurements set above, the following rig details are also recorded:
- Inner stay , which may be adjustable or fixed
- Foresetay tension , which may be controlled by Forestay, Backstay, Both or be Fixed.
- Number of spreaders
- Number of runners
- Carbon mast and fiber rigging
- Mainsail furler
- Headsail furler
- Use of non-manual power for adjusting running rigging or spars
Offshore Racing Congress Partners

Log in to ORC Sailor services using email and password
ORC Sailor Services allows you access to ORC Database of all ORC certificates issued worldwide such as accessing speed guides, target speeds and do test runs on any certificate.
ORC Sailor Services - Password reminder
Please enter the e-mail address registered for the ORC Sailor Services to receive your password
ORC Sailor Services
With an ORC Certificate you are getting more than just a rating. ORC Sailor Services allows you access to the ORC Database of all ORC certificates issued worldwide.
Sailboat Rigging Specifications: Everything You Need to Know
by Emma Sullivan | Aug 1, 2023 | Sailboat Maintenance

Short answer: Sailboat rigging specifications
Sailboat rigging specifications refer to the measurements and details of the various components that make up a sailboat’s rig. This includes the type and size of the standing rigging (such as shrouds and stays), running rigging (such as halyards and sheets), mast height, boom length, and sail dimensions. These specifications are essential for proper performance, safety, and handling of a sailboat.
1) Understanding Sailboat Rigging Specifications: A Comprehensive Guide
Understanding Sailboat Rigging Specifications: A Comprehensive Guide
Sailing enthusiasts often find themselves entranced by the beauty and grace of a sailboat slicing through the water, powered solely by the wind . But behind every successful sailboat is a well-designed rigging system that plays a crucial role in its performance and safety. In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the world of sailboat rigging specifications, unraveling the intricacies and shedding light on the key aspects every sailor should understand.
To embark on this journey of unraveling sailboat rigging specifications, one must first comprehend their fundamental purpose. Rigging refers to the various components that support and control the sails, enhancing their efficiency in harnessing wind power. It comprises intricate networks of wires, ropes, blocks, pulleys, and fittings meticulously designed to distribute loads evenly across the hull while enabling precise control over sail adjustments.
The importance of understanding these specifications cannot be overstated. Rigging functions as an interconnected system where even slight adjustments can have a profound impact on sailing performance . Familiarity with rigging specifications empowers sailors to optimize their boat’s performance while ensuring safe navigation under diverse weather conditions.
Let’s dive deeper into some essential elements that make up a sailboat ‘s rigging specification:
1) Standing Rigging: The standing rigging forms the backbone of any sailboat ‘s rigging system. It consists predominantly of stainless steel wire cables known as ‘stays’ or ‘shrouds,’ which hold up the mast and distribute its loads across multiple points on the hull. Understanding how factors like wire diameter (gauge), construction (1×19 or 7×7), material grade (316 or 304 stainless steel), and tension affect overall stability plays a vital role in maintaining a balanced vessel capable of handling varying wind conditions.
2) Running Rigging: Unlike standing rigging that remains static during normal sailing operations, running rigging controls various sail adjustments in response to wind conditions. It includes halyards, sheets, and control lines that enable raising and lowering sails, trimming them for maximum efficiency, and altering boom positions. Knowing the properties of different ropes (known as lines) like rope material (nylon, polyester, or Dyneema), diameter, and construction allows sailors to optimize their boat’s performance while ensuring ease of handling.
3) Sail Controls: Sail controls encompass a variety of mechanisms essential for regulating the shape and tension of the sails. Devices such as sail tracks, winches, blocks, travelers, and cleats collaborate harmoniously with rigging components to achieve precise control over sail shape, twist, camber, draft position – all crucial factors influencing both speed and safety. Familiarity with these specifications enables sailors to adeptly adjust their sails’ performance based on wind strength and direction.
4) Safety Considerations: Rigging specifications hold a critical role in ensuring safety during sailing ventures. Inspecting the rigging thoroughly before setting sail is imperative. Checking for corrosion or wear on wire cables, fraying on ropes or lines can help prevent disastrous failures mid-journey. Additionally, understanding load limits associated with each component guarantees sailors neither underload nor overload any part of their rigging system.
By now it should be evident that understanding sailboat rigging specifications is indispensable for every sailor aiming to unlock their vessel’s true potential while prioritizing safety. With constant advancements in materials technology providing an array of options for upgrading rigging systems tailored to specific sailing needs – from club racing to bluewater cruising – keeping abreast of new developments becomes even more crucial.
Maintaining a well-maintained rigging system is not merely about technicalities; it represents an art form that requires skillful orchestration by blending engineering prowess with a deep appreciation for the timeless elegance embodied by these majestic vessels. So next time you set out on your sailboat, take a moment to marvel at the intricate rigging system that steers you toward adventure and understanding .
2) How to Determine the Right Sailboat Rigging Specifications for Your Vessel
In the exciting world of sailing, the rigging of your sailboat plays a crucial role in ensuring a successful, safe, and enjoyable voyage. Just like a well-tailored suit, finding the right specifications for your vessel’s rigging is essential to maximize performance on the water. Whether you’re an experienced sailor or a novice embarking on your first adventure, understanding how to determine the ideal sailboat rigging specifications can make all the difference.
But fear not! We’ve got you covered with some expert tips to help you navigate through this process. Let’s dive in and unravel the mysteries behind finding the perfect rigging setup for your vessel.
1) Understand Your Boat
Before delving into determining proper sailboat rigging specifications, it’s important to comprehend your boat inside out. Consider its design, size, weight distribution, and intended use. No two boats are exactly alike, and thus each requires specific considerations when it comes to rigging .
For example, if you own a racing yacht designed for speed and agility, your rigging will likely be tuned for optimal aerodynamics while maintaining stability. On the other hand, if you have a leisurely cruising boat built for comfort and relaxation, your rigging may focus more on ease of handling without compromising safety.
2) Seek Professional Advice
While it’s tempting to rely solely on your own instincts and knowledge when determining sailboat rigging specifications, consulting a professional is highly recommended. An experienced rigger or naval architect can provide valuable insights based on their expertise and extensive background in handling various vessels.
These professionals can assess factors such as mast height/length ratio (aspect ratio), headstay tension requirements, shroud angles/tensions (depending on single or multiple spreaders), boom height relative to deck level – just to name a few critical parameters that contribute to successful sailboat performance.
3) Analyze Sail Plan
Your boat’s unique characteristics should be accounted for when analyzing the sail plan. Consider the number and types of sails you have or plan to use—main, jib, genoa, or spinnaker—and their respective sizes and geometries. The size and positioning of your sail ‘s luff length, foot length, and clew height will influence rigging decisions.
By understanding the relationship between your vessel’s sail plan and rigging, you can optimize control and response while sailing in various wind conditions. For instance, a high-performance racing yacht may require a more powerful rig with adjustable backstays or hydraulic tensioners to handle large headsails effectively.
4) Safety First
While we all love chasing speed on the water, it’s crucial not to neglect safety considerations when determining rigging specifications. Overloading the rigging beyond its limits can lead to disastrous consequences. Carefully analyze the breaking load ratings of wires/ropes and fittings used in your sailboat’s rig system.
Additionally, regular inspections and maintenance are paramount to detect any potential weaknesses before they become serious issues during your sailing adventures . Never compromise safety for performance gains; instead, strike a balance between both aspects for an enjoyable and secure experience on board.
5) Experiment & Fine-Tune
When it comes to sailboat rigging specifications, finding the perfect setup might require some trial-and-error experimentation combined with meticulous fine-tuning. Keep track of changes made and their effect on different sailing conditions.
Don’t be afraid to reach out to other sailors within your community who might have similar vessels or experiences as they can offer valuable suggestions based on their firsthand encounters. Joining online forums or attending boat shows/seminars can also provide opportunities for networking with like-minded enthusiasts eager to share insights into optimizing sailboat rigging setups.
In conclusion, determining the right sailboat rigging specifications is an art that combines science, experience, and personal preferences. By thoroughly understanding your boat ‘s characteristics, seeking professional advice, analyzing your sail plan, prioritizing safety, and embracing experimentation, you can find the perfect balance that suits your vessel’s needs. So, hoist the sails high and set off on unforgettable sailing adventures with confidence and finesse!
3) Step-by-Step Process: Setting Sailboat Rigging Specifications like a Pro
Title: Mastering the Art of Setting Sailboat Rigging Specifications: A Professional’s Step-by-Step Process
Introduction: Setting sail on a mesmerizing adventure calls for meticulous attention to detail when it comes to sailboat rigging. Even the slightest miscalculation or oversight can have a significant impact on safety, performance, and overall sailing experience. In this article, we unveil a comprehensive step-by-step process that will empower you to set sailboat rigging specifications like a true professional – ensuring smooth navigation and maximizing your boat’s potential. So, fasten your seatbelts (or should we say lifelines), as we embark on this exciting journey!
1) Understanding the Basics: Before diving into the specifics, let’s brush up our understanding of sailboat rigging. Sailboat rigging refers to the collection of intricate systems that support and control the sails aboard a boat . It includes elements such as mast, shrouds, stays, halyards, sheets, and various fittings responsible for tensioning and maneuvering sails .
2) Inspection is Key: To begin our step-by-step process, inspect your entire sailboat meticulously. Look out for signs of wear and tear in the hardware components including shackles, turnbuckles, blocks, cleats – anything that plays a crucial role in securing your rigging. Ensure all fixings are tight and secure; any loose connections can be disastrous while hoisting sails in rough waters .
3) Evaluate the Lines: Next up is evaluating your lines – halyards and sheets. Check for degradation caused by exposure to UV radiation or harsh weather conditions . Replace worn-out lines promptly as frail ropes pose great risks during maneuvers when under high loads.
4) Determine Your Sailing Style: Now it’s time to assess your unique sailing style! Are you an adrenaline-seeking racer or more inclined towards leisurely cruising? This assessment helps understand the necessary adjustments required in rigging setup. Racers typically prefer minimal weight and maximum control, while cruisers prioritize ease of handling and comfort. Knowing your preference will allow you to fine-tune your rigging specifications accordingly.
5) Measurements That Matter: Precise measurements play a vital role in achieving the desired rigging tension and performance. Carefully measure the heights of your mast, boom, and other essential spars to ensure proper alignment during installation . Always refer to manufacturer guidelines for recommended measurements as they vary across different sailboats.
6) Understanding Tension: To create optimal sail shape and performance, understanding tension is crucial. Referred to as tuning the rig, setting proper tension in shrouds and stays allows for controlled sail draft and minimizes distortion under varying wind conditions. Consult professional tuning guides or seek assistance from sailing experts if needed; mastering this skill could significantly impact your boat’s overall stability and speed.
7) Partnering with Professionals: Suppose you find yourself overwhelmed by the complex world of sailboat rigging specifications. In that case, partnering with professionals can be an excellent way to gain valuable insights and guidance specific to your boat’s make and model. Rigging specialists possess extensive knowledge regarding different components, methodologies, and cutting-edge advancements in the industry – guiding you towards optimal rigging configurations tailored to suit your needs.
8) Going Beyond Theory: Putting theoretical knowledge into practice through experimentation is essential when it comes to refining sailboat rigging specifications like a pro. Head out on shorter cruises initially where you can gradually fine-tune adjustments based on real-world sailing experiences . This hands-on approach ensures you become intimately familiar with your boat ‘s behavior under various wind conditions – turning you into a confident skipper who knows their vessel inside out.
Conclusion: Rigging a sailboat may seem daunting but breaking it down into manageable steps demystifies this intricate process. By understanding the basics, inspecting meticulously, evaluating lines, accounting for sailing style, measuring accurately, tensioning skillfully, seeking professional guidance when needed, and continuously experimenting, you’ll be well on your way to becoming a pro at setting sailboat rigging specifications. So go ahead – seize the wind and waves with confidence as you embark on unforgettable journeys aboard your perfectly rigged vessel !
4) FAQs about Sailboat Rigging Specifications Answered
When it comes to sailboat rigging, there are lots of questions that may arise. Understanding the specifications and requirements can be a bit confusing for beginners and even experienced sailors. Fear not! We have compiled some frequently asked questions about sailboat rigging specifications to provide you with comprehensive answers.
1. What are sailboat rigging specifications? Sailboat rigging specifications refer to the guidelines and requirements set for the rigging components on a boat. It includes details such as the type and size of wire used, fittings, tensions, and other important measurements needed to ensure the stability and safety of your sailboat’s mast and sails.
2. Which factors determine the sailboat’s rigging specifications? Several factors come into play when determining sailboat rigging specifications: boat size, displacement, type of sailing (cruising or racing), mast height, length overall, beam width, keel design, mast construction material (aluminum or carbon fiber), among other considerations. Different boats will have different specific requirements based on these factors.
3. Why is it important to adhere to proper sailboat rigging specifications? Adhering to proper sailboat rigging specifications is crucial for maintaining safety while at sea. Rigging components are responsible for supporting the mast and sails in changing weather conditions and intense pressures caused by wind. Without adhering to appropriate specifications, the integrity of your rig could compromise stability or even lead to catastrophic failures like broken masts or torn sails .
4. How often should I inspect my sailboat’s rigging ? Regular inspections of your sailboat’s rigging are essential for identifying any signs of wear or damage which could lead to failure. The frequency of inspections depends on various factors such as how often you use your boat, sailing conditions (rough or calm waters), saltwater exposure (corrosion risks), and age of components. Most experts recommend at least an annual rig inspection, but it’s always a good idea to consult your boat manufacturer or a professional rigger for specific guidance.
5. Can I upgrade my sailboat’s rigging specifications? Yes, upgrading a sailboat’s rigging is possible and sometimes even necessary. Upgrading can improve performance, reduce weight aloft, increase durability, and enhance safety. However, determining the appropriate upgrades requires careful evaluation of your boat ‘s characteristics and intended use. Consulting with experienced sailors or professional riggers will help you make informed decisions about potential upgrades.
6. What are some common signs of worn-out or damaged rigging components? There are several signs that indicate worn-out or damaged rigging components: loose wires or strands, broken strands, rust or corrosion on fittings and wire surfaces, elongation/stretching of wire cables beyond their original length, fraying or chafing of cables near attachment points. Recognizing these symptoms early allows for prompt replacement before they compromise the structural integrity of your sailboat.
In conclusion, understanding sailboat rigging specifications is crucial for the safety and longevity of your vessel. Adhering to proper specifications not only ensures stability but also minimizes the risk of failures while sailing. Regular inspections and timely replacements are key to maintaining reliable rigging. Remember to seek advice from professionals when making changes or upgrades to ensure you choose the right specifications for your boat . Keep sailing safe and enjoy the adventure!
5) The Importance of Sailboat Rigging Specifications: Ensuring Safety and Performance
When it comes to sailboats, safety and performance are paramount. One crucial aspect that often gets overlooked is the rigging specifications. Rigging refers to the system of ropes, wires, and hardware that support and control the sails, ensuring smooth navigation on the water . While it may seem like a mundane technicality, proper sailboat rigging specifications play a pivotal role in both the safety of the crew and the boat’s overall performance.
First and foremost, sailboat rigging specifications are essential for ensuring the safety of everyone onboard. A well-maintained and correctly installed rigging system reduces the risk of accidents, such as mast failure or rig collapse. Sailboats can encounter powerful winds and turbulent waters that put immense strain on their rigging. With precise specifications, sailors can have peace of mind knowing that their boat’s rigging is up to par and capable of withstanding challenging conditions.
Additionally, sailboat rigging specifications are crucial for optimizing performance on the water. An improperly rigged boat can experience inefficiencies in sail trim, resulting in decreased speed and maneuverability. Precision is key when it comes to adjusting tensions in various parts of a sailing vessel’s rigging system – from shrouds and stays to halyards and sheets – as these adjustments directly impact how efficiently a boat harnesses wind power for propulsion.
Not only do accurate sailboat rigging specifications enhance a boat’s speed potential but they also contribute to improved handling characteristics. When every element of the rigging is properly tensioned according to manufacturer recommendations or customized preferences, sailors have better control over their vessel’s stability both while cruising or racing competitively.
Furthermore, maintaining appropriate sailboat rigging specifications aids in prolonging the lifespan of an entire sailing craft. Regular inspections will help identify any signs of wear or damage on hardware components such as clevis pins, turnbuckles, or swage fittings; thus allowing timely replacements before they lead to catastrophic failures. Moreover, old or worn-out rigging can gradually cause stress points to develop on the mast, deck, and hull – compromising structural integrity over time. With meticulous attention to detail and adherence to specifications, sailboat owners can prevent costly repairs or potentially life-threatening situations .
Aside from safety and performance benefits, adhering to sailboat rigging specifications also demonstrates a high level of professionalism. Whether you are an experienced sailor or a novice boat owner, consulting and complying with manufacturer guidelines or hiring expert riggers showcases a deep understanding and respect for the intricate mechanics of sailing vessels. It exemplifies a commitment towards mastering the art of sailing and upholding industry standards.
In conclusion, sailboat rigging specifications might appear insignificant at first glance; however, their importance cannot be underestimated when it comes to safety, performance optimization, vessel longevity, and professional responsibility. By ensuring that every aspect of a sailboat’s rigging complies with established guidelines or customized preferences within safe parameters provided by manufacturers and experts alike — sailors can enjoy not only smooth-sailing experiences but also preserve the overall value of their prized watercraft. So before setting off on your next nautical adventure, take the time to pay attention to your sailboat’s rigging specifications – it could make all the difference in creating a memorable voyage while safeguarding everyone onboard.
6) Top Factors to Consider when Choosing Sailboat Rigging Specifications
When it comes to sailboat rigging specifications, there are several factors that every sailor should consider before making a decision. The rigging plays a crucial role in the performance and safety of your sailboat, so choosing the right specifications is paramount. In this article, we will outline the top factors to consider when selecting sailboat riggin…
1) Type of Sailboat : The first factor to consider is the type of sailboat you own or plan to purchase. Different types of sailboats have different rigging requirements. For example, a racing yacht would require a more sophisticated and adjustable rigging system compared to a small pleasure cruiser. Understanding your sailboat’s design and intended use will help you narrow down your options.
2) Material: The material used for the rigging greatly impacts its durability and performance. Stainless steel is widely regarded as the best choice due to its resistance to corrosion and high tensile strength. However, there are different grades of stainless steel, such as 316 marine-grade or 304 structural-grade, each offering varying levels of durability and cost-effectiveness.
3) Size and Diameter: Choosing the appropriate size and diameter for your sailboat’s rigging is crucial. It is important to find a balance between strength and weight. Thicker rigging provides more strength but adds unnecessary weight that may impact sailing performance . On the other hand, skimping on thickness compromises safety during heavy winds or rough seas.
4) Rig Configuration: Consider how you want your sailboat rigged – whether it’s a single mast with one main sail or multiple masts with various sails. The type of rig configuration affects not only your boat ‘s maneuverability but also its overall complexity and maintenance requirements.
5) Cost: While it’s tempting to opt for cheaper options, remember that quality always comes at a price. Investing in high-quality rigging may save you money in the long run by minimizing maintenance costs or potential failures. However, this doesn’t mean you have to break the bank – finding a balance between quality and cost-effectiveness is key.
6) Expert Advice: Finally, consulting with industry professionals or experienced sailors can provide valuable insights before finalizing your rigging specifications. They can offer advice based on their expertise and personal experiences, helping you navigate the vast array of choices in the market.
In conclusion, sailboat rigging specifications should not be taken lightly. Considering factors such as sailboat type , material, size and diameter, rig configuration, cost, and seeking expert advice will ensure that your sailboat’s rigging meets your specific needs. By carefully assessing these factors, you can set sail with confidence knowing that your rigging is both reliable and efficient.
Recent Posts
- Approaching a Mooring Buoy: Essential Tips for Safe Navigation
- Best Tiller Autopilot: Enhance Your Sailing Experience
- Nautical Navigator: Essential Tools and Techniques for Seamanship
- Sail Making Material: A Comprehensive Guide
- 2 Person Dinghy: The Ultimate Guide to Choosing the Perfect Boat
- Sailboat Gear and Equipment
- Sailboat Lifestyle
- Sailboat Maintenance
- Sailboat Racing
- Sailboat Tips and Tricks
- Sailboat Types
- Sailing Adventures
- Sailing Destinations
- Sailing Safety
- Sailing Techniques
Home > Resources > Rig Specification Diagram For Sailboats: Mainsail & Headsail
Rig Specification Diagram For Sailboats: Mainsail & Headsail
30 December 2020
Ask Precision Sails , Design , Featuring - Partners , Headsail , Mainsail , Measurements , Sails , Technical Tags: Furling , Headsail , Mainsail , Precision Sails , rig , Sails , Specifications , Specs
Sailboat Rig Specs: Precision Sails Defined
The above infographic shows how Precision Sails label sailboat rig specifications. Continue reading below to see definitions and basic how-to tips on how to measure them below. Rig specs are important for designing a sail suited for your applications and boat. When you decide to get a custom sail from Precision, in most cases, you will be taking your own boats measurements. So it’s important to know about rig specs!
One thing we tell sailors here at precision is “The effort you put into measuring really does translate into the quality of sail you get” If quality measurements are given to designers, it allows them to create an excellent performing sail. It’s essential that good information is passed on to the designers when they create your sail.
The more information you can give to us, the better. One detail we strive to get right with sailors is the sailboats measurements. Taking your own sail boats measurements is an imperative part of creating a custom sail.
Photographs are also a handy tool. They let our designers understand your rigs better and can make suggestions and improvements.
Sometimes sailors think sails are like Lego, or the marine equivalent of a Honda Civic car part, where you can just swap out sails like its nothing. But this isn’t further from the truth. Sailboats are handmade. There can be many differences from one model to the next. Your boat might not be fresh out of the boatyard. It might be 36 or more years old, all this time equates to the boat changing, modifications being made, new parts being installed, break in periods, different maintenance intervals. There are a whole slew of reasons why your boat’s rig specs could be, and probably are, different from the next. This is the main reason we are so thorough with our measurement forms and design process.
Mainsail Rig Specs
P – Maximum Mainsail Hoist Length (Maximum luff): On the main halyard, hoist a measuring tape measure until it stops without jamming the halyard into the shiv. Measure straight down along the mast to the top of the boom at the tack. Disconnect Mainsail from Halyard. Be sure the boom is in the normal sailing position.
E – Maximum Foot Length: Measure from the aft face of the mast to the shackle of the outhaul. Make sure the outhaul is pulled back to it’s tightest position. When you get a maximum foot length we are not actually going to design the sail exactly to that length but rather a couple inches shorter. This allows you to adjust your outhull and not have your adjustments pushed against the shiv at the end of the boom, as well as changing tension in the sail.
Backstay Measurement: This measurement serves as a guide so we know how far the leech of your sail can be pushed without it overlapping the backstay. Sometimes you want this for certain performance reasons, but most cruisers do not want it to overlap, because it results in less wear.
Headsail Rig Specs
I – Foretriangle Height: Measure from the top of the halyard to the side deck on the forward side of the mast.
J – Foretriangle Base: Measure along deck from the forestay to the Forward face of mast. The J measurement is just a secondary check to make sure nothing has been changed over the years and there’s no surprises.
1. First Hank: Measure from tack to the first hank position on headstay wire above turnbuckle.
2. Maximum Luff Measurement: Measure from top of halyard to the bearing point of tack fitting
3. Waterline to Forestay: At the bow, measure the vertical distance from the waterline up to the intersection of the deck and forestay.
4. Waterline to Base: At the front of the mast, measure the vertical distance from the waterline up to the deck.
5. Headstay to Forward Track: Measure from tack attachment on deck to the forward edge of the headsail track you will be sheeting to.
Furling Head Sails
Headsail rig dimensions change slightly with a furling unit. The following videos do a good job of displaying the process of taking the measurements.
Furling drum height: Measure from the deck to the location of the tack attachment point on your furling drum. Measure the pennant separately.
After you get us your measurements. We will start customizing the design of your sail. There will be a consultation during the design process. We get you involved with this process because there are several things you can adjust for your sail – how far do you want the clew off the deck, where do you want the clew to sit and any thing else you might think of.
Put the knowledge you just gained into good use and take some good measurements! If you’re in need of a sail request a quote!
precisionsails
Related Posts

Full Battens vs Partial Battens vs 2 Full plus 2 Partial Battens
Full Battens VS Partial Battens At
Precision Sails we are asked every day during our customer quote consultation “Should I choose Full Battens or Partial Battens for my new mainsail?” Whether you are cruising or racing you will need to examine the pros and cons of adding full battens to your main sail.Positive Aspects of Full […]
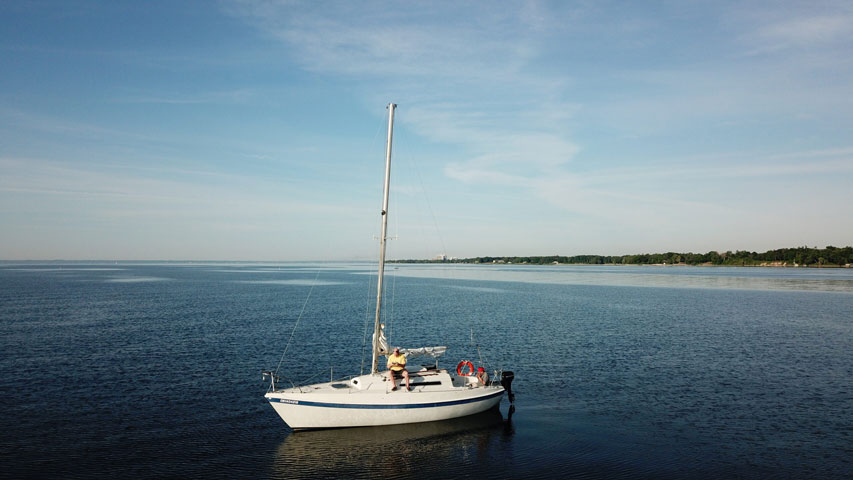

Memories of Sail Repairs, Replacement Sails and FINALLY New Sails
I have had a Tanzer 26 for over 20 years now. The vessel, without much imagination I call The Boat, has served me well and without complaint through yearly cruises on Lake Ontario with my three kids and day sailing with the wife. Did I mention that my wife is a good sport but a definitive lover of a good.

My Need for Cruising Speed Demands a Great Suit of Sails
My Need for Cruising Speed Demands a Great Suit of SailsI like to sail fast mostly in the heavy winds that Lake Ontario throws.
" * " indicates required fields
- Types of Sailboats
- Parts of a Sailboat
- Cruising Boats
- Small Sailboats
- Design Basics
- Sailboats under 30'
- Sailboats 30'-35
- Sailboats 35'-40'
- Sailboats 40'-45'
- Sailboats 45'-50'
- Sailboats 50'-55'
- Sailboats over 55'
- Masts & Spars
- Knots, Bends & Hitches
- The 12v Energy Equation
- Electronics & Instrumentation
- Build Your Own Boat
- Buying a Used Boat
- Choosing Accessories
- Living on a Boat
- Cruising Offshore
- Sailing in the Caribbean
- Anchoring Skills
- Sailing Authors & Their Writings
- Mary's Journal
- Nautical Terms
- Cruising Sailboats for Sale
- List your Boat for Sale Here!
- Used Sailing Equipment for Sale
- Sell Your Unwanted Gear
- Sailing eBooks: Download them here!
- Your Sailboats
- Your Sailing Stories
- Your Fishing Stories
- Advertising
- What's New?
- Chartering a Sailboat
- Sail Dimensions
What Sail Dimensions are Required to Calculate Sail Areas?
The required sail dimensions for calculating the area of any triangular sails are usually its height and the length of its foot. But that only works for mainsails and mizzens with no roach, and jibs with a 90 degree angle at the clew - and what about high-cut headsails, spinakers and cruising chutes? Read on...
Foresail and mainsail dimensions are universally referenced with the letters 'J', 'I', 'E' and 'P' approximating to the length of the foredeck, height of the mast, length of the boom and the height of the main sail - but more accurately defined further down this page.
Yacht designers need these sail dimensions to calculate thought provoking stuff such as the sail-area/displacement ratios of their creations, and sailmakers need them before they put scissors to sailcloth.
If our sailboat's sails were perfectly triangular then, as every schoolboy knows, their area would be 'half the height, times the base' - but with the possible exception of a mainsail with a straight luff, generally they're not. Here's how it works...
Main and Mizzen Sail Dimensions
These are almost right-angled triangles except for the curvature of the leach (the 'roach') which increases the sail area.

It's usually calculated as:~
Area = (luff x foot)/1.8, or
Area = ( P x E )/1.8, where:~
- 'P' is the distance along the aft face of the mast from the top of the boom to the highest point that the mainsail can be hoisted, and
- 'E' is the distance along the boom from the aft face of the mast to the outermost point on the boom to which the main can be pulled.
For the mizzen sails on ketches and yawls , 'P' and 'E' relate to the mizzen mast and boom.
For more heavily roached sails, the increased area can be accounted for by reducing the denominator in the formula to 1.6.
Clearly calculating sail areas isn't going to be an exact science...
Jibs, Genoas and Staysail Dimensions

For a working jib that fills the fore triangle - but no more - and with a foot that's parallel to the deck, then you've got a 'proper' right-angled triangular sail, whose area is:~
Area = (luff x foot)/2, or
Area = ( I x J )/2, where:~
- 'I' is the distance down the front of mast from the genoa halyard to the level of the main deck, and
- 'J' is the distance along the deck from the headstay pin to the front of the mast.
Genoas, by definition, have a clew which extends past the mast and are described by the amount by which they do so. For instance a 135% genoa has a foot 35% longer than 'J' and a 155% genoa 55% longer. Areas are calculated as follows:~
Area (135% genoa) = (1.44 x I x J )/2, and
Area (155% genoa) = (1.65 x I x J )/2
High-cut Headsails

But these formulae don't work for a high-cut jib with a raised clew - unless you imagine the sail turned on its side such that the luff is the base and the luff perpendicular is the height.
It's still a simple calculation though, once you know the length of the luff perpendicular ( LP ), the sail area is:~
Area = (luff x luff perpendicular)/2, or
Area = ( L x LP )/2, where:~
- 'L' is the distance along the forestay from the headstay pin to the front of the mast, and
- 'LP' is the shortest distance between the clew and the luff of the genoa.
Spinnaker Sail Dimensions
Much like calculating foresail areas, but with different multipliers for conventional spinnakers and asymmetric spinnakers...
Conventional Spinnakers
Area = (0.9 x luff x foot), or
Area = (0.9 x I x J ), where:~
- 'I' is the distance from the highest spinnaker halyard to the deck, and
- 'J' is the length of the spinnaker pole.
Asymmetric Spinnakers
Area = (0.8 x luff x foot), or
Area = (0.8 x I x J ), where:~
- 'I' is the distance from the highest spinnaker halyard to the deck, and
- 'J' is the distance from the front face of the mast to the attachment block for the tackline.
More about Sails...

Are Molded and Laminate Sails One Step Too Far for Cruising Sailors?
Although woven sails are the popular choice of most cruising sailors, laminate sails and molded sails are the way to go for top performance. But how long can you expect them to last?

Is Carrying Storm Sails on Your Cruising Boat Really Necessary?
It's good insurance to have storm sails available in your sail locker if you are going offshore, and these are recommended fabric weights and dimensions for the storm jib and trysail

Using Spinnaker Sails for Cruising without the Drama!
When the wind moves aft and the lightweight genoa collapses, you need one of the spinnaker sails. But which one; conventional or asymmetric? Star cut, radial head or tri-radial?

The Mainsail on a Sailboat Is a Powerful Beast and Must Be Controlled
Learn how to hoist the mainsail, jibe it, tack it, trim it, reef it and control it with the main halyard, the outhaul, the mainsheet and the kicker.

Is Dacron Sail Cloth Good Enough for Your Standard Cruising Sails?
Whilst Dacron sail cloth is the least expensive woven fabric for standard cruising sails, do the superior qualities of the more hi-tech fabrics represent better value for money?
Recent Articles
'Natalya', a Jeanneau Sun Odyssey 54DS for Sale
Mar 17, 24 04:07 PM
'Wahoo', a Hunter Passage 42 for Sale
Mar 17, 24 08:13 AM
Used Sailing Equipment For Sale
Feb 28, 24 05:58 AM
Here's where to:
- Find Used Sailboats for Sale...
- Find Used Sailing Gear for Sale...
- List your Sailboat for Sale...
- List your Used Sailing Gear...
- Sign-up for our newsletter, 'The Sailboat Cruiser' ...
- Identify this month's Mystery Boat...
Our eBooks...

A few of our Most Popular Pages...

Copyright © 2024 Dick McClary Sailboat-Cruising.com
Sailboat Parts Explained: Illustrated Guide (with Diagrams)
When you first get into sailing, there are a lot of sailboat parts to learn. Scouting for a good guide to all the parts, I couldn't find any, so I wrote one myself.
Below, I'll go over each different sailboat part. And I mean each and every one of them. I'll walk you through them one by one, and explain each part's function. I've also made sure to add good illustrations and clear diagrams.
This article is a great reference for beginners and experienced sailors alike. It's a great starting point, but also a great reference manual. Let's kick off with a quick general overview of the different sailboat parts.
General Overview
The different segments
You can divide up a sailboat in four general segments. These segments are arbitrary (I made them up) but it will help us to understand the parts more quickly. Some are super straightforward and some have a bit more ninja names.
Something like that. You can see the different segments highlighted in this diagram below:
The hull is what most people would consider 'the boat'. It's the part that provides buoyancy and carries everything else: sails, masts, rigging, and so on. Without the hull, there would be no boat. The hull can be divided into different parts: deck, keel, cabin, waterline, bilge, bow, stern, rudder, and many more.
I'll show you those specific parts later on. First, let's move on to the mast.

Sailboats Explained
The mast is the long, standing pole holding the sails. It is typically placed just off-center of a sailboat (a little bit to the front) and gives the sailboat its characteristic shape. The mast is crucial for any sailboat: without a mast, any sailboat would become just a regular boat.
I think this segment speaks mostly for itself. Most modern sailboats you see will have two sails up, but they can carry a variety of other specialty sails. And there are all kinds of sail plans out there, which determine the amount and shape of sails that are used.
The Rigging
This is probably the most complex category of all of them.
Rigging is the means with which the sails are attached to the mast. The rigging consists of all kinds of lines, cables, spars, and hardware. It's the segment with the most different parts.
The most important parts
If you learn anything from this article, here are the most important parts of any sailboat. You will find all of these parts in some shape or form on almost any sailboat.

Okay, we now have a good starting point and a good basic understanding of the different sailboat parts. It's time for the good stuff. We're going to dive into each segment in detail.
Below, I'll go over them one by one, pointing out its different parts on a diagram, listing them with a brief explanation, and showing you examples as well.
After reading this article, you'll recognize every single sailboat part and know them by name. And if you forget one, you're free to look it up in this guide.
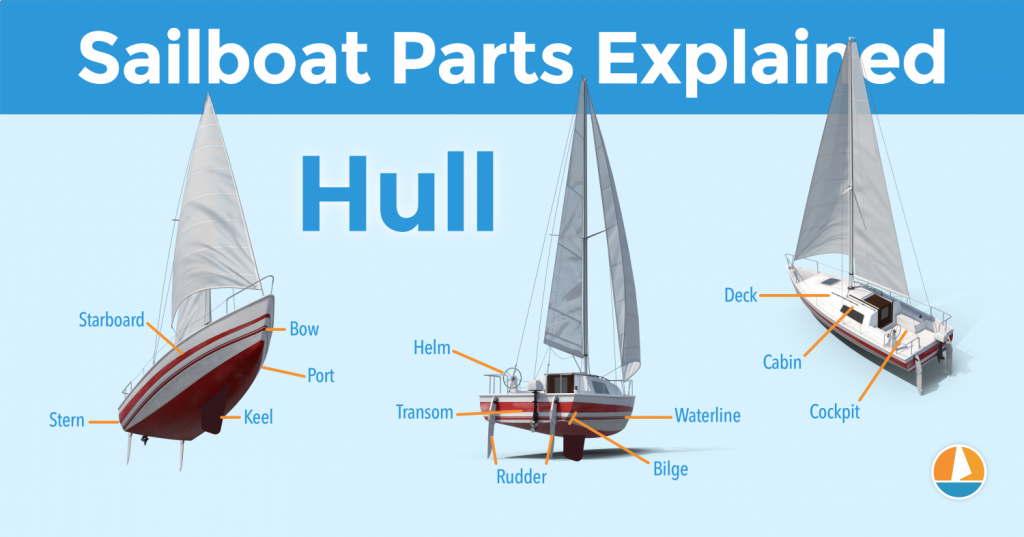
On this page:
The hull is the heart of the boat. It's what carries everything: the mast, the sails, the rigging, the passengers. The hull is what provides the sailboat with its buoyancy, allowing it to stay afloat.
Sailboats mostly use displacement hulls, which is a shape that displaces water when moving through it. They are generally very round and use buoyancy to support its own weight. These two characteristics make sure it is a smooth ride.
There are different hull shapes that work and handle differently. If you want to learn more about them, here's the Illustrated Guide to Boat Hull Types (with 11 Examples ). But for now, all we need to know is that the hull is the rounded, floating part of any sailboat.
Instead of simply calling the different sides of a hull front, back, left and right , we use different names in sailing. Let's take a look at them.
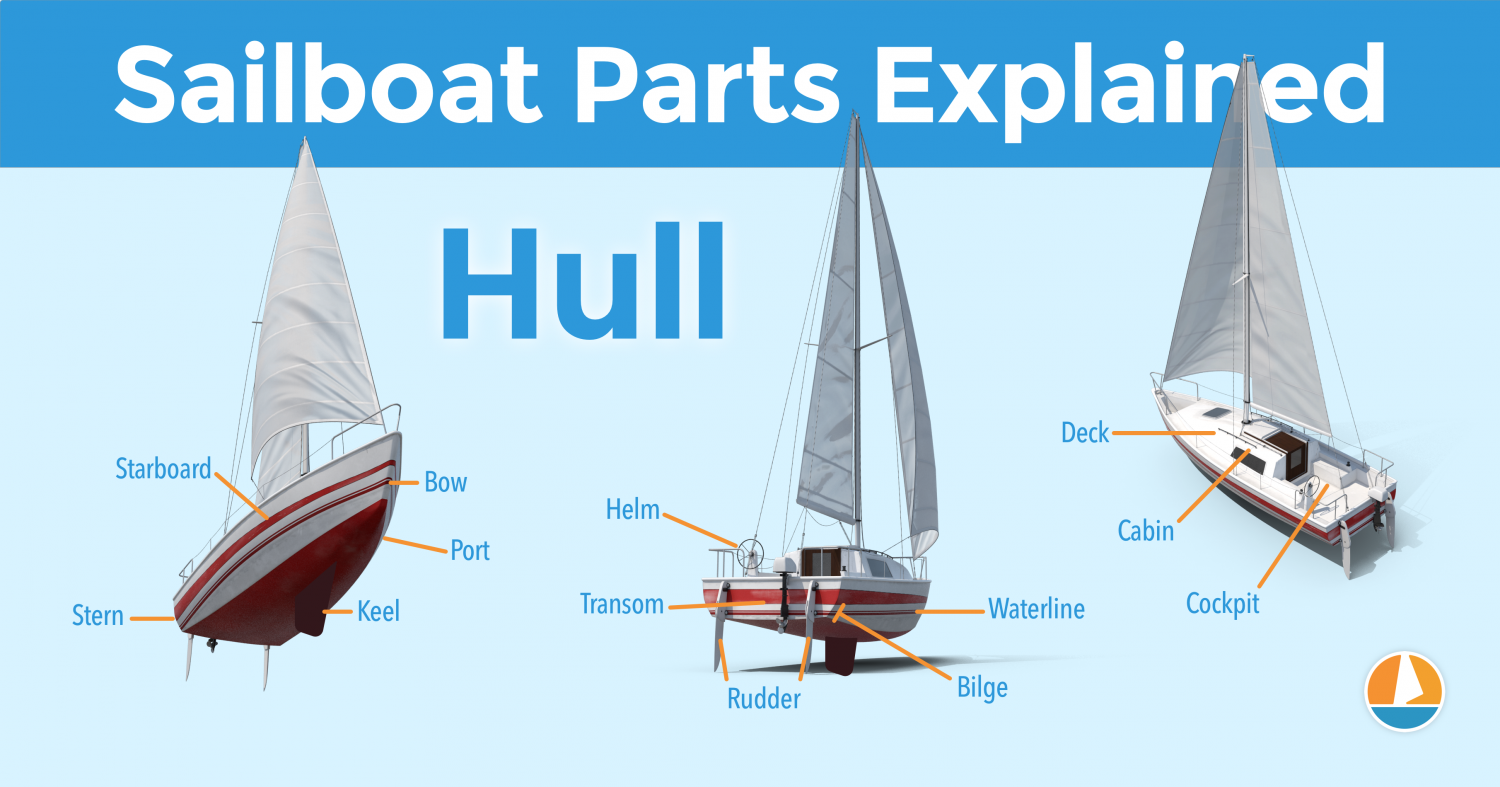
The bow is the front part of the hull. It's simply the nautical word for 'front'. It's the pointy bit that cuts through the water. The shape of the bow determines partially how the boat handles.
The stern is the back part of the hull. It's simply the nautical word for 'back'. The shape of the stern partially determines the stability and speed of the boat. With motorboats, the stern lies deep inside the water, and the hull is flatter aft. Aft also means back. This allows it to plane, increasing the hull speed. For sailboats, stability is much more important, so the hull is rounded throughout, increasing its buoyancy and hydrodynamic properties.
The transom is the backplate of the boat's hull. It's the most aft (rear) part of the boat.
Port is the left side of a sailboat.
Starboard is the right side of a sailboat
The bilges are the part where the bottom and the sides of the hull meet. On sailboats, these are typically very round, which helps with hydrodynamics. On powerboats, they tend to have an angle.
The waterline is the point where the boat's hull meets the water. Generally, boat owners paint the waterline and use antifouling paint below it, to protect it from marine growth.
The deck is the top part of the boat's hull. In a way, it's the cap of the boat, and it holds the deck hardware and rigging.
Displacement hulls are very round and smooth, which makes them very efficient and comfortable. But it also makes them very easy to capsize: think of a canoe, for example.
The keel is a large fin that offsets the tendency to capsize by providing counterbalance. Typically, the keel carries ballast in the tip, creating a counterweight to the wind's force on the sails.
The rudder is the horizontal plate at the back of the boat that is used to steer by setting a course and maintaining it. It is connected to the helm or tiller.
Tiller or Helm
- The helm is simply the nautical term for the wheel.
- The tiller is simply the nautical term for the steering stick.
The tiller or helm is attached to the rudder and is used to steer the boat. Most smaller sailboats (below 30') have a tiller, most larger sailboats use a helm. Large ocean-going vessels tend to have two helms.
The cockpit is the recessed part in the deck where the helmsman sits or stands. It tends to have some benches. It houses the outside navigation and systems interfaces, like the compass, chartplotter, and so on. It also houses the mainsheet traveler and winches for the jib. Most boats are set up so that the entire vessel can be operated from the cockpit (hence the name). More on those different parts later.
Most larger boats have some sort of roofed part, which is called the cabin. The cabin is used as a shelter, and on cruising sailboats you'll find the galley for cooking, a bed, bath room, and so on.
The mast is the pole on a sailboat that holds the sails. Sailboats can have one or multiple masts, depending on the mast configuration. Most sailboats have only one or two masts. Three masts or more is less common.
The boom is the horizontal pole on the mast, that holds the mainsail in place.
The sails seem simple, but actually consist of many moving parts. The parts I list below work for most modern sailboats - I mean 90% of them. However, there are all sorts of specialty sails that are not included here, to keep things concise.

The mainsail is the largest sail on the largest mast. Most sailboats use a sloop rigging (just one mast with one bermuda mainsail). In that case, the main is easy to recognize. With other rig types, it gets more difficult, since there can be multiple tall masts and large sails.
If you want to take a look at the different sail plans and rig types that are out there, I suggest reading my previous guide on how to recognize any sailboat here (opens in new tab).
Sail sides:
- Leech - Leech is the name for the back side of the sail, running from the top to the bottom.
- Luff - Luff is the name for the front side of the sail, running from the top to the bottom.
- Foot - Foot is the name for the lower side of the sail, where it meets the boom.
Sail corners:
- Clew - The clew is the lower aft (back) corner of the mainsail, where the leech is connected to the foot. The clew is attached to the boom.
- Tack - The tack is the lower front corner of the mainsail
- Head - The head is the top corner of the mainsail
Battens are horizontal sail reinforcers that flatten and stiffen the sail.
Telltales are small strings that show you whether your sail trim is correct. You'll find telltales on both your jib and mainsail.
The jib is the standard sized headsail on a Bermuda Sloop rig (which is the sail plan most modern sailboats use).
As I mentioned: there are all kinds, types, and shapes of sails. For an overview of the most common sail types, check out my Guide on Sail Types here (with photos).
The rigging is what is used to attach your sails and mast to your boat. Rigging, in other words, mostly consists of all kinds of lines. Lines are just another word for ropes. Come to think of it, sailors really find all kinds of ways to complicate the word rope ...
Two types of rigging
There are two types of rigging: running and standing rigging. The difference between the two is very simple.
- The running rigging is the rigging on a sailboat that's used to operate the sails. For example, the halyard, which is used to lower and heave the mainsail.
- The standing rigging is the rigging that is used to support the mast and sail plan.
Standing Rigging
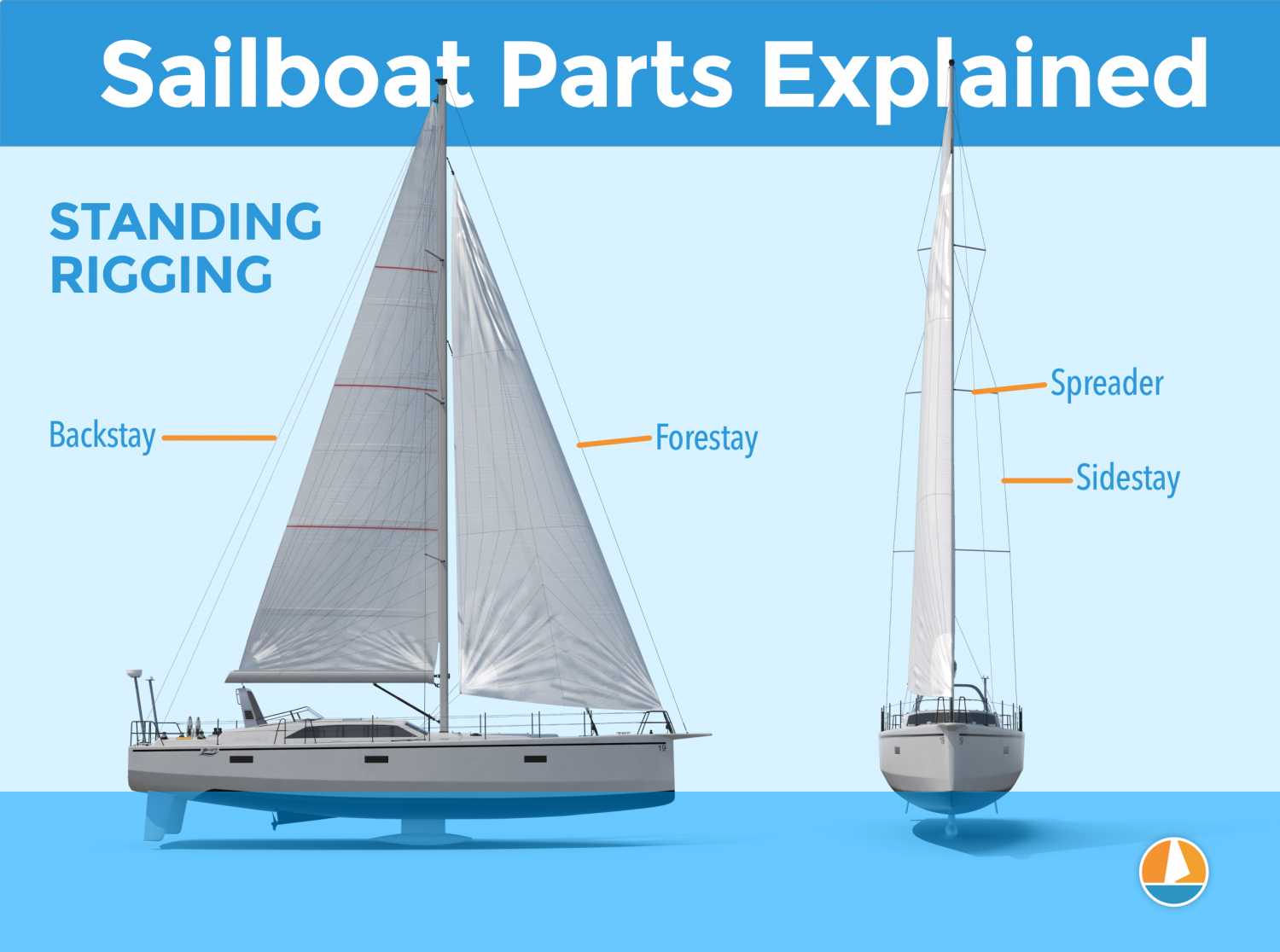
Here are the different parts that belong to the standing rigging:
- Forestay or Headstay - Line or cable that supports the mast and is attached to the bow of the boat. This is often a steel cable.
- Backstay - Line or cable that supports the mast and is attached to the stern of the boat. This is often a steel cable.
- Sidestay or Shroud - Line or cable that supports the mast from the sides of the boat. Most sailboats use at least two sidestays (one on each side).
- Spreader - The sidestays are spaced to steer clear from the mast using spreaders.
Running Rigging: different words for rope
Ropes play a big part in sailing, and especially in control over the sails. In sailboat jargon, we call ropes 'lines'. But there are some lines with a specific function that have a different name. I think this makes it easier to communicate with your crew: you don't have to define which line you mean. Instead, you simply shout 'mainsheet!'. Yeah, that works.
Running rigging consists of the lines, sheets, and hardware that are used to control, raise, lower, shape and manipulate the sails on a sailboat. Rigging varies for different rig types, but since most sailboats are use a sloop rig, nearly all sailboats use the following running rigging:
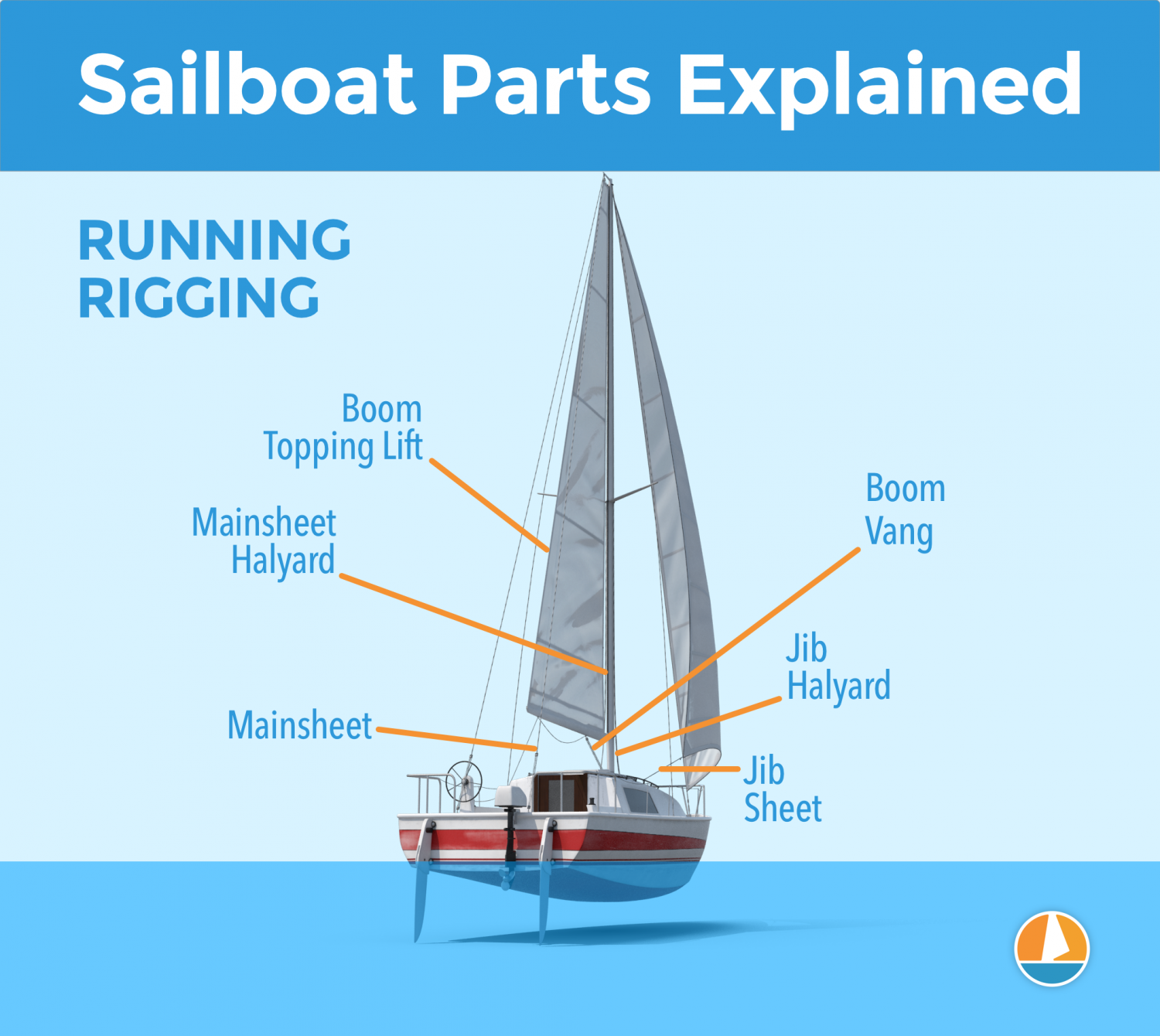
- Halyards -'Halyard' is simply the nautical name for lines or ropes that are used to raise and lower the mainsail. The halyard is attached to the top of the mainsail sheet, or the gaffer, which is a top spar that attaches to the mainsail. You'll find halyards on both the mainsail and jib.
- Sheets - 'Sheet' is simply the nautical term for lines or ropes that are used to set the angle of the sail.
- Mainsheet - The line, or sheet, that is used to set the angle of the mainsail. The mainsheet is attached to the Mainsheet traveler. More on that under hardware.
- Jib Sheet - The jib mostly comes with two sheets: one on each side of the mast. This prevents you from having to loosen your sheet, throwing it around the other side of the mast, and tightening it. The jib sheets are often controlled using winches (more on that under hardware).
- Cleats are small on-deck hooks that can be used to tie down sheets and lines after trimming them.
- Reefing lines - Lines that run through the mainsail, used to put a reef in the main.
- The Boom Topping Lift is a line that is attached to the aft (back) end of the boom and runs to the top of the mast. It supports the boom whenever you take down the mainsail.
- The Boom Vang is a line that places downward tension on the boom.
There are some more tensioning lines, but I'll leave them for now. I could probably do an entire guide on the different sheets on a sailboat. Who knows, perhaps I'll write it.
This is a new segment, that I didn't mention before. It's a bit of an odd duck, so I threw all sorts of stuff into this category. But they are just as important as all the other parts. Your hardware consists of cleats, winches, traveler and so on. If you don't know what all of this means, no worries: neither did I. Below, you'll find a complete overview of the different parts.
Deck Hardware
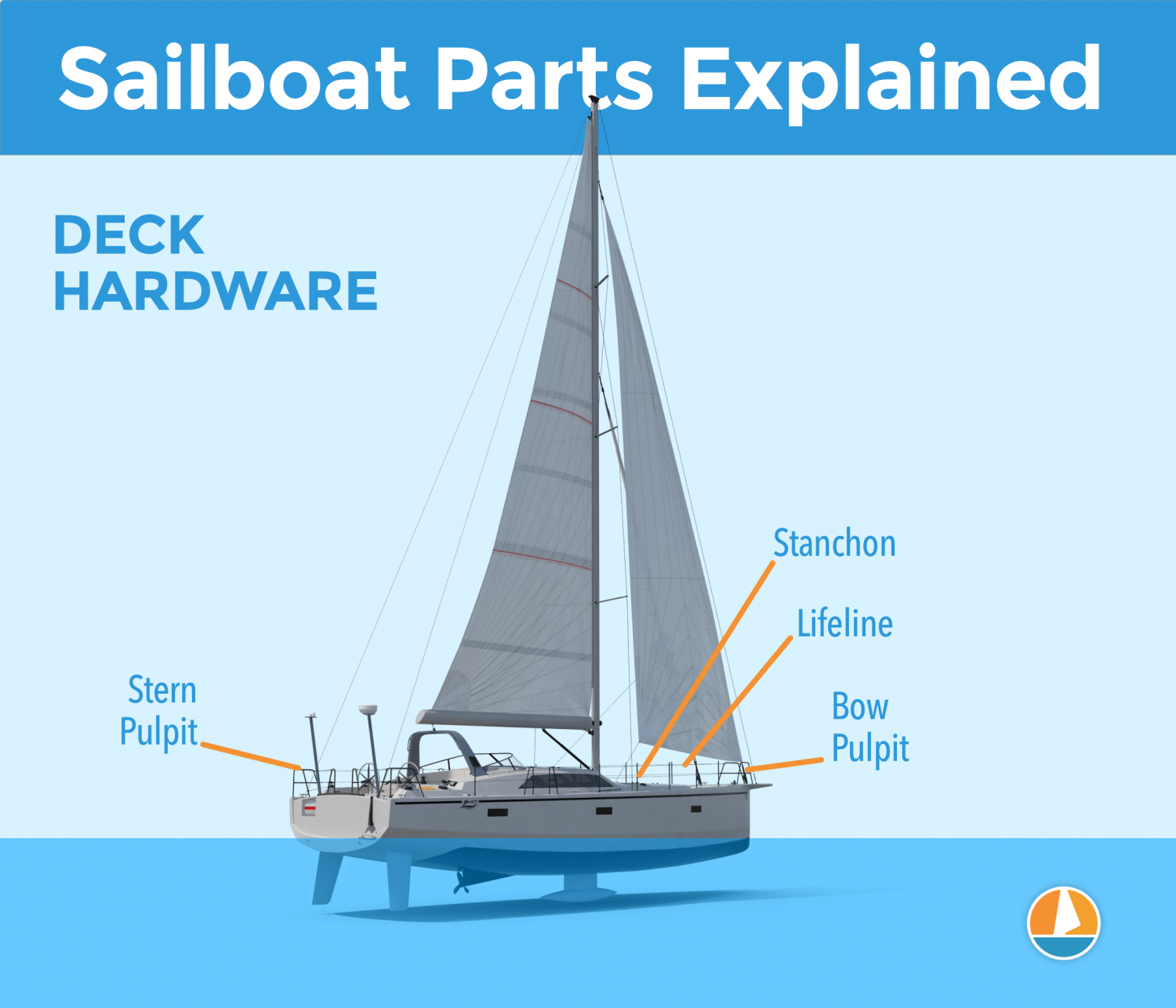
Just a brief mention of the different deck hardware parts:
- Pulpits are fenced platforms on the sailboat's stern and bow, which is why they are called the bow pulpit and stern pulpit here. They typically have a solid steel framing for safety.
- Stanchons are the standing poles supporting the lifeline , which combined for a sort of fencing around the sailboat's deck. On most sailboats, steel and steel cables are used for the stanchons and lifelines.
Mainsheet Traveler
The mainsheet traveler is a rail in the cockpit that is used to control the mainsheet. It helps to lock the mainsheet in place, fixing the mainsails angle to the wind.

If you're interested in learning more about how to use the mainsheet traveler, Matej has written a great list of tips for using your mainsheet traveler the right way . It's a good starting point for beginners.
Winches are mechanical or electronic spools that are used to easily trim lines and sheets. Most sailboats use winches to control the jib sheets. Modern large sailing yachts use electronic winches for nearly all lines. This makes it incredibly easy to trim your lines.

You'll find the compass typically in the cockpit. It's the most old-skool navigation tool out there, but I'm convinced it's also one of the most reliable. In any way, it definitely is the most solid backup navigator you can get for the money.
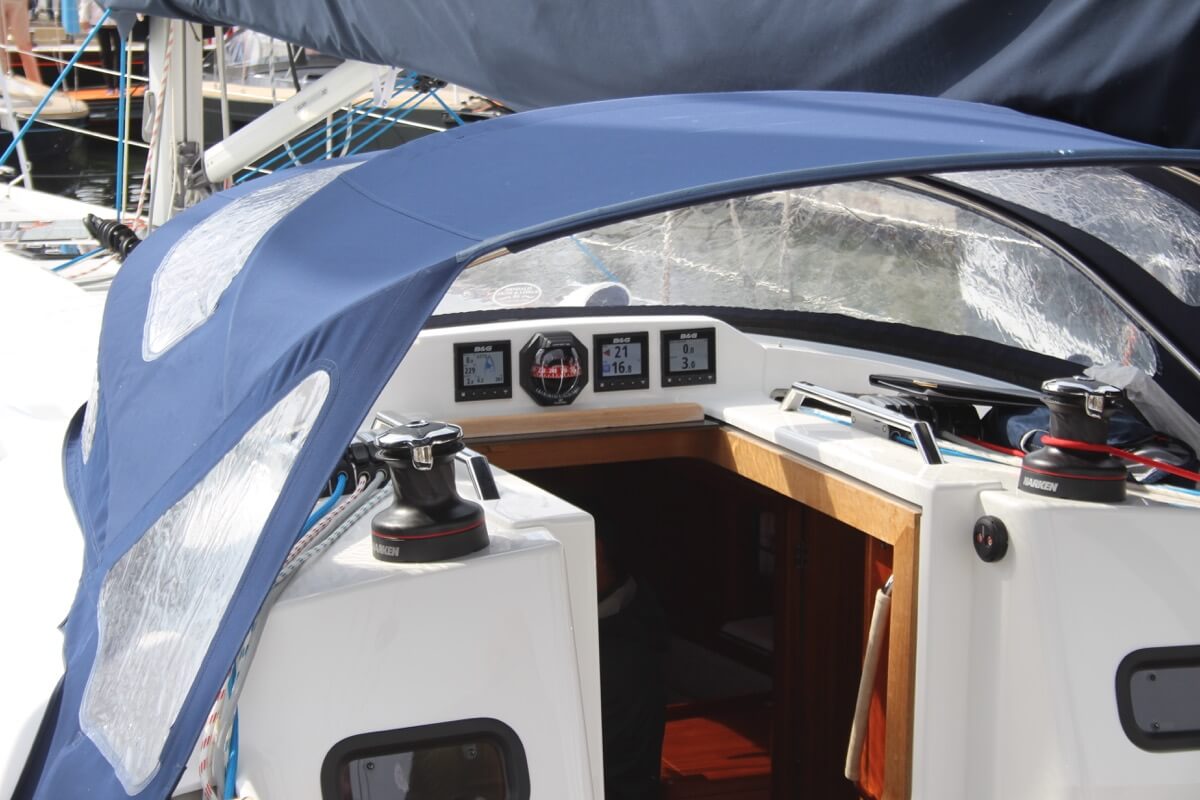

Want to learn how to use a compass quickly and reliably? It's easy. Just read my step-by-step beginner guide on How To Use a Compass (opens in new tab .
Chartplotter
Most sailboats nowadays use, besides a compass and a map, a chartplotter. Chartplotters are GPS devices that show a map and a course. It's very similar to your normal car navigation.

Outboard motor
Most sailboats have some sort of motor to help out when there's just the slightest breeze. These engines aren't very big or powerful, and most sailboats up to 32' use an outboard motor. You'll find these at the back of the boat.

Most sailboats carry 1 - 3 anchors: one bow anchor (the main one) and two stern anchors. The last two are optional and are mostly used by bluewater cruisers.

I hope this was helpful, and that you've gained a good understanding of the different parts involved in sailing. I wanted to write a good walk-through instead of overwhelming you with lists and lists of nautical terms. I hope I've succeeded. If so, I appreciate any comments and tips below.
I've tried to be as comprehensive as possible, without getting into the real nitty gritty. That would make for a gigantic article. However, if you feel I've left something out that really should be in here, please let me know in the comments below, so I can update the article.
I own a small 20 foot yacht called a Red witch made locally back in the 70s here in Western Australia i found your article great and enjoyed reading it i know it will be a great help for me in my future leaning to sail regards John.
David Gardner
İ think this is a good explanation of the difference between a ”rope” and a ”line”:
Rope is unemployed cordage. In other words, when it is in a coil and has not been assigned a job, it is just a rope.
On the other hand, when you prepare a rope for a specific task, it becomes employed and is a line. The line is labeled by the job it performs; for example, anchor line, dock line, fender line, etc.
Hey Mr. Buckles
I am taking on new crew to race with me on my Flying Scot (19ft dingy). I find your Sailboat Parts Explained to be clear and concise. I believe it will help my new crew learn the language that we use on the boat quickly without being overwhelmed.
PS: my grandparents were from Friesland and emigrated to America.
Thank you Shawn for the well written, clear and easy to digest introductory article. Just after reading this first article I feel excited and ready to set sails and go!! LOL!! Cheers! Daniel.
steve Balog
well done, chap
Great intro. However, the overview diagram misidentifies the cockpit location. The cockpit is located aft of the helm. Your diagram points to a location to the fore of the helm.
William Thompson-Ambrose
An excellent introduction to the basic anatomy and function of the sailboat. Anyone who wants to start sailing should consider the above article before stepping aboard! Thank-you
James Huskisson
Thanks for you efforts mate. We’ve all got to start somewhere. Thanks for sharing. Hoping to my first yacht. 25ft Holland. Would love to cross the Bass Strait one day to Tasmania. 👌 Cheers mate
Alan Alexander Percy
thankyou ijust aquired my first sailboat at 66yrs of age its down at pelican point a beautifull place in virginia usa my sailboat is a redwing 30 if you are ever in the area i wouldnt mind your guidance and superior knowledge of how to sail but iam sure your fantastic article will help my sailboat is wings 30 ft
Thanks for quick refresher course. Having sailed in California for 20+ years I now live in Spain where I have to take a spanish exam for a sailboat license. Problem is, it’s only in spanish. So a lot to learn for an old guy like me.
Very comprehensive, thank you
Your article really brought all the pieces together for me today. I have been adventuring my first sailing voyage for 2 months from the Carolinas and am now in Eleuthera waiting on weather to make the Exumas!!! Great job and thanks
Helen Ballard
I’ve at last found something of an adventure to have in sailing, so I’m starting at the basics, I have done a little sailing but need more despite being over 60 life in the old dog etc, thanks for your information 😊
Barbara Scott
I don’t have a sailboat, neither do l plan to literally take to the waters. But for mental exercise, l have decided to take to sailing in my Bermuda sloop, learning what it takes to become a good sailor and run a tight ship, even if it’s just imaginary. Thank you for helping me on my journey to countless adventures and misadventures, just to keep it out of the doldrums! (I’m a 69 year old African American female who have rediscovered why l enjoyed reading The Adventures of Robert Louis Stevenson as well as his captivating description of sea, wind, sailboat,and sailor).
Great article and very good information source for a beginner like me. But I didn’t find out what I had hoped to, which is, what are all those noisy bits of kit on top of the mast? I know the one with the arrow is a weather vane, but the rest? Many thanks, Jay.
Louis Cohen
The main halyard is attached to the head of the mainsail, not the to the mainsheet. In the USA, we say gaff, not gaffer. The gaff often has its own halyard separate from the main halyard.
Other than that it’s a nice article with good diagrams.
A Girl Who Has an Open Sail Dream
Wow! That was a lot of great detail! Thank you, this is going to help me a lot on my project!
Hi, good info, do u know a book that explains all the systems on a candc 27,
Emma Delaney
As a hobbyist, I was hesitant to invest in expensive CAD software, but CADHOBBY IntelliCAD has proven to be a cost-effective alternative that delivers the same quality and performance.
https://www.cadhobby.com/
Leave a comment
You may also like, guide to understanding sail rig types (with pictures).
There are a lot of different sail rig types and it can be difficult to remember what's what. So I've come up with a system. Let me explain it in this article.

The Ultimate Guide to Sail Types and Rigs (with Pictures)

The Illustrated Guide To Boat Hull Types (11 Examples)

How To Live On a Boat For Free: How I'd Do It

How To Live on a Sailboat: Consider These 5 Things
Own your first boat within a year on any budget.
A sailboat doesn't have to be expensive if you know what you're doing. If you want to learn how to make your sailing dream reality within a year, leave your email and I'll send you free updates . I don't like spam - I will only send helpful content.
Ready to Own Your First Boat?
Just tell us the best email address to send your tips to:

Sailboat Rig Dimensions
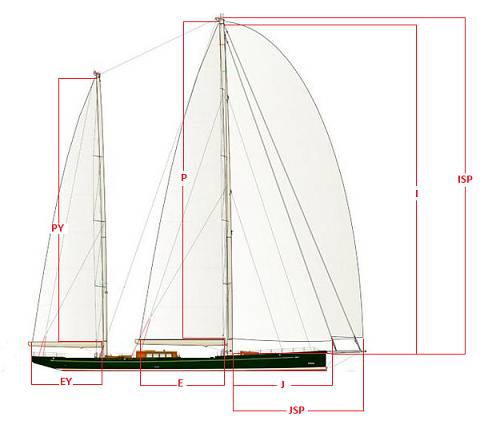
I = Height of headstay termination above the sheer line. J = Distance between the headstay termination at the deck and the front of the mast at the sheer line. P = Distance between black bands on the mast, or the maximum luff length of the main. E = Distance between black bands on the boom, or the maximum foot length of the main. PY & EY are similar to P & E , but indicate mizzen dimensions.
Free Shipping Over $99* - 366 Day Returns - Dedicated Customer Support

- Call Us +1-503-285-5536
- Sign in & Register
- Recently Viewed
Guide to Laser Sail and Rig Sizes

Over 200,000 Laser sailboats have been built over the last 40 years, more than most other small dinghy sailboats. In this article we are going to answer one of the most common questions we get: What size rig do I have? This will help answer what size sail and/or rig you already have and what size sail and/or rig you need to purchase to update your Laser.
What size rig / sail do I have? Standard vs. Radial vs 4.7 Explained
The Laser sailboat has had a number of different rig sizes, with the intention of making the boat sailable by a wide range of sailors (and different sailor weights) by simply swapping out the lower mast section and sail while keeping all other components the same. There are currently three different rig sizes and they are commonly referred to as 'Standard', 'Radial' and '4.7'. Below you will find an image that shows the three rigs side by side, and in the following section we'll explain each one.

Laser Standard / MK2 / ILCA 7
This is the most common Laser rig size, and the original rig on the boat when it was designed. It features a 7.06 square meter sail (about 76 square feet). In 2018, the Laser Class approved a new 'Standard' sail, which is referred to as the 'MKII' or 'Mark 2' to distinguish it from the first version. The difference, among other things, is in the panels. The original 'Standard' sail featured horizontal cut panels. The new MkII sail has radial cut panels. There is no difference in size between these two versions, and as of 2020 all new Laser Standard sails are available in this updated cut.
How to tell if you have a 'Standard' sail: The first and most obvious way to tell if you have a 'Standard' sail is to look at the panels. If they are horizontal, it is most likely a standard sail. Next, you can measure the luff (the front edge of the sail along the mast sleeve). This measurement should be about 5130 mm or 200 inches from the top of the sail to the bottom.
How to tell if you have a 'Standard' lower mast section: The 'Standard' lower mast section should measure about 2865 mm or 113 inches . It is a fairly stout mast section compared to the two smaller mast sections.
Laser Radial / ILCA 6
Originally called the 'M' rig when first designed, the Laser 'Radial' sail is smaller than the 'Standard' sail at 5.76 square meters (62 square feet). At the time, it was the only Laser sail to feature the radial cut panels, which allowed the sail to be de-powered more easily in bigh winds. Per the notes about the 'Standard' rig above, both the Standard and Radial sail feature the radial cut design. Another typical indicator of a Radial size sail are the blue panels at the tack and clew of the sail.
How to tell if you have a 'Radial' sail: The first and most obvious way to tell if you have a 'Standard' sail is to look at the panels. If they are radial, as in emanating out from the center, it is most likely a radial sail. Next, you can measure the luff (the front edge of the sail along the mast sleeve). This measurement should be about 4560 mm or 180 inches from the top of the sail to the bottom.
How to tell if you have a 'Radial' lower mast section: The 'Radial' lower mast section should measure about 2262 mm or 89 inches . It is also a bit smaller in diameter than the standard section.
Laser 4.7 / ILCA 5
The Laser 4.7 (or ILCA 5) is the smallest of the three Laser sails and was designed for young sailors just getting into Laser sailing. The 4.7 lower mast section is also different from the others in that is has a pre-bend near the boom fitting, allowing the sail to depower much easier. This is the least common Laser sail size, and if you have an old one around, chances are it is not a 4.7 sail.

How to tell if you have a '4.7' sail: The 4.7 is similar to the old 'Standard' sail as it has cross cut panels. Many 4.7 sails also have an obvious 4.7 logo somewhere on the cloth. Next, you can measure the luff (the front edge of the sail along the mast sleeve). This measurement should be about 4080 mm or 160 inches from the top of the sail to the bottom.
How to tell if you have a '4.7' lower mast section: The '4.7 lower mast section has a pre-bend in it and should measure about 1810 mm or 71 inches . The bend is the easiest way to tell it apart from the others.
Subscribe To Our Newsletter
Sign up for our newsletter to receive exclusive discounts, new product announcements, and upcoming sales.
- My Wishlist
- United States
- Sets by theme
- Price Ranges
- LEGO Merchandise
- Pick and Build
- Bestsellers
- Offers & Sale
- Coming Soon
- Find inspiration
- Last Chance to Buy
- Architecture
- Botanical Collection New
- Creator 3in1
- Creator Expert
- Harry Potter™
- Jurassic World
- LEGO® Animal Crossing™ New
- LEGO® Avatar
- LEGO® Braille Bricks New
- LEGO® DREAMZzz™
- LEGO® Education
- LEGO® Gabby's Dollhouse
- LEGO® Icons
- LEGO® Indiana Jones™
- LEGO® Super Mario™
- Lord of the Rings™
- Minifigures
- Monkie Kid™
- SERIOUS PLAY®
- Sonic the Hedgehog™
- Speed Champions
- Star Wars ™
- Accessories
- LEGO® Throw Blankets New
- Lunch Boxes
- Puzzles & Board games
- Role Play & Costumes
- Video Games
- LEGO® Water Bottles
- Adults Welcome
- Arts and Crafts
- Coding for Kids
- Learn to build
- Real-Life Heroes
- Robots for Kids
- Pick a Brick
- Brick Accessories & Kits
- Minifigure Factory
- Our Magazines
- Black Friday Livestream
- All LEGO Themes
- All LEGO Interests
- Looking For a Gift?
- For Families
- LEGO® Fortnite®
- LEGO® Insiders
- LEGO® Mosaic Maker
- LEGO® Gift Ideas
- Sustainability
- LEGO Builder
- LEGO Life App
- LEGO Catalogs
- FREE LEGO Life Magazine
- Check Order Status
- Delivery & Returns
- Find a LEGO Store
- Find Building Instructions
- Common Questions
- Replacement Parts
Easter Sale, 3/12-3/21* Shop now
Spring Garden House gift with purchases of $80 or more* Learn more
Sweet bunny gift with purchases of $40 or more* Learn more
FREE Shipping with orders over $35!* Learn more

Available now
We restrict the limit a household can buy in order to be fair to all of our fans. If you’ve already reached that limit through previous orders your entire order may be cancelled.
Become a LEGO® Insider!
Time to set sail, a fun build-and-sail toy for ages 5+, lego® city sailboat, elegant design.
Check out the tall mast and printed sail.
Welcome aboard
Includes a boat’s wheel and a cozy cabin with a bed.
Characters for creative play
Fun adventures with 2 minifigures and a dolphin figure.
Enter a digital world of building
A treat for sailing fans, specifications, customer reviews.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Genoa Area 150% = ( 1.5 x J x I ) / 2 Genoa Area 135% = ( 1.35 x J x I ) / 2 Fore-triangle 100% = ( I x J ) / 2 Spinnaker Area = 1.8 x J x I Sailboats Manufacturer Sailboat Rigging S ailboat rigging on a sailboat is the collection of apparatuses through which the force of the wind is transferred to the ship, in order to propel it forward.
1. Anatomy of a Sailboat Mast: To understand how a sailboat mast functions, let's start by dissecting its anatomy. The mast consists of several essential components such as: - Luff track: This vertical groove allows the mainsail to slide up or down smoothly. - Spreaders: These diagonal bars help strengthen and stabilize the mast.
Sail Plan Dimensions SAIL PLAN DIMENSIONS Figure Out Your Rig Dimensions When It Comes To Your Sails © Jesus Renedo The basic rig dimension for a yacht are generally understood. However, there are some differences in how some sailors describe these dimensions. Here is how we define them at North Sails. I - Height of Foretriangle
Small sailboats, under 20 feet in length, rarely have masts taller than 20 ft or shorter than 8 ft. Sailboats between 20 and 30 feet have masts up to 30 feet tall, and large 40+ foot sailboats often have masts that exceed 50 feet in height.
So, if you were going to average the mast heights of all 20-foot boats, you'd have about a 26-foot high mast and about 39 feet on 30-foot boats. Boats built solely for cruising, particularly in offshore winds, will have shorter masts, and performance boats will have taller masts. How do you Determine the Height of a Sailboat Mast?
" JC " is the greater of the following three dimensions: " J ", the length of the spinnaker pole, or the maximum width of the spinnaker divided by 1.8. Under most measurement rules, " JC " is used, along with "I", to determine the size of a spinnaker.
2023 Sailboat masts are the unsung heroes of the sailing world, silently supporting the sails and ensuring a smooth journey across the open waters. Whether you're a seasoned sailor or a novice, understanding the intricacies of sailboat masts is essential for a safe and enjoyable voyage.
Nomenclature For square-sail carrying ships, masts in their standard names in bow to stern (front to back) order, are: Sprit topmast: a small mast set on the end of the bowsprit (discontinued after the early 18th century); not usually counted as a mast, however, when identifying a ship as "two-masted" or "three-masted"
Short answer sailboat masts: Sailboat masts are vertical structures that support the sails on a sailboat. Typically made of aluminum, wood, or carbon fiber, masts vary in length and design depending on the type and size of the boat. ... Remember to account for any changes in boat specifications since the last mast installation. Step 3: Prepare ...
Rig Dimensions The following abbreviations are often used to describe various measurements on a sailboat. Precise technical definitions exist for each abbreviation, but the following is a list of simple descriptions. If you would like to link to or reprint this article please contact [email protected].
Sloop Masts Nowadays, sloop rig vessels are the most popular type of sailing boat. Sloops typically have only one mast positioned somewhere on the front third or the middle of the deck, even though some boat models might vary a bit. A sloop mast is equipped with a big mainsail and a jib sail (see also ' Why Are Sails Made In A Triangular Shape? ').
Mast profiles are measured for maximum dimensions above 0.5 * P transversely (MDT1) and longitudinally (MDL1) as well as for the minimum dimensions transversely (MDT2) and longitudinally (MDTL2). Taper length TL is the vertical distance from the upper black band to the point where maximum mast profile dimensions occurs.
Sailboat rigging specifications refer to the measurements and details of the various components that make up a sailboat's rig. This includes the type and size of the standing rigging (such as shrouds and stays), running rigging (such as halyards and sheets), mast height, boom length, and sail dimensions. These specifications are essential for ...
Headsail Rig Specs. I - Foretriangle Height: Measure from the top of the halyard to the side deck on the forward side of the mast. J - Foretriangle Base: Measure along deck from the forestay to the Forward face of mast. The J measurement is just a secondary check to make sure nothing has been changed over the years and there's no surprises.
Primary dimensions for calculating areas of triangular sails. It's usually calculated as:~. Area = (luff x foot)/1.8, or. Area = ( P x E )/1.8, where:~. 'P' is the distance along the aft face of the mast from the top of the boom to the highest point that the mainsail can be hoisted, and. 'E' is the distance along the boom from the aft face of ...
Search for sail data such as measurements and rig dimensions for your sailboat in Sailrite's Sail Plan Database. ... Offshore 44 Ketch Tall Rig By Cheoy Lee Sail Data. Dufour 35 Std Sail Data. J 50 Sail Data. Kraken 18 Sail Data. San Juan 26 Sail Data. Kalic 54 Sail Data. Maxi 87 Sail Data. Seidelmann 24 Sail Data.
The two-masted rigs are: Lugger - two masts (mizzen), with lugsail (a cross between gaff rig and lateen rig) on both masts. Yawl - two masts (mizzen), fore-and-aft rigged on both masts. Main mast is much taller than mizzen. Mizzen without a mainsail. Ketch - two masts (mizzen), fore-and-aft rigged on both masts.
The hull can be divided into different parts: deck, keel, cabin, waterline, bilge, bow, stern, rudder, and many more. I'll show you those specific parts later on. First, let's move on to the mast. Also read: Sailboats Explained The Mast The mast is the long, standing pole holding the sails.
Sailboat Rig Dimensions. I = Height of headstay termination above the sheer line. J = Distance between the headstay termination at the deck and the front of the mast at the sheer line. P = Distance between black bands on the mast, or the maximum luff length of the main. E = Distance between black bands on the boom, or the maximum foot length of ...
The Laser sailboat has had a number of different rig sizes, with the intention of making the boat sailable by a wide range of sailors (and different sailor weights) by simply swapping out the lower mast section and sail while keeping all other components the same.
Foreguy 5/16" Ultralite. Vang Line 5/16" STA-SET. Main Cunningham 1:1 - 1/8" Spectra and 3/16" Ultralite. Two Tone Deck. Lightweight outboard motor bracket. V-Berth cushions. Spinnaker Launching Bag (installed). J/22 Technical specifications & dimensions- including layouts, sailplan and hull profile.
It takes into consideration "reported" sail area, displacement and length at waterline. The higher the number the faster speed prediction for the boat. A cat with a number 0.6 is likely to sail 6kts in 10kts wind, a cat with a number of 0.7 is likely to sail at 7kts in 10kts wind. KSP = (Lwl*SA÷D)^0.5*0.5
A fun build-and-sail toy for ages 5+ ... Check out the tall mast and printed sail. Welcome aboard. Includes a boat's wheel and a cozy cabin with a bed. Characters for creative play. Fun adventures with 2 minifigures and a dolphin figure. ... Specifications. Customer Reviews. Shop more like this: Vehicles;
Sailboat Specifications Definitions Hull Type: Wing Keel: Rigging Type: Fractional Sloop: LOA: 23.25 ft / 7.09 m ... Mast Height from DWL: 33.00 ft / 10.06 m: Sailboat Links ... it will vary with the weights of fuel, water, stores and equipment. A boat's actual draft is usually somewhat more than the original designed or advertised draft. For ...